There are two main types of pumps: Dynamic Pumps and Positive Displacement Pumps, i will break down what follows by these two types of pumps, and from the working, features, and application of the three perspectives for you to explain.
If you have questions about the different types of pumps, this article might help you.
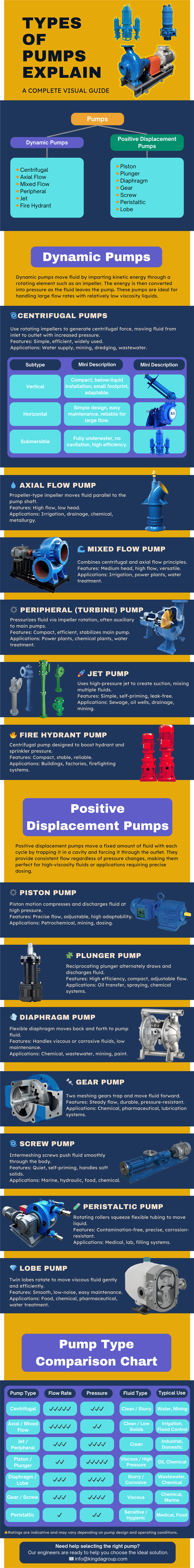
Infographic | Types of Pumps
Embed This Infographic on Your Site
Click the button to copy the embed code:
Embed code copied!
Different Types of Industrial Pumps

| Dynamic Pumps | Positive Displacement Pumps |
| 🔸Centrifugal Pumps 🔸Axial Flow Pumps 🔸Mixed Flow Pumps 🔸Peripheral Pumps 🔸Jet Pumps 🔸Fire Hydrant Pumps | 🔸Piston Pumps 🔸Plunger Pumps 🔸Diaphragm Pumps 🔸Gear Pumps 🔸Screw Pumps 🔸Peristaltic Pumps 🔸Lobe Pumps |
Types of Pumps PDF
Types of Dynamic Pumps
Dynamic types of pumps are a kind of fluid conveying equipment, first the impeller rotation generates centrifugal force, drawing the fluid into the pump, then the impeller pushes the fluid to the outlet, and in the end, fluid exits through the outlet.
They have high efficiency and wide adaptability, so they can transport large volumes of medium to high-pressure fluids.
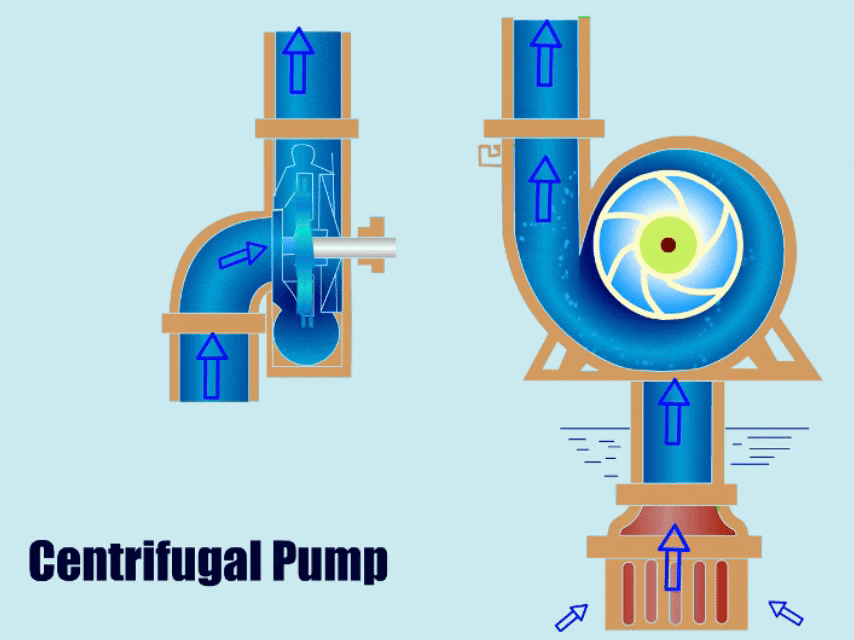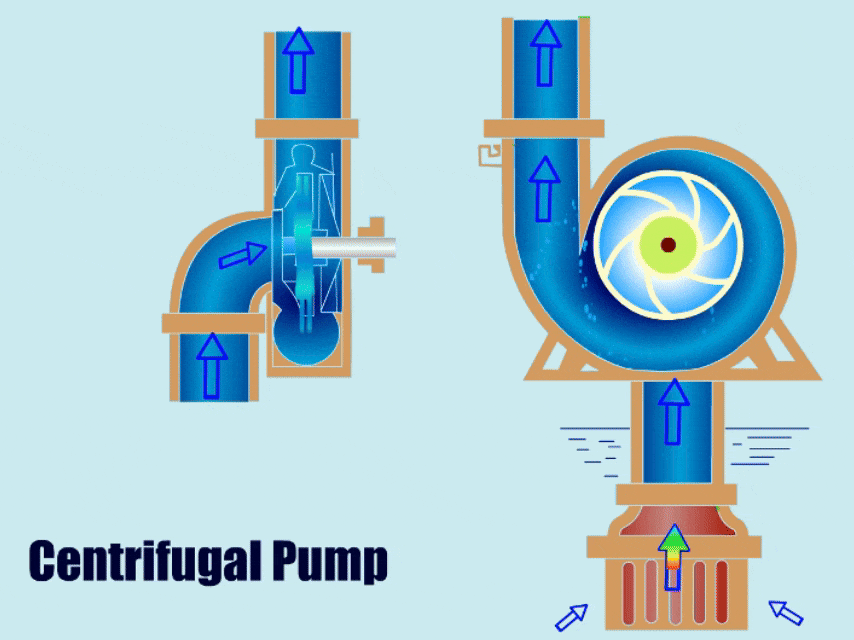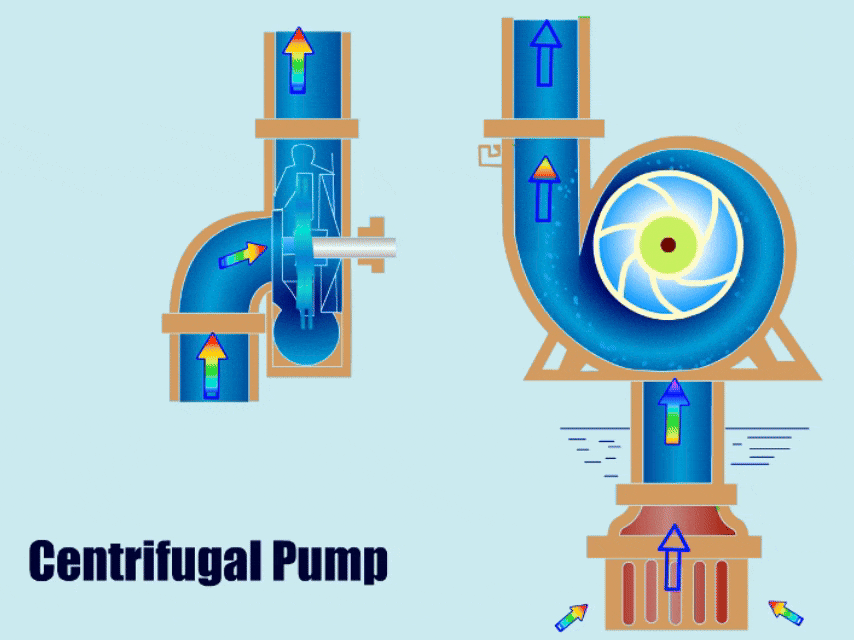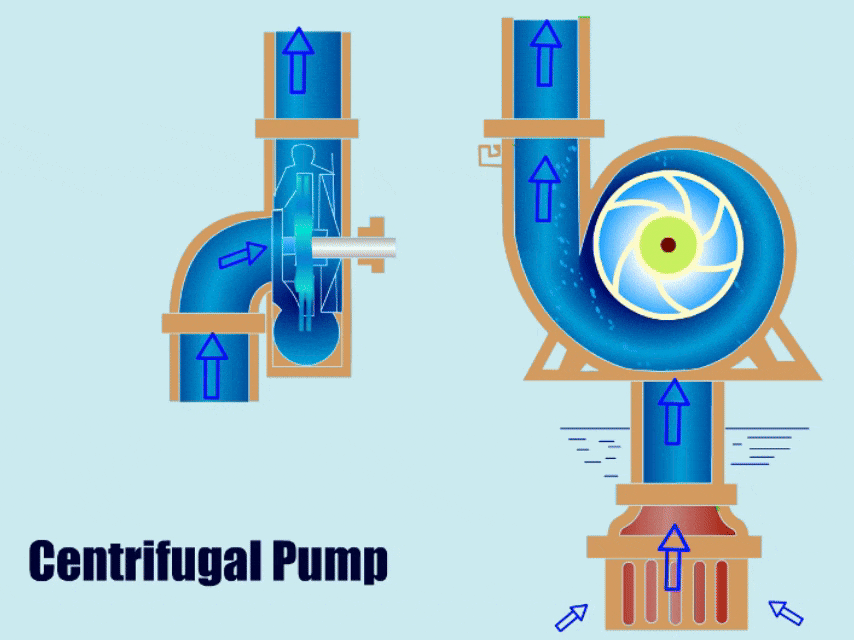
1. Types of Centrifugal Pumps

Among dynamic pumps, centrifugal pumps are most common in operation, centrifugal pumps mainly through the rotation of the impeller to produce centrifugal force to suction fluid, impeller high-speed rotation so that the fluid to increase the pressure, and fluid discharge from the outlet.
| Centrifugal Pumps Types | How it works | Features | Applications |
| Vertical Centrifugal Pumps | A vertical pump draws in fluid below the surface, and then transports it through pipes to the surface. | ● Small footprint ● Adjustable length ● Highly adaptable | ● Sewage ● Industrial wastewater ● Mine slurry |
| Horizontal Centrifugal Pumps | The horizontal centrifugal pump draws in fluid through the centrifugal force, and then the impeller throws the fluid out from the outlet. | ● Simple structure ● Low failure rate ● Easy to install and maintain | ● Irrigation ● Mine slurry ● Metallurgy ● Tunnel Boring ● Dredging |
| Submersible Pumps | Submersible pumps draw liquid underwater and then deliver it to the surface through pipes. | ● Works underwater ● No cavitation ● High efficiency | ● Municipal water ● Agricultural irrigation ● Dredging ● Mining |
2. Axial Flow Pump
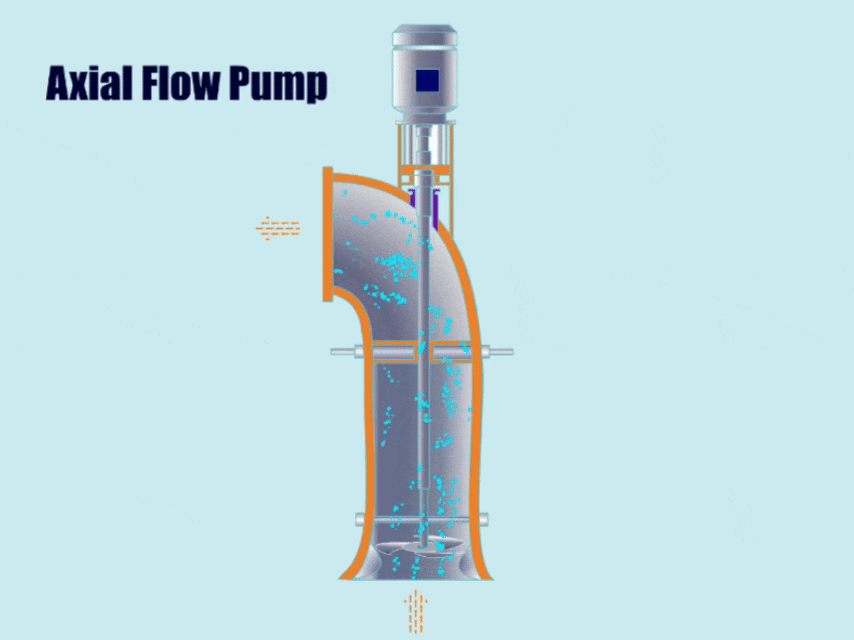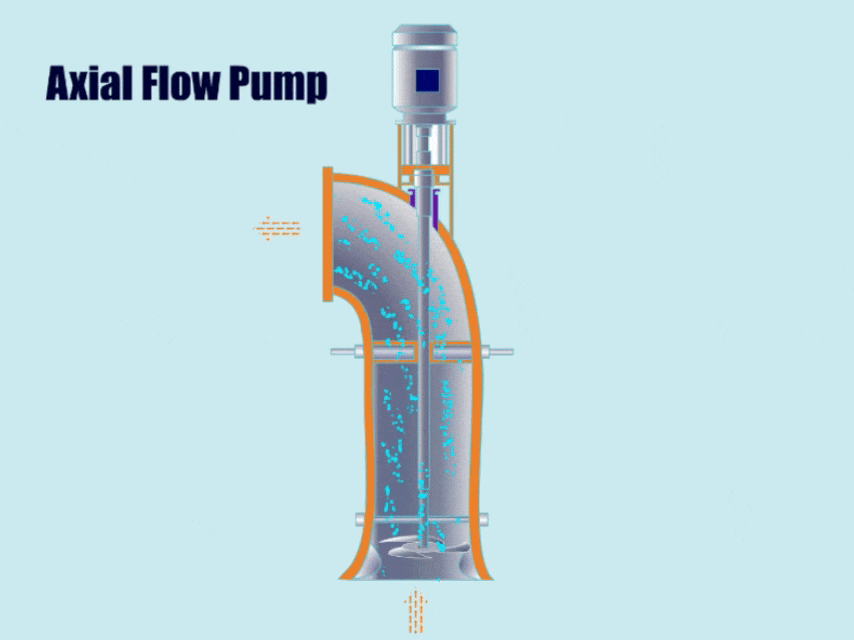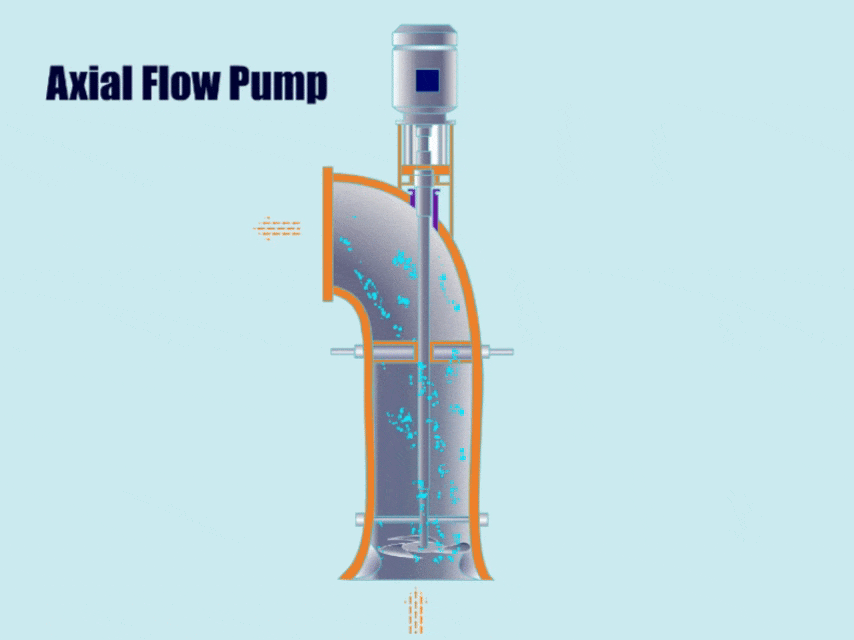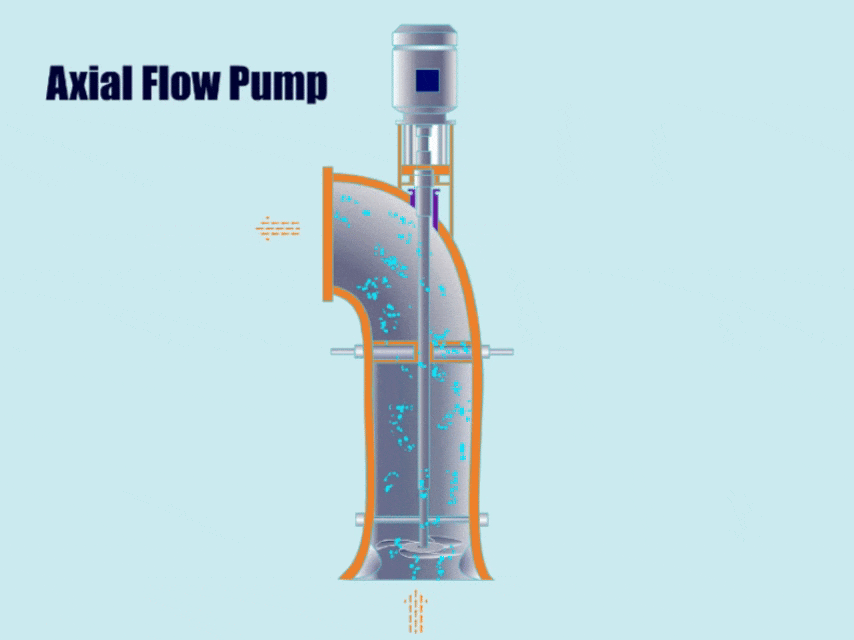
How Axial Flow Pump Work?
First, the axial flow pump generates axial thrust through the rotation of the propeller impeller, and then, under the action of the thrust, the impeller discharges the fluid from the outlet.
Because the discharge direction of the axial flow pump is almost horizontal to the pump shaft, the fluid flows out from the outlet in an almost horizontal direction.
| Overview | |
| Features | Because the axial flow pump can convey large flow rates under low head conditions, compared with common centrifugal pumps, axial flow pumps can convey 3-4 times more fluid than common centrifugal pumps under roughly the same head conditions. |
| Application | Axial flow pumps can not only be used under conditions of large flow and low head, but also can transport fluids containing solid particles, for example, in sewage treatment plants, chemical industry, metallurgy and other industries. |
3. Mixed Flow Pump
How A Mixed Flow Pump Work?
Since the mixed flow pump has a tilted impeller, it is a combination of an axial flow pump and a centrifugal pump.
When the impeller rotates, some of the fluid flows in the direction of the pump shaft, while the other part flows around the impeller under the action of centrifugal force.

| Overview | |
| Features | Mixed-flow pumps combine the advantages of axial flow pumps and centrifugal pumps, and make up for the shortcomings of both. So that the mixed flow pump not only has a high flow rate and medium head characteristics. Mixed flow pumps generally have a head between 3-30 meters, which makes the application scenario of mixed flow pumps even wider. |
| Application | Mixed flow pumps can be used in agricultural irrigation, power plant cooling circulating water, water treatment industry, chemical industry and so on. |
4. Peripheral Pump / Turbine Pump

How Peripheral Pump Work?
Peripheral pumps and turbine pumps belong to a kind of centrifugal pumps, from the inlet suction fluid through the impeller rotation to make the fluid pressurization, and then discharged from the outlet.
In fact, they are auxiliary pumps of the main pump in the conveying system, conveying fluid additives required for production or work.
| Overview | |
| Features | Peripheral pumps have the advantages of auxiliary, wide application and high efficiency, which can help the main pump to be more stable and significantly improve the working efficiency of the main pump. |
| Application | Because peripheral pumps can maintain the stability of water flow, they are mainly used in working conditions such as transporting coolants in power plants, transporting production media in chemical plants, and water treatment. |
5. Jet Pump
How Jet Pump Work?
Jet pumps can utilize the principles of fluid mechanics to transport gases, fluids, or gas-solid-liquid mixtures.
First, the high-pressure fluid enters the pump body from the inlet, and then forms a low-pressure area near the high-pressure fluid. Then, under the action of the low pressure, the jet pump draws in other fluids, and in the end, mixes the different fluids in the mixing chamber.
At this point, the mixed fluid flow rate slows down, the pressure gradually rises, and finally discharged from the outlet pipe.
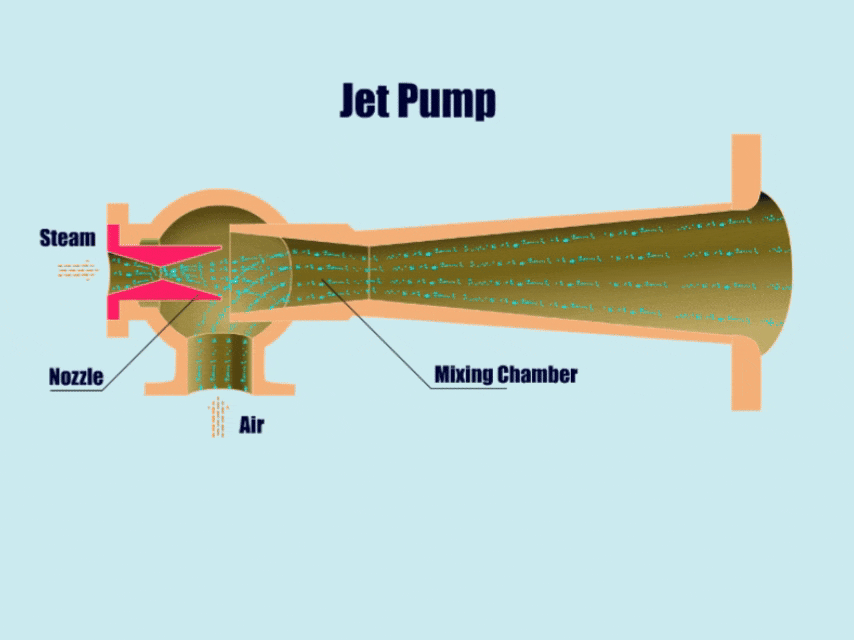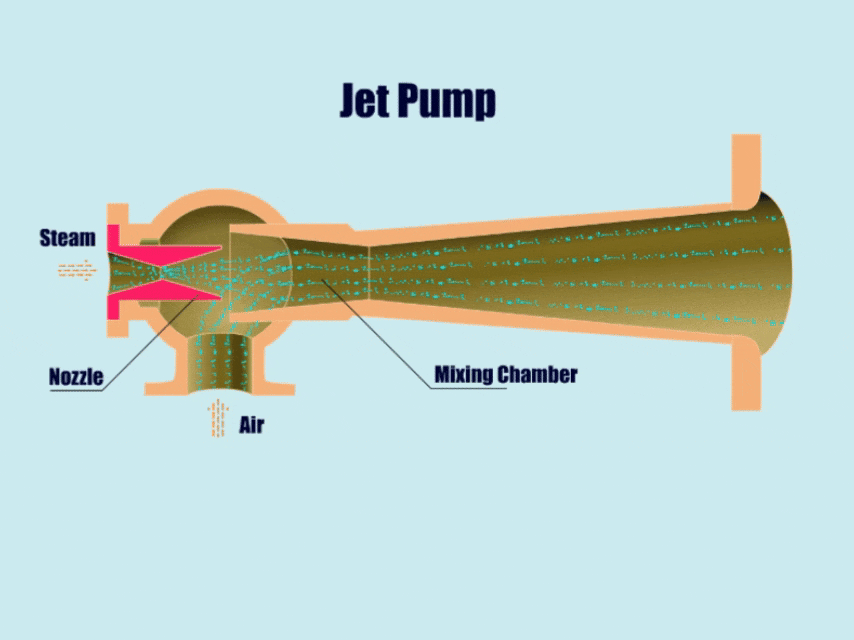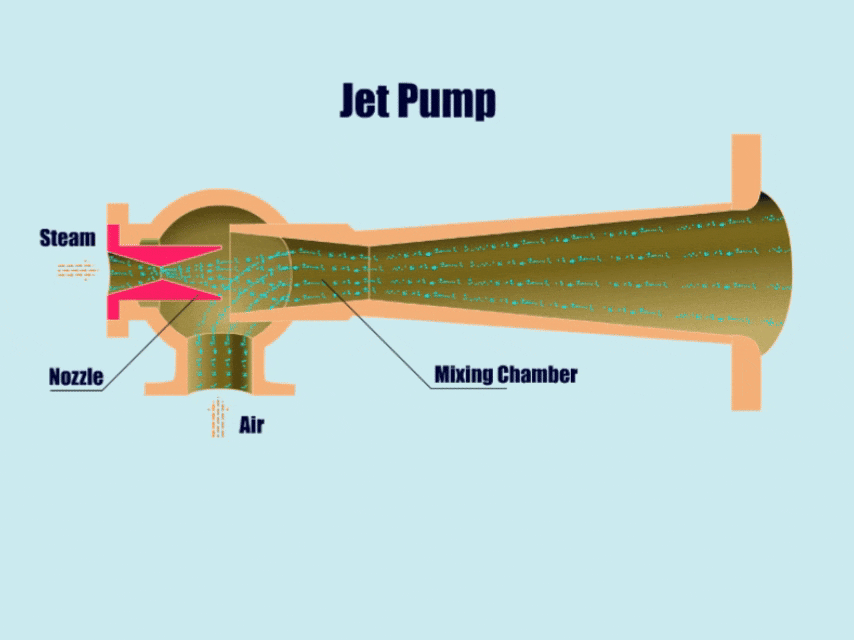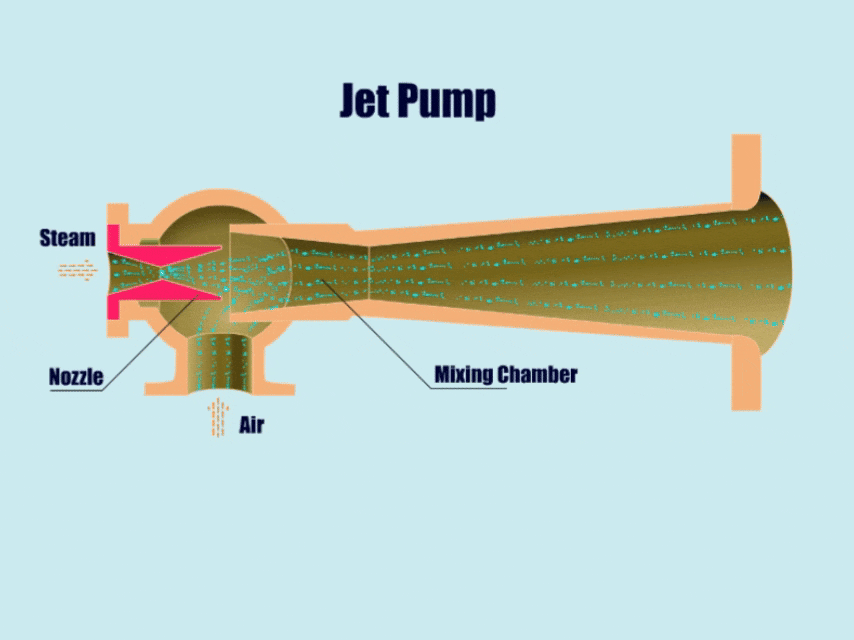
| Overview | |
| Features | Simple structure, reliable work, self-priming ability, no leakage. |
| Application | Sewage treatment, chemical industry, drainage systems, oil wells, mines, etc. |
6. Fire Hydrant Systems

How Fire Hydrant Pump Work?
Fire hydrant pumps are centrifugal pumps. They first use the principle of centrifugal force to increase pressure and flow, and then transport water to fire hydrants and sprinkler systems.
| Overview | |
| Features | Hydrant pumps are small, stable and reliable, and can be used with multi-stage centrifugal pumps to increase water pressure as needed. |
| Application | Fire hydrant system pumps can be used in hydrant systems, for example, high-rise buildings, streets, factories, houses, and so on. |
Types of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement types of pumps mainly rely on the pump piston, gears, lobe, diaphragm and other pump parts in the pump reciprocating motion, so that the pump volume cyclic changes, so as to suction and discharge fluid.
1. Piston Pump
How A Piston Pump Work?
The piston pump relies on the periodic compression and release movement of the piston in the pump to inhale and discharge fluid. In short, the plunger pump converts the mechanical energy of the piston into pressure energy to transport fluid.
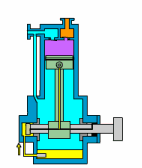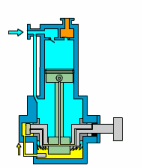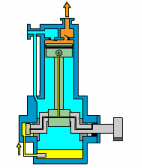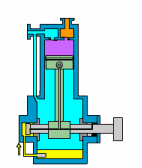
| Overview | |
| Features | The piston pump can not only output a stable flow rate under high pressure, but also adjust the flow rate according to the stroke length of the plunger pump, and has strong adaptability. |
| Application | Piston pumps can handle fluids of different mediums and viscosities, and are usually used in petrochemical, mining and metallurgy, or in scenarios where precise output of fluid flow is required. |
2. Plunger Pump
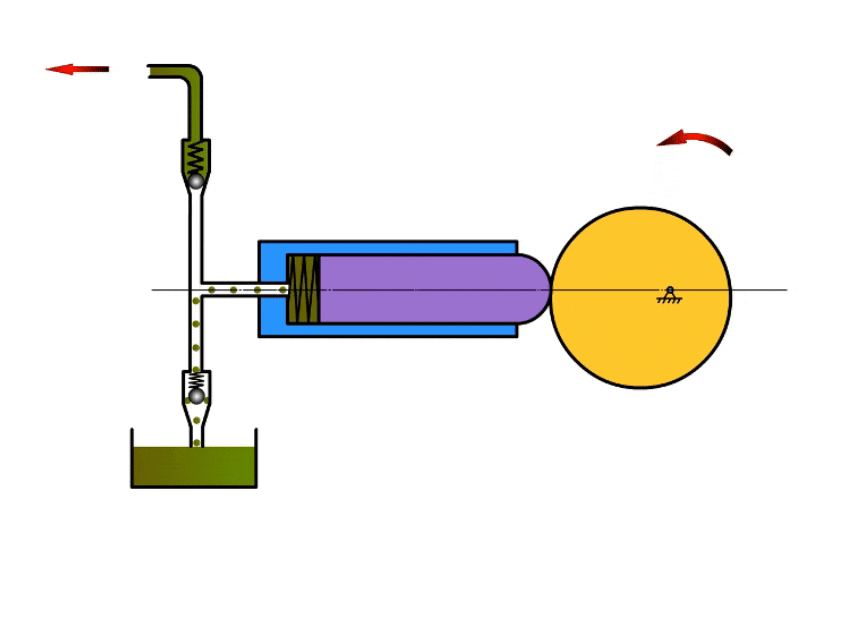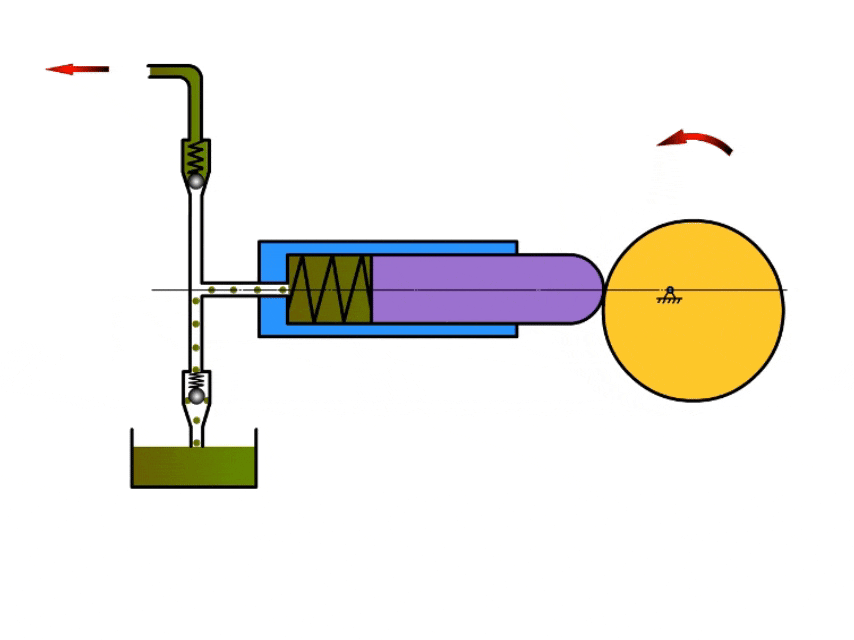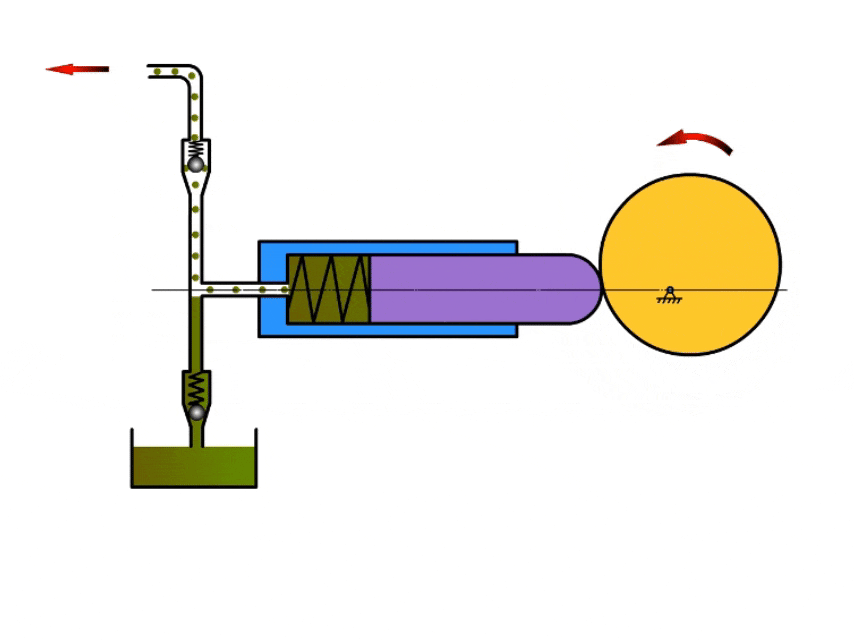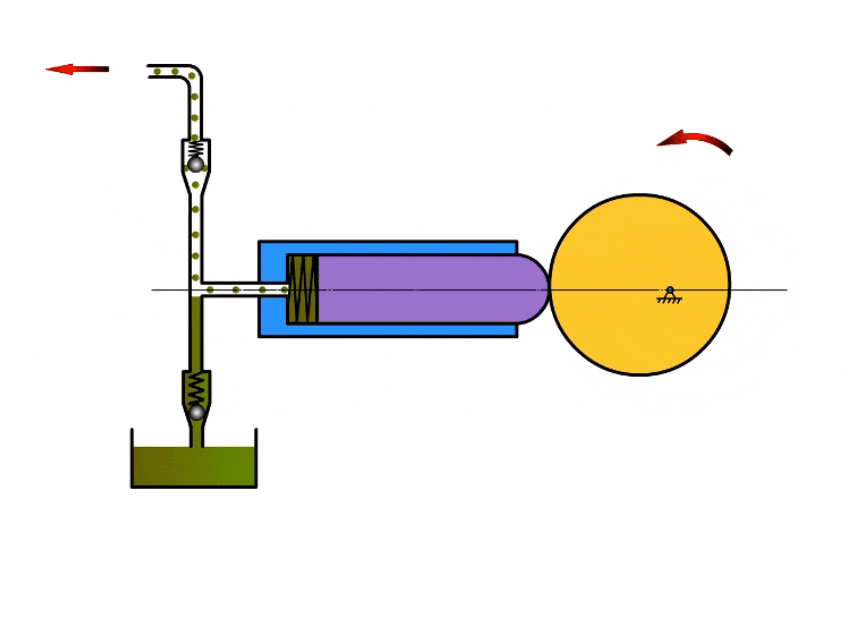
How A Plunger Pump Work?
Plunger pumps mainly rely on the reciprocating movement of the plunger in the pump body to inhale and discharge fluid.
When the plunger moves in one direction, the pump volume increases and the pressure in the pump chamber decreases, at which time the valve at the pump inlet opens and draws fluid into the pump body.
When the plunger reaches the apex, it moves in the opposite direction, at which time the pressure in the pump chamber increases, the inlet valve closes, the outlet valve opens, and the fluid flows out from the outlet.
| Overview | |
| Features | Plunger pumps have the advantages of high rated pressure, compact structure, high efficiency and adjustable flow rate. |
| Application | Plunger pumps can be widely used in high-pressure, high-flow and flow rate needs to be adjusted working conditions, such as oil, slurry transfer, chemical addition, spraying and other industries. |
3. Diaphragm Pump
How A Diaphragm Pump Work?
Diaphragm pumps use connecting rods, pneumatic devices or hydraulic devices to drive the flexible diaphragm in the pump body to carry out linear reciprocating motion, the diaphragm moves periodically so that the volume of the pump cavity changes, thus generating pressure to inhale and discharge the flow body.
When the diaphragm moves to one side, the valve at the suction port opens and fluid enters the pump. When the diaphragm moves to the other side, the valve at the outlet opens and lets the fluid flow out.
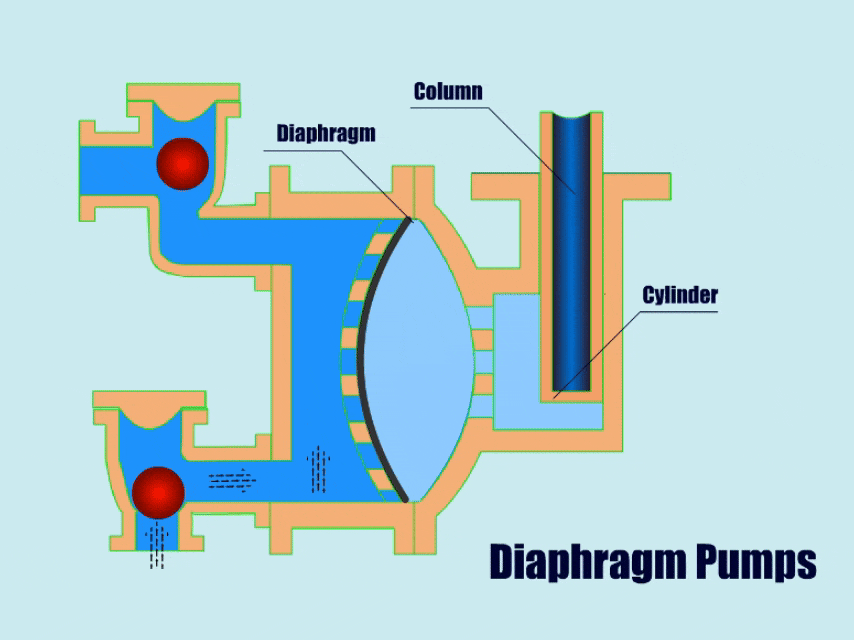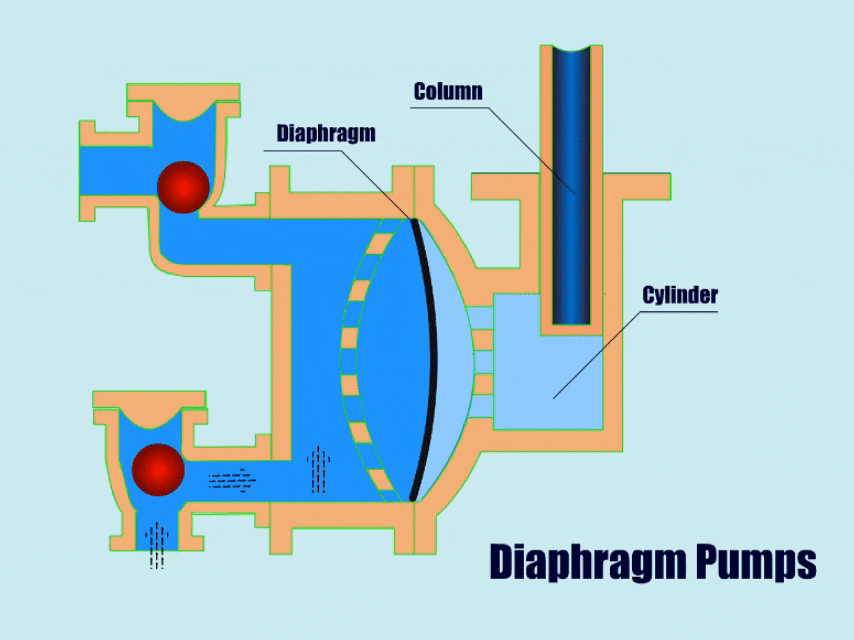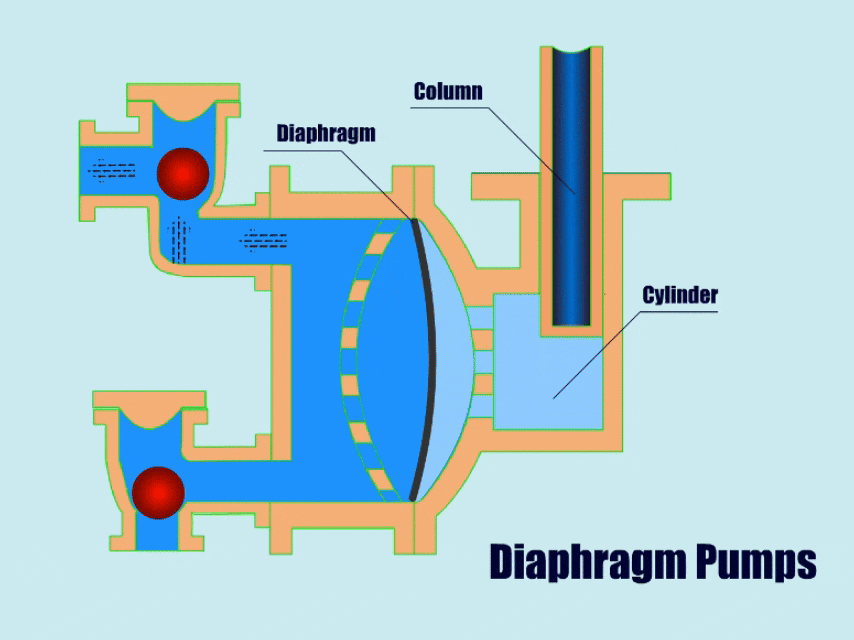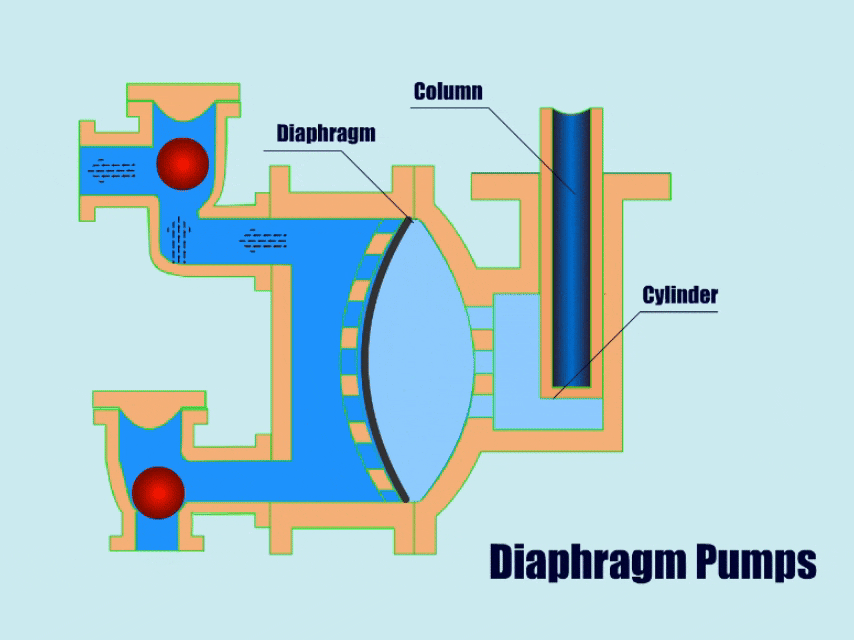
| Overview | |
| Features | Capable of conveying high viscosity fluids such as mud. Simple structure, low maintenance cost, adjustable flow rate, strong adaptability. |
| Application | Diaphragm pumps can transport high-viscosity, solid particle fluids in industries such as chemicals, sewage treatment, mining, paint, etc. |
4. Gear Pump
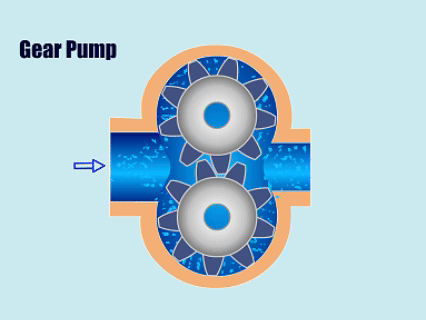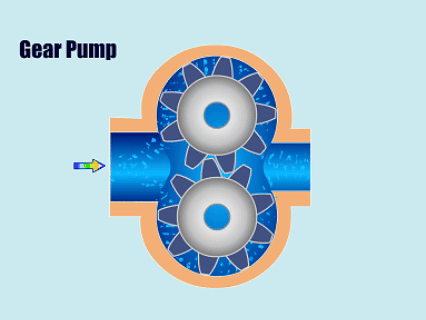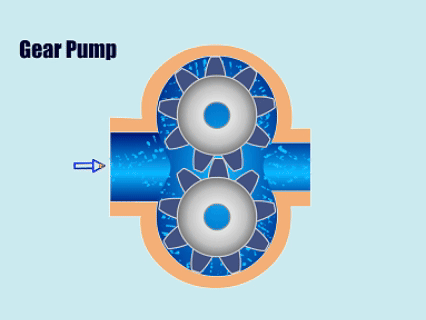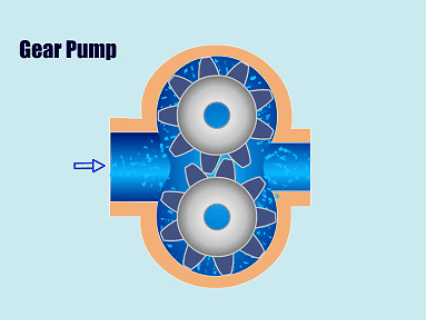
How Gear Pump Work?
Gear pump through the pump body of the two meshing gears will suction chamber and discharge chamber separated, when the gears rotate, the mesh area of the fluid by the two gears before the gap to the discharge chamber, the gears through the reciprocating motion to suction and discharge of fluid.
| Overview | |
| Features | Simple structure, long working life, uniform and controllable flow, high pressure resistance, and strong adaptability. |
| Application | Gear pumps have stable efficiency and are widely used in chemical and pharmaceutical industries and other working scenarios that require stable flow and pressure. |
5. Screw Pump
How Screw Pump Work?
Screw pumps are similar to gear pumps in that there are two intermeshing screws that separate the suction chamber from the discharge chamber.
First, through the movement of the screw, the volume of the suction chamber in the meshing area increases and the pressure decreases. Then, under low pressure, the pump draws fluid into the pump body, and in the end, under the movement of the screw, the screw gradually pushes the fluid in the gap to the discharge chamber and discharges it from the outlet.
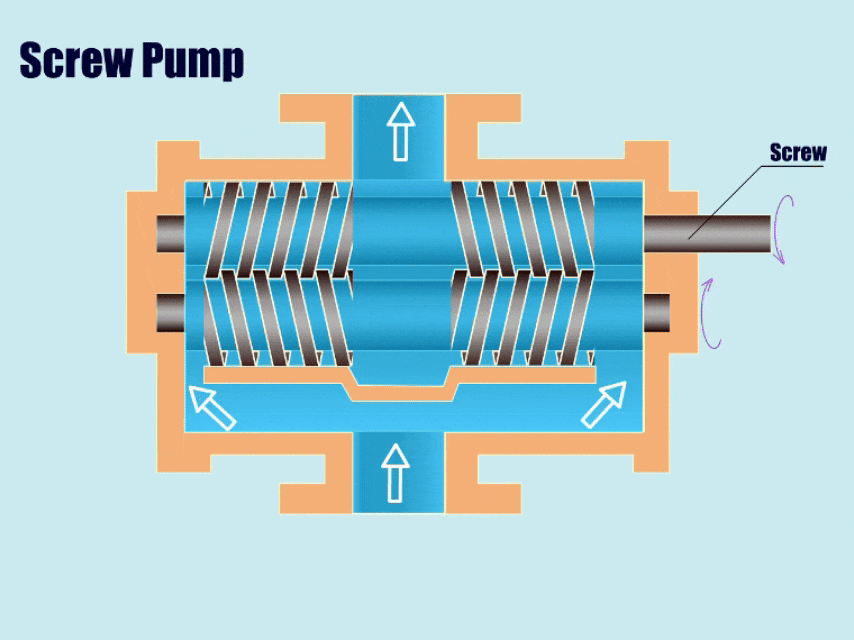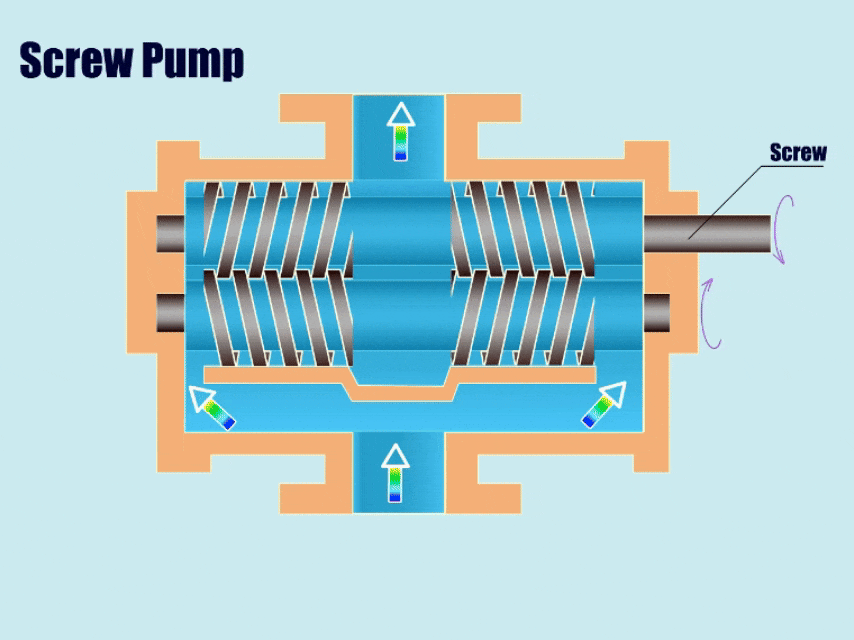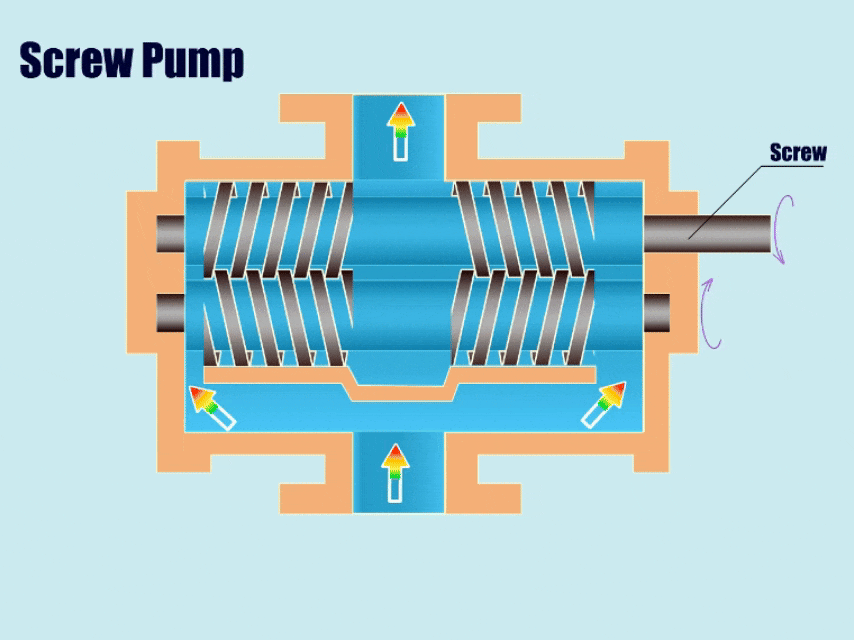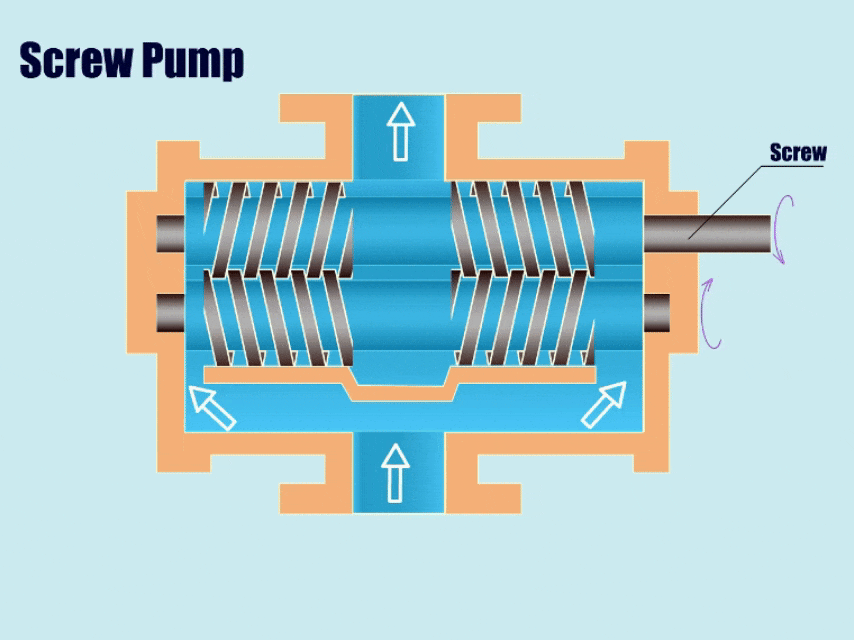
| Overview | |
| Features | Self-absorption ability, low noise and vibration, long working life and wide adaptability. |
| Application | Widely used in hydraulic systems of ships, elevators, machine tools, etc. It can also be used in chemical and food industries to convey scenarios containing soft suspended particles. |
6. Peristaltic Pump

How Peristaltic Pump Work?
Peristaltic pumps are equipped with a drive and a flexible pump hose. First, the roller on the pump drive rotates, creating pressure in the hose, which moves the liquid.
Then, at the point where the roller separates from the hose, the hose returns to its original shape, and finally, the peristaltic pump discharges the fluid from the outlet under the continuous cyclic motion of the pump drive.
| Overview | |
| Features | Non-polluting transportation, the fluid will not contact the pump body, only contact with the hose. It can accurately control the flow rate, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant. |
| Application | Peristaltic pumps can be used in experiments, medical, production line filling and other work scenarios. |
7. Lobe Pump
How Lobe Pump Work?
Lobe pumps have a rotor with multiple lobes inside, the rotor drives the lobes to rotate to draw in and discharge the fluid.
When the impeller turns to the inlet, the gap between the impeller and the pump body increases, and the lobe pump draws fluid. During rotation, the gap decreases and the pressure increases.
As the impeller rotates to the outlet, the impeller pushes the pressurized fluid out of the outlet.
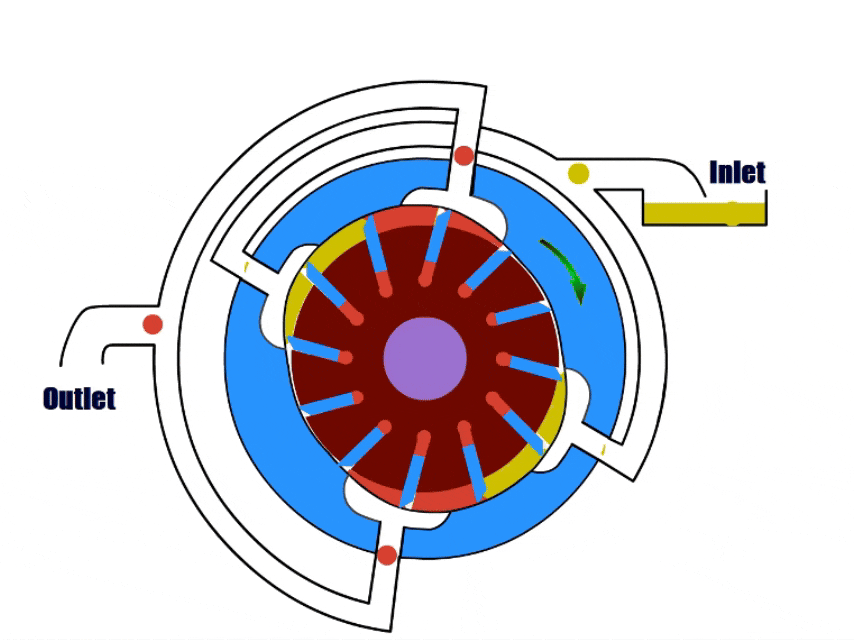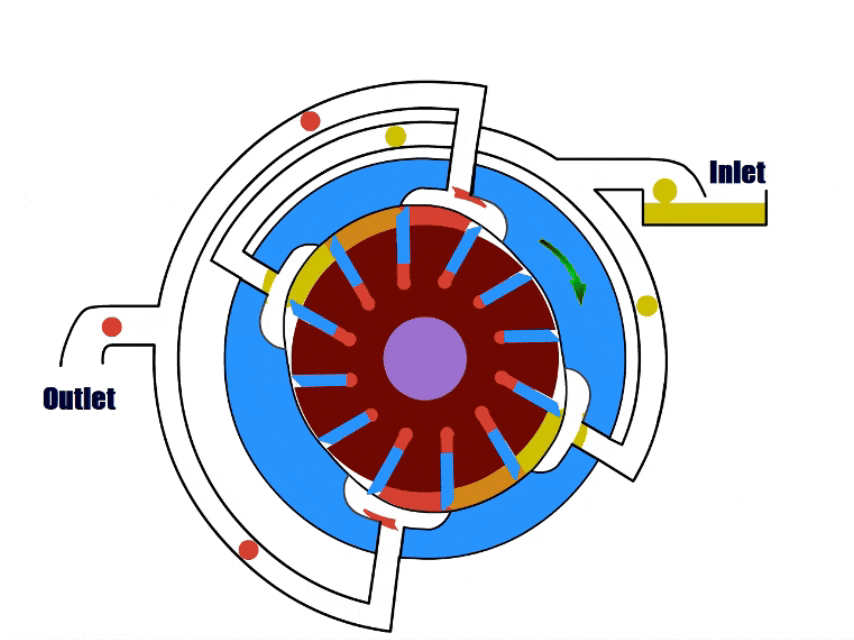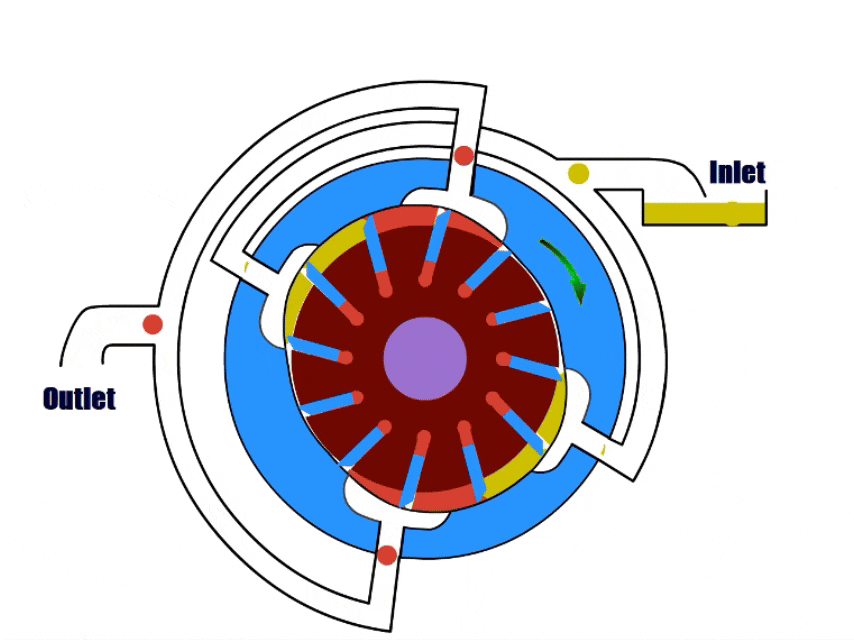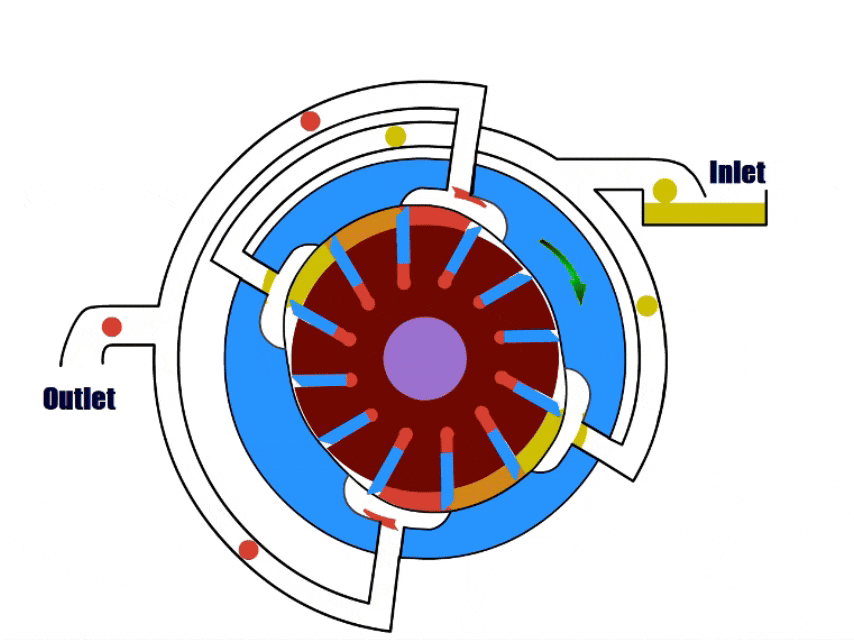
| Overview | |
| Features | Lobe pumps can output a stable and adjustable flow rate, easy maintenance, high efficiency and low noise. |
| Application | Lobe pumps can be used in chemical and petroleum, water treatment, pharmaceutical and other industries to transport fluids with viscous and solid particles. |
Pump Type Comparison
| Pumps Types | Flow Rate | Pressure | Fluid Type | Typical Use |
| Centrifugal Pump | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | Clean / Slurry | Water, Mining |
| Axial / Mixed Flow Pump | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ | Clean / Low Solids | Irrigation, Flood Control |
| Jet / Peripheral Pump | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | Clean | Industrial, Domestic |
| Piston / Plunger Pump | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ | Viscous / High Pressure | Oil, Chemical |
| Diaphragm / Lobe Pump | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | Slurry / Corrosive | Wastewater, Chemical |
| Gear / Screw Pump | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | Viscous | Chemical, Marine |
| Peristaltic Pumps | ★☆☆☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | Sensitive / Hygienic | Medical, Food |
Conclusion of Types of Pumps
No matter what types of pumps, the pumping process is the process of energy conversion, through the energy conversion to make the fluid move, so as to improve the efficiency of our work through the pump, if you still have more questions on the different types of pumps, please feel free to contact us.
FAQ About Types of Pumps
Dynamic Pumps VS Positive Displacement Pumps
| Features | Dynamic Pump | Positive Displacement Pump |
| Working Principle | Impeller rotation generates centrifugal force to push fluid movement | Mechanical movement causes the pump volume to change to move the fluid |
| Flow Rate | Suitable for high flow rates | Suitable for low flow rates |
| Pressure Versus Flow Rate | Pressure and flow rate are inversely proportional (except for special conditions) | Constant flow, does not vary with pressure |
| Fluid Type | Suitable for low to medium viscosity fluids | Suitable for highly viscous or poorly flowing fluids |
| Application | Suitable for high-flow conveying scenarios, such as mines, dredging, reservoirs, etc. | Suitable for fluid transportation that requires precise flow and high pressure, such as petrochemical, medical, etc. |
Which Is The Most Commonly Used Industrial Pump?
The most used in industrial scenarios are centrifugal pumps, which are simple and relatively easy to maintain. It is also the most adaptable, and centrifugal pumps can stably transport both clear water and fluids containing solid particles.