In industrial or commercial uses, pneumatic systems mostly use pushed gas or air to move and are often powered by compressed insert gases or air. FA centrally positioned compressor drives cylinders, motors, and another pneumatic slurry pump. These systems, which are frequently controlled by a manual or automatic solenoid valve, can offer a more flexible, lower-cost, and safer alternative.
What is Pneumatic Slurry Pump?
Abrasives, stringy materials, heavy solids, slurries, and corrosives are commonly utilized in industrial transmission pumping operations even in other industries. Under these challenging conditions, centrifugal due to sealing, engine, diaphragm, or part wear attrition and failure blockage, hydraulic systems require regular care. When traditional pumps fail, the pneumatic transfer pump’s basic architecture, which uses compressed air, keeps pumping.
Pumps with pneumatic diaphragms are developed explicitly for tough mining conditions
responsibilities to outperform and outlast the competitors as a result of several patent design elements. The lightweight design allows for greater mobility and decreases the danger of injury. Low air consumption and a long service life Long-lasting lubrication-free parts imply cheap costs. operational costs and reduced maintenance
Selection of materials:
- The shell materials include aluminum alloy, cast iron, and stainless steel.
- Butadiene rubber, neoprene rubber, fluorine rubber, and polytetrafluoroethylene are the materials used in diaphragms.
Application of Pneumatic Slurry Pump

Pneumatic transfer pumps are ideal for demanding or continuous-use operations such as cargo ship offloading, container sludge transfer, oil/gas drilling muds, tank cleansing, stone grinding, and pulp and paper making. Because there are no moving parts other than two check valves, there is minor wear, and far less maintenance is required. The compressed-air-driven design is critical: once liquid enters the pump’s chamber through the intake check valve, compressed air pressurizes the chamber, and fluid exits through the outflow check valve to complete the cycle.
Typical industrial usage for pneumatic diaphragmatic pumps and their common use:
- Laundry, body wash, moisturizer, dispersant, hand lotion, and surface activators are chemicals used regularly and most commonly.
- Mud, porcelain, lime, and clay slurry are all used in ceramics.
- Digging uses charcoal slurry, volcanic, mud, brickwork, and lubricated lubricant.
- Cement slurry, soft soil, sludge, fertilizers, and drainage are all used in water treatment. They prefer to use these materials.
- Liquid moderately caramel, brines, lemon juice, syrup, vegetable oil, soy protein, honey, and animal feeds are all food products.
- Asthma, combination, wine, fruit and vegetable juice, and other fruit pulp are all products of the beverage business.
- Solvent, acid, alkali, plant extract liquid, ointment, plasma, and other pharmaceutical ingredients are used in the pharmaceutical sector.
- Binder, glue, paint, ink, pigment, and hydrogen peroxide are all used in the paper business.
- Electronics: electroplating solution, cleaning solution
- Adhesives for the textile sector
- Construction materials
- Polishing emulsion, oil, coolant, automotive primer, oil emulsion, varnish, varnish additives, and degreasing fluid are all used in the automotive sector.
- In furniture painting, cement, gloss, dispersed method, dissolvable, color agents, white wood glue applied to the stator, and starch cement are all required.
- Coloring agents, solvents, resin, paint, ink, coating, and other industries
- Metal print, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, woody biomass, dust cleaning pulp, and other industries such as pharmacology, forging, and dyeing are all produced.
Characteristics of Pneumatic Slurry Pump

Pneumatic diaphragm pumps are a novel form of conveying machinery that uses compressed air as its power source and the diaphragm in the cylinder back and forth agitation operation to get all types of media.
The pneumatic diaphragm pump can transfer various corrosive, particle-laden liquids and high immunity, volatile, flammable, and highly toxic liquids.
Features of Pneumatic Slurry Pump
Pneumatic pumps are developed explicitly for demanding oil and gas production applications, as well as applications in pulp and paper, fertilizer dosing, water treatment, and food processing.
- Patented design components
- Simple design with fewer wear parts
- Large particle handling
- Low air consumption
- Lightweight
- Rugged & impact resistant
- Lubrication free
- No end of life – can always be repaired.
- ATEX M2 certified
- Low noise levels
- The flow performance is good, allowing particles with a maximum diameter of 10mm to pass through. Pumping mud, contaminants, and minor pump wear
- There are no revolving parts in the pump and no shaft seal. Pumping a wide range of materials has been used in many ways, like using the rotating action of a diaphragm, since the moving portions of the compressor and the conveying medium are entirely separated, preventing environmental damage and psychological damage.
- Do not use a power supply; it is safe and dependable in flammable and explosive environments.
- It can be embedded in the material instead of a submerged compressor circulating fluids.
- Open and close the gas valve to turn the pump on or off. The compressor will not be affected if no material is circulating for an extended period or an abrupt cutoff due to unanticipated circumstances. When the pump detects an overload, it will shut down immediately, with self-protection. It can automatically restart when the load is restored to normal.
- The structure is simple, and there are fewer moving components. The design of a diaphragm pump is straightforward, making installation and maintenance simple. To minimize equipment oxidation and wear, the compressor carrying means of communication will not come into contact with the valve, connecting rod, or other moving elements.
- More clear liquid can be transported in the dump area.
- Even if idling does not influence the engine, use oil lubrication sparingly.
Work in Principle of the Pneumatic Slurry Pump

The hydraulic system will unite the 2 rubber gaskets into one, encouraging diaphragm action in the pump’s two symmetrical functional cavities and propelling the workpiece attached to the 2 diaphragms’ simultaneous action in the pump’s right and left operating compartments.
Simultaneously, the oxygen inside another enclosed beneath will be expelled from the pump’s rear diaphragm. When it reaches the end of the trip, the gas distribution mechanism will automatically lead the compressed air into another working chamber and promote the diaphragm to move in the opposite direction, forming the synchronous reciprocating motion of the two diaphragms. The reciprocating movement of the diaphragm results in variations in the content of the working chamber, pushing the two one-way ball valves to alternately open and close, allowing the liquid to be sucked and discharged constantly.
Different Types of Pneumatic Slurry Pumps
Pneumatic pumps are commonly positive displacement, double-acting pumps with no return spring that can use a variety of pressured gases or fluids as drivers. There are numerous varieties of pneumatic pumps. However, the following are the most well-known:
- Pneumatic Diaphragm Pumps (both piston and plunger variants) – They transport media through a cylindrical chamber using a plunger or piston mechanism. This mechanism is powered by gas, electromechanical, hydrological, or vapors transmission. These are everyday use in industries.
- Pneumatic liquid pumps are used to transport liquid.
- Pneumatic Refrigerant Pumps – Two-stage pumps used to transfer refrigerant.
- Pneumatic Test Pumps – These pumps are designed and developed to evaluate the efficacy of a specific pneumatic system.
Pros and Cons of a Pneumatic Slurry Pump
Pneumatic pumps offer a lower total cost of ownership than regular pumps since they use pressurized air to function. Other benefits include reduced chemical waste, reduced lost output, increased program efficacy, decreased repair time, lower energy consumption, and additional related operating expenditure reductions.
In the case of pneumatic diaphragm pumps, they can handle a wide range of fluids, including those containing solid particles and different materials. The design of these pumps protects them against piston corrosion and decreases the likelihood of seal failure.
- Increased productivity
- Reduced costs – pays for themselves.
- Increased reliability & longer life
- Less downtime & maintenance
- Easier to diagnose & repair
- Save on energy costs –more air available for other equipment.
- Fewer injuries
- No pollutants (oil-free)
- Safe for hazardous environments
Solid particles and waste can continue to flow via compressors, but how?

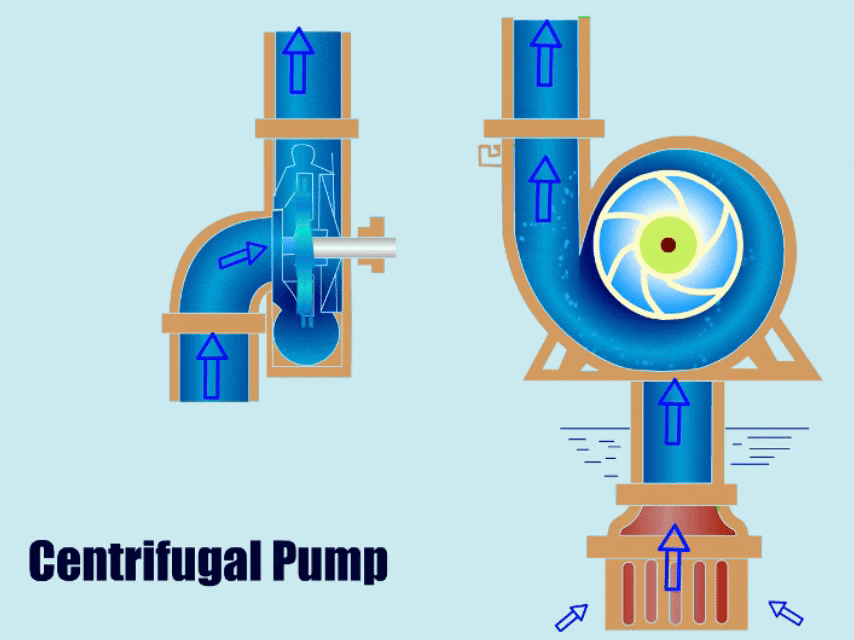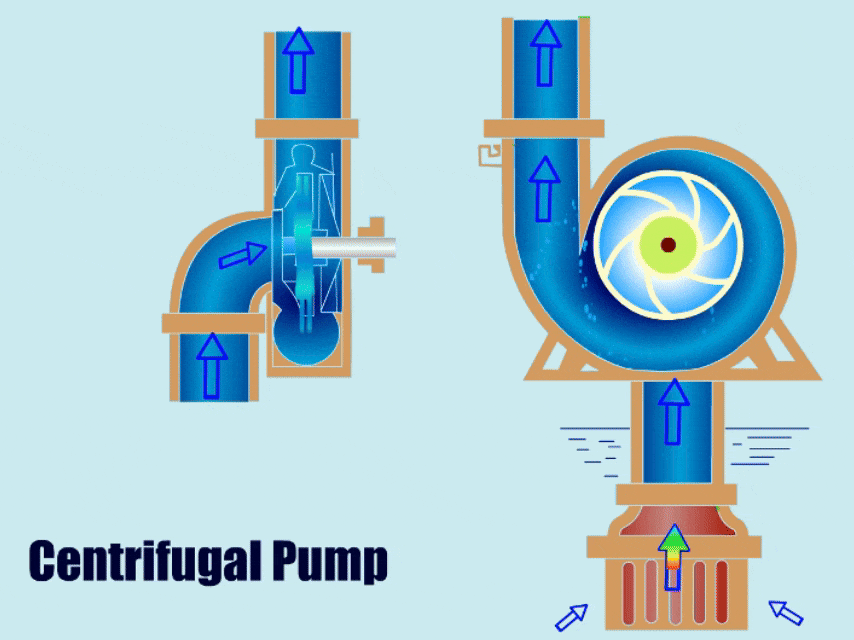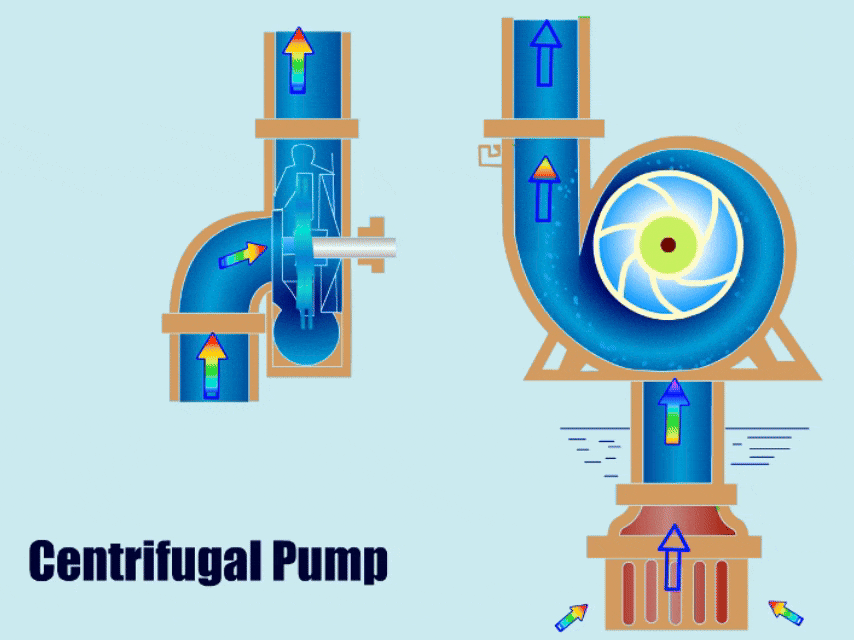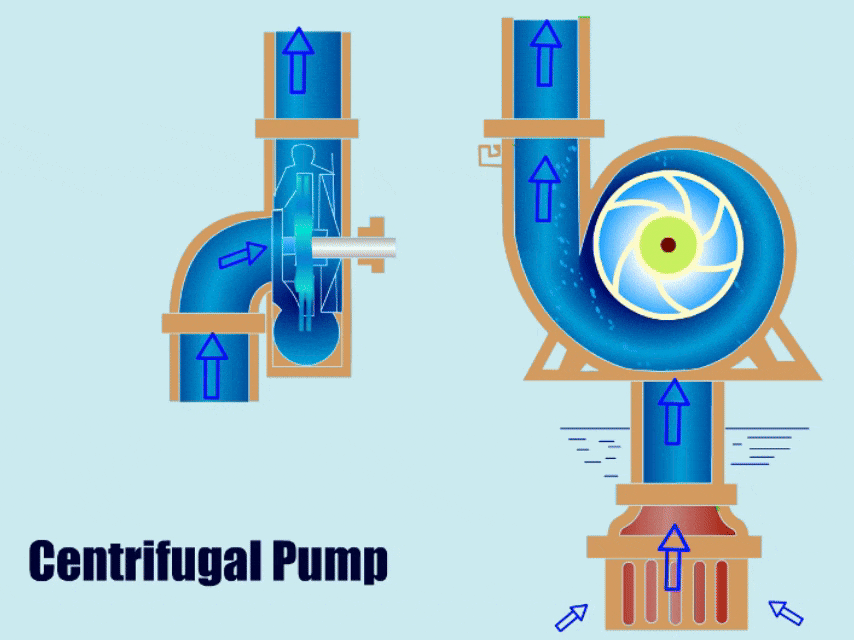
Centrifugal pumps lose efficiency due to wear in solids or debris-handling transfer pump applications, and they frequently clog due to solids becoming trapped in the pump’s inlet or impeller. Pumps feature wide-open passageways that can handle high-density slurries like sludge, mud, ash, or scale. Low velocity is maintained to reduce wear. The pneumatic displacement pump’s pump cycle motion is naturally declogging, dislodging materials that may be trapped in the check valves. This innovative design can handle granular or sticky solids, solvents, slurries, large particles, and acidic compounds.
Pneumatic transmission compressors are intended for powdered operations and can be gravitational attraction or adapted for suction lift.
Pumps are available in steel and 316 stainless steel within/outflow diameters of 2″, 3″, 4″, and 6″. The Pump’s simple, seal-less design, capable of passing up to 5.5′′ diameter solids as well as abrasives, stringy materials, slurries, and corrosives
If you have, please feel free to about the Pneumatic slurry pump, you can contact us anytime or call for faster transactions, and our senior engineers will answer you at any time.