Slurry is one of the most challenging fluids to move. It’s highly abrasive, thick, sometimes corrosive, and contains a high concentration of solids. No doubt about it, slurry is tough on pumps. But selecting the right pump for these abrasive applications can make all the difference in the long-term performance.
WHAT IS A “SLURRY”?
Slurry is any mixture of fluid and fine solid particles. Examples of slurries would include: manure, cement, starch, or coal suspended in water. Slurries are used as a convenient way to handle solids in mining, steel processing, foundries, power generation, and most recently, the Frac Sand mining industry.
Slurries generally behave the same way as thick, viscous fluids, flowing under gravity, but also pumped as needed. Slurries are divided into two general categories: non-settling or settling.
Non-settling slurries consist of very fine particles, which give the illusion of increased apparent viscosity. These slurries usually have low wearing properties, but do require very careful consideration when selecting the right pump because they do not behave in the same manner as a normal liquid does.
Settling slurries are formed by coarse particles that tend to form an unstable mixture. Particular attention should be given to flow and power calculations when selecting a pump. The majority of slurry applications are made up of coarse particles and because of this, have higher wear properties.
Slurries are mixtures of solids and liquids, with the liquid serving as the transport mechanism used to move the solid. The size of the particles (or solids) in slurries ranges from one micron in diameter up to hundreds of millimeters in diameter. The particle size significantly impacts a pump’s ability to move a slurry through a process line.
All slurries share five essential characteristics:
More abrasive than pure liquids.
Thicker in consistency than pure liquids.
May contain a high number of solids (measured as a percentage of the total volume).
The solid particles usually settle out of the slurry’s precipitate relatively quickly when not in motion (depending on the particle size).
Slurries require more energy to move than do pure liquids.
Below are common characteristics of slurries:
Abrasive
Thick consistency
Can contain a high amount of solids
Usually settle quickly
Require more power to operate than a “water” pump
Slurry Pump Selection
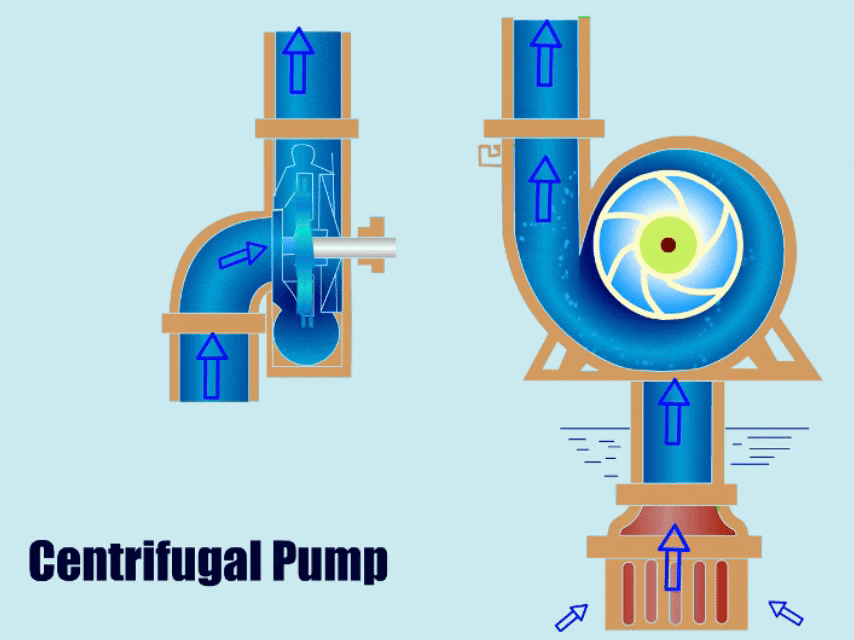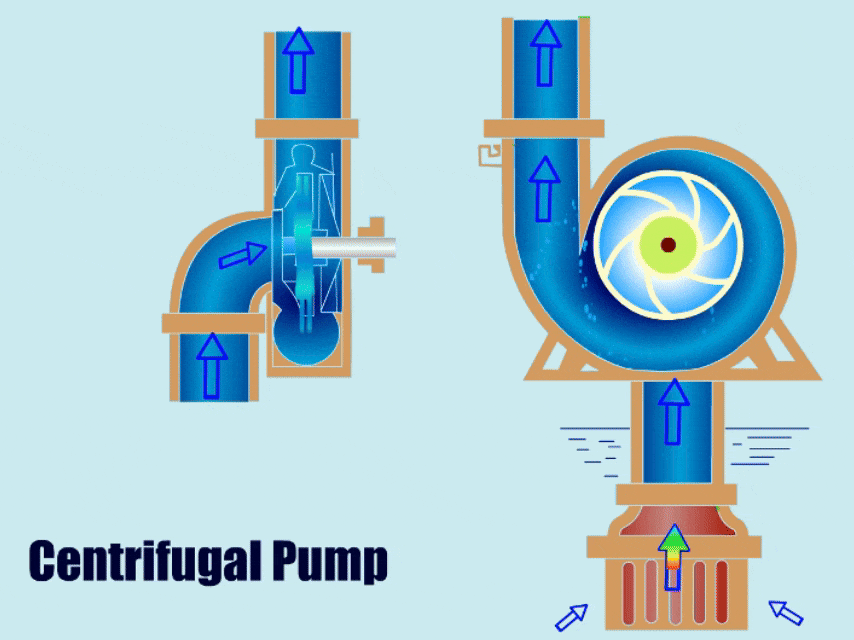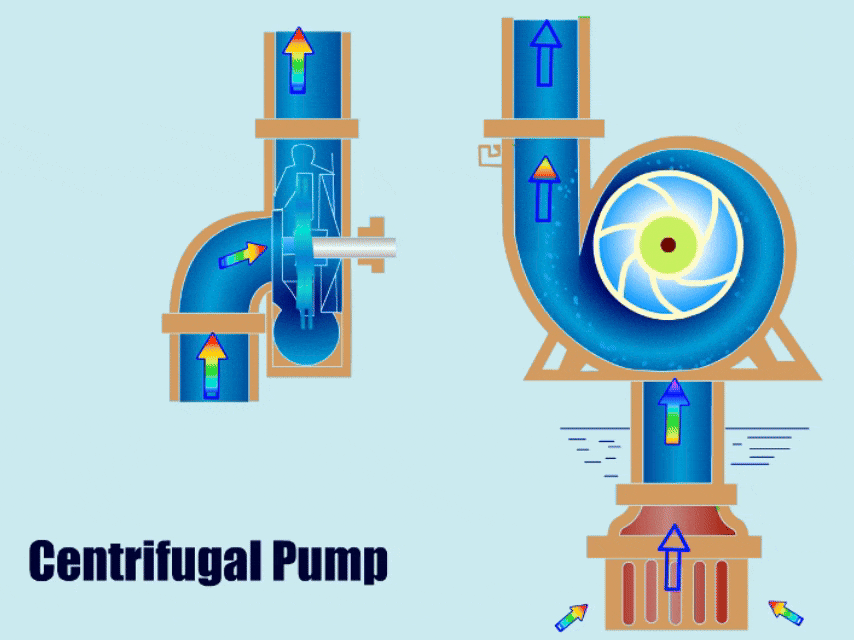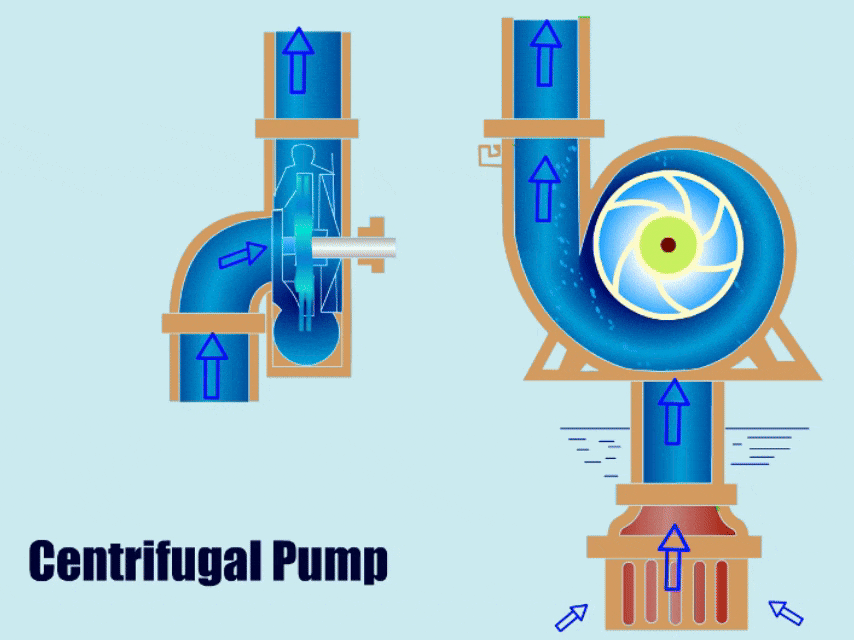
Many types of pumps are used for pumping slurries, but the most common slurry pump is the centrifugal pump. The centrifugal slurry pump uses the centrifugal force generated by a rotating impeller to impact kinetic energy to the slurry, similar to how a water-like liquid would move through a standard centrifugal pump.
Slurry applications greatly reduce the expected wear life of pumping components. It’s critical that pumps designed for these heavy-duty applications are selected from the start. Consider the following when making selections:
Basic Pump Components
To ensure the pump will hold up against abrasive wear, the impeller size/design, material of construction, and discharge configurations must be properly selected.
Open impellers are the most common on slurry pumps because they’re the least likely to clog. Closed impellers on the other hand are the most likely to clog and the most difficult to clean if they clog.
Slurry impellers are large and thick. This helps them operate longer in harsh slurry mixtures.
Slurry Pump Construction
Slurry pumps are generally larger in size when compared to low-viscosity liquid pumps and usually require more horsepower to operate because they’re less efficient. Bearings and shafts must be more rugged and rigid as well.
To protect the pump’s casing from abrasion, slurry pumps are oftentimes lined with metal or rubber.
Metal casings are composed of hard alloys. These casings are built to withstand the erosion caused by increased pressure and circulation.
The casings are selected to suit the needs of the application. For instance, pumps used in cement production handle fine particles at low pressures. Therefore, a light construction casing is acceptable. If the pump is handling rocks, the pump casing and impeller will need a thicker and stronger casing.

Slurry Pumping Considerations
Those with experience pumping slurries know it’s not an easy task. Slurries are heavy and difficult to pump. They cause excessive wear on pumps, their components, and are known to clog suction and discharge lines if not moving fast enough.
It’s a challenge to make slurry pumps last for a reasonable amount of time. But, there are a few things you can do to extend the life of your slurry pump and make pumping slurry less of a challenge.
Find the sweet spot that allows the pump to run as slow as possible (to reduce wear), but fast enough to keep solids from settling and clogging the lines
To reduce wear, lower the pump’s discharge pressure to the lowest point possible
Follow proper piping principles to ensure a constant and uniform delivery of the slurry to the pump.
Kingda Slurry Pump has gained great reputation in the markets, we welcome friends to contact us for better pumping solutions in the following fields.
Mining & Mineral Processing
Construction Aggregate
Dredging Industry
Electronic & Power Plants
Tunnel Boring Machine
Types Of Slurry Pumps
Horizontal Slurry Pump
The horizontal slurry pump is a horizontal pump installed on the ground. It usually needs an inverted installation so that the slurry can automatically flow into the pump cavity without opening the pump.
Vertical Slurry Pump
Vertical slurry pumps are highly configurable pumping equipment designed. They require less floorspace than horizontal pumps and wear parts are available in hard metal or rubber.
Submersible Slurry Pump
submersible sewage pump is a new type of slurry pump developed in recent years to meet the needs of users. It is different from the traditional horizontal slurry pump and the submerged slurry pump.
Related Of Slurry Pumps
Water & Sewage Pump
Kingda could well meet the need of large flow and high head water &sewage pump for pump station and waste water treatment, we offer the life-long and full circle service from the initial design to the final building up.
Gravel & Sand Pump
Pumps that are used to pump water and sand or gravel mixture to the recovery system such as sluice box or jig are named gravel & sand pump, Since sand & gravel is a kind of main construction aggregate , such a pump is offen used in making sand and gravel, It is a centrifugal pump with renewable impellers and liner, and in recent years there is also submersible pump used in this field.
Dredge Pump
Dredge pumps are used to move sediment, sand, gravel, debris, and a variety of other solids from the river or sea to a discharge site. They are usually heavy-duty centrifugal pumps.The abrasive granular materials and solids of various sizes and weights will be in suspension by flushing or other external affections, and then the mixture will be transferred by special pipe or hose with the help of dredge pump.
FGD Pump
FGD Pump in the applications
SO2 is an acid gas which will cause big trouble for the environment, and Flue-gas desulfurization (FGD) is the technologies used to remove SO2 from exhaust flue gases of fossil-fuel power plants and processes such as waste incineration. With the help of Special designed slurry pump we use CaCO3 (limestone) slurry to absorb the SO2 and produces CaSO3( calcium sulfite) which could be reused in the construction.
Froth Pump
Kingda Froth Pump are designed to better handle highly abrasive and corrosive frothy slurry by an induced vortex effect before it enters the pump impeller. It is always used for heavy duty and continuous pumping.
Pump Parts
:Slurry Pump Parts Ready Stocks
Pump parts from Kingda are interchangeable with the different slurry pumps, they have been rigorously reverse engineered using computer and modeling.
Supporting Equipment
High Quality Pump Supporting Equipment
You could always get all the things in need about the pumping system from Kingda who offers you one-stop purchasing service and will be your only one and reliable pumping partner.