The existence of sewage pump makes it possible to transport solid particle slurry, which greatly improves the efficiency of our work. This article aims to explain the definition, design, working principle, types and daily maintenance of sewage pump. I hope this article will be helpful to you.
What is Sewage Pump?
Sewage Pump Definition
Sewage pumps are centrifugal pumps specifically designed for transporting liquids containing solid particles or long fibers. They are generally available in horizontal or submersible configurations and offer excellent anti-clogging performance.
The impellers and flow paths of conventional water pumps are not optimized for solids handling. When we use traditional pumps to transport sewage, the pump inlet often becomes clogged. Long fibers and debris in the sewage also often clog the impeller.
Sewage pumps, on the other hand, offer a high solids handling capacity, ensuring they can smoothly transport gravel, feces, garbage, long fibers, and other contaminants.
Sewage Pump Design
🔸Solids Handling Capacity
In order to have good solid passing capacity, engineers optimized the impeller and flow path of the sewage pump. By increasing the impeller diameter and widening the flow channel, it has achieved excellent anti-clogging ability.
🔸Long Service Life
In order to meet the needs of long-term transportation of abrasive materials, engineers usually use high wear-resistant alloy materials to manufacture sewage pumps, thereby maximizing the service life of sewage pumps.
🔸Heavy-Duty Motors
To improve sewage transportation efficiency, heavy-duty motors are typically used. Their robust performance prevents clogging when transporting viscous, solids-laden sewage, improving efficiency.
🔸Durable Seals
In order to ensure that the sewage pump is leak-free, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant, sewage pumps usually use high-quality seals to prevent seal failure and liquid leakage due to long-term contact with liquid.
Sewage Pump Diagram
The following sewage pump diagram shows the basic structure and main components. Impeller, outlet, pump casing, bearing assembly, etc., so that you can more intuitively understand how the sewage pump works.

How Does A Sewage Pump Work?
The sewage pump plays a crucial role in the entire sewage pumping station. As the heart of the sewage pumping system, it is crucial for smooth sewage transportation. Read below to learn how sewage pumping begins.
Sewage Pump Working Process
❶ Sewage Collection
Domestic sewage and factory wastewater enter a sewage tank through pipes. Sewage tanks typically have screens to filter out larger objects such as garbage and feces. In order to automate wastewater pumping, there is usually a float switch inside the wastewater tank to monitor the water level.
❷ Sewage Pump Startup
Sewage pumping systems are typically automated, relying on a float switch equipped with a level sensor. When the sewage tank level reaches a set limit, the float switch transmits a start signal to the motor, which then receives the signal and starts.
❸ Sewage Intake
First, the motor starts, the motor drives the pump shaft to rotate, and then the impeller starts to rotate at high speed, generating centrifugal force. Then, under the action of centrifugal force, the sewage pump sucks the sewage into the pump, and under the action of the impeller, the sewage rotates at high speed in the pump.
❹ Sewage Discharge
Under the action of the volute, the sewage gradually reduces its speed and converts the kinetic energy of the liquid into pressure energy. When it moves to the pump outlet, the high-pressure liquid will quickly flow out of the pump outlet and eventually flow into the sewage treatment plant or sewer.
❺ Sewage Pump Stop
As the sewage level in the sump continues to drain, gradually dropping to a safe level, the float switch sends a stop signal to the motor, causing it to stop and enter sleep mode, awaiting the next start.
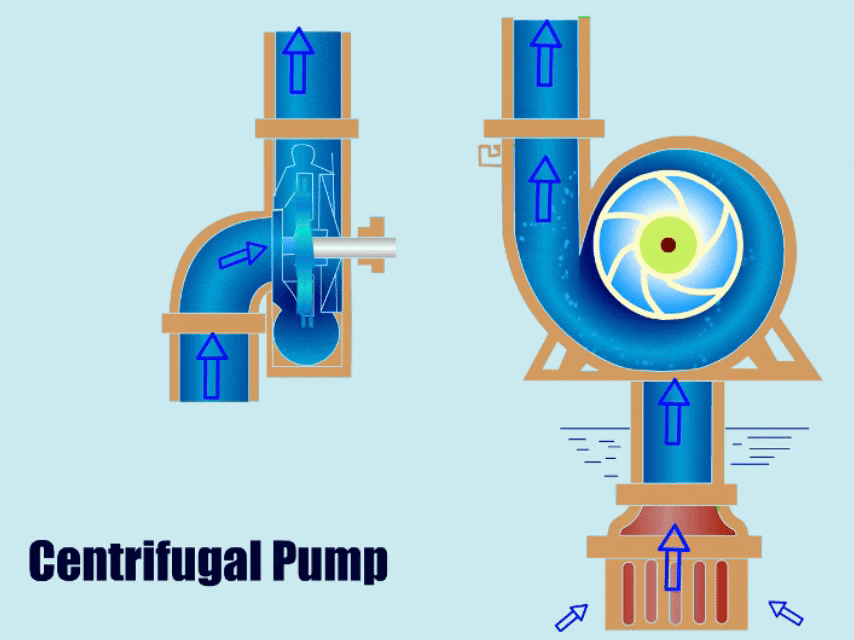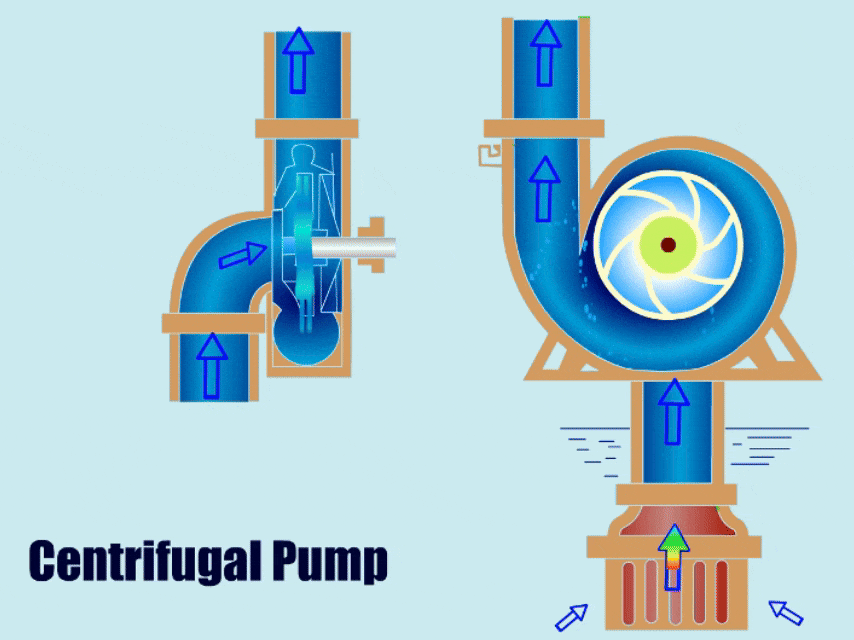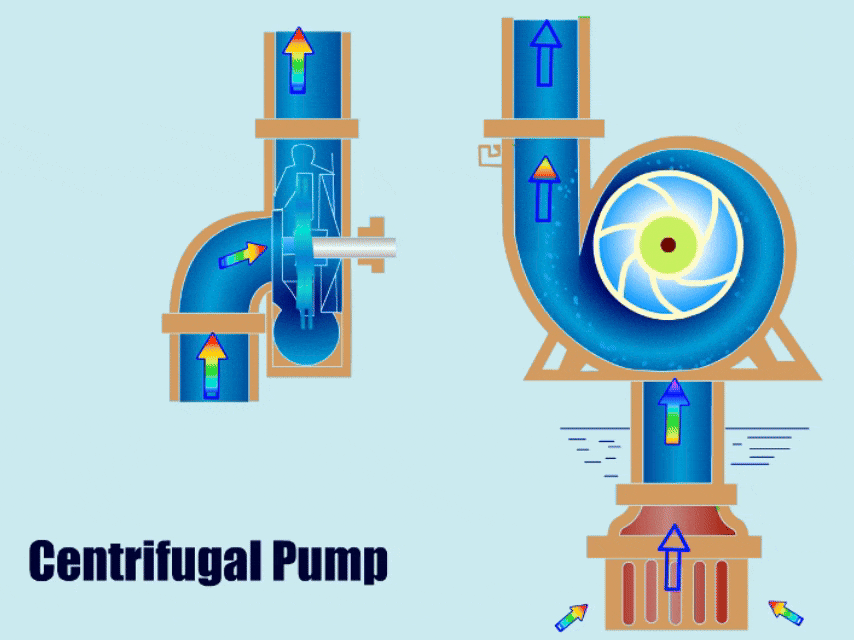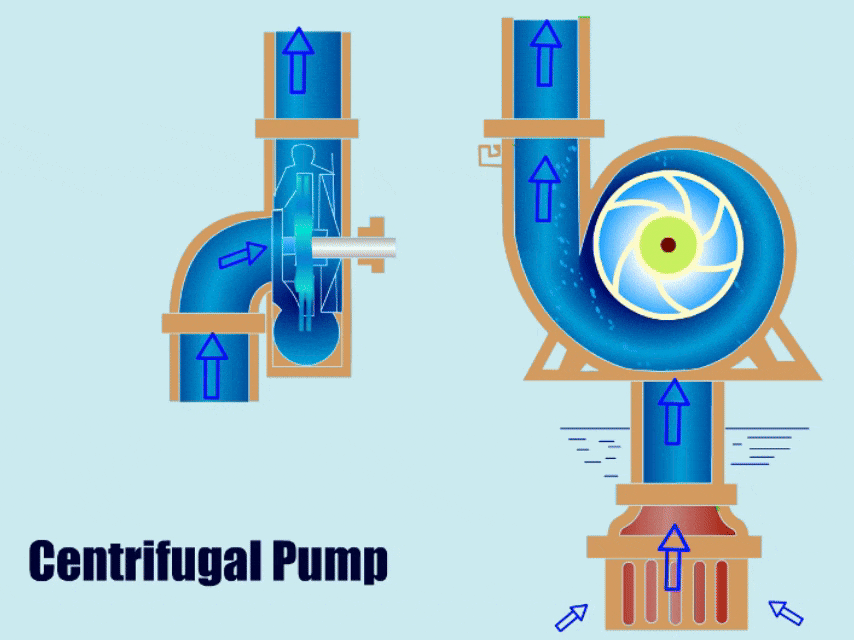
See How Does a Centrifugal Pump Work?
Types Of Sewage Pumps
In our lives, although there are many types of wastewater pumps, each type of wastewater pump has different application scenarios, and each type of wastewater pump has different structures and characteristics. Read the following content to learn about the 5 most common types of sewage pumps.
Submersible Sewage Pump
Submersible sewage pumps can operate submerged in water and feature waterproof motors, making them easy to handle sewage containing solid particles.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 🔸Space-saving No separate pump room is required for installation; simply place the submersible sewage pump in the sewage tank. 🔸High efficiency No sewage inlet piping is required, reducing pipe friction. 🔸Good cooling The water surrounding the pump not only cools the motor but also reduces noise. | 🔸Complex maintenance The submersible sewage pump must be lifted out of the water for repairs. 🔸Strict sealing If the seal is not tight or of poor quality, leaks are likely to occur, damaging the equipment. 🔸Corrosion-prone Prolonged immersion in sewage can easily corrode the submersible sewage pump due to various decaying substances. |
Horizontal Sewage Pump
Horizontal sewage pumps, also known as dry pit sewage pumps, do not come into direct contact with liquids. They are typically installed in a dry pump room and are suitable for high-flow applications.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 🔸Easy Maintenance Maintenance personnel can perform routine maintenance or replace spare parts directly on the ground. 🔸Long Service Life The dry environment prevents corrosion from sewage, significantly extending the service life of horizontal sewage pumps. 🔸Wide Application They can be used in both small and medium-flow applications and high-flow applications. | 🔸Large Floor Space The initial investment is high, and a separate pump room is required to protect the pump from rainwater and wind erosion. 🔸Cavitation Cavitation is prone to occur when the flow rate is unstable, causing vibration or abnormal noise in the horizontal sewage pump. 🔸Low Efficiency Compared to submersible sewage pumps, friction losses in the pipeline must be overcome. |
Sewage Grinder Pump
These pumps typically feature a cutter impeller or cutting mechanism, which can cut large solids, waste, and other materials before conveying, improving efficiency.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 🔸No clogging Able to grind large particles and long fibers, minimizing the risk of clogging. 🔸High Power Sewage grinder pumps typically feature a high-power motor, enabling long-term, long-distance pumping. 🔸Wide Application Suitable for most sewage pumping applications. | 🔸Difficult to maintain Complex structure, including blades and cutting mechanism, requires regular inspection by a professional. 🔸High Energy Consumption High-power motors result in higher energy consumption and increased utility costs. 🔸Noisy When the cutter impeller or cutting mechanism is operating, it creates a loud noise as it cuts debris. |
Sewage Ejector Pump
Sewage ejector pumps are primarily responsible for lifting sewage from low-lying areas to higher levels. It transports solids-laden sewage from underground sewage tanks to municipal sewer lines or sewage treatment plants. They are primarily used in residential areas, shopping malls, and other locations.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 🔸Easy Installation Compact, suitable for installation in confined spaces. 🔸Easy Maintenance Simple structure, allowing users to perform repairs and replace parts. 🔸Easy Maintenance Easily handles sewage containing solids (such as feces and household waste). | 🔸Limited Performance Suitable for small to medium flow applications, not suitable for large commercial or industrial applications. 🔸Limited Solids Handling The size of the solids in the sewage must be determined when selecting a pump. Sewage ejector pumps cannot handle large or hard solids. 🔸Short Lifespan Sewage ejector pumps can easily overheat during long-term operation, resulting in a shorter overall service life than horizontal sewage pumps. |
Vortex Sewage Pump
Vortex sewage pumps use the rotation of a vortex impeller to create a vortex effect, which moves sewage. The impeller does not come into direct contact with the sewage, effectively reducing clogging and corrosion.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 🔸Wear-Resistant Because the main moving parts of a vortex sewage pump do not come into direct contact with the liquid during operation, wear and tear on the sewage pump is minimized. 🔸Anti-Clogging The vortex effect of the vortex sewage pump ensures that the impeller does not come into contact with the sewage, ensuring smooth transportation of long fibers and solid wastewater without clogging. 🔸Stability Because it is less prone to clogging, it can operate for long periods without downtime, making it more durable, reliable, and stable. | 🔸Low Efficiency Compared to traditional centrifugal pumps, vortex pumps have lower efficiency, as the internal vortex flow loses some energy. 🔸Large Size Because vortex sewage pumps require vortex flow to operate, they are larger, heavier, and require more space. 🔸High Energy Consumption Due to their lower efficiency, vortex sewage pumps consume more energy than traditional sewage pumps. |
What is a Sewage Pumping Station?
A sewage pump system is a complete sewage transportation solution, not just a sewage pump. Each component in the sewage pump system works together to enable the sewage pump to smoothly extract sewage from the sewage tank or pipeline.
A sewage pumping station includes a sewage tank, sewage pipeline, sewage pump, float switch, PLC control system, and other equipment. The smooth operation of a sewage pumping station depends on the coordination of all these components.

Sewage Pump Maintenance Guide
To maintain a sewage pump for a long time, it must be regularly maintained to keep it in optimal condition. Proper maintenance will maximize its lifespan.
The following is a sewage pump maintenance checklist. You may wish to review the necessary maintenance information for optimal assistance.
📌 Daily
Noise: Check for abnormal noise and vibration.
Voltage: Check the motor voltage for normal operation and any abnormal fluctuations.
Flow: Observe the sewage pump’s flow rate and head for stability.
Leaks: Check for leaks around the pump and at the bearings.
📌 Weekly
Cleaning: Clean the screen or filter of debris, long fibers, and other debris weekly.
Pipes: Check the sewage pump’s inlet and outlet pipes and valves for damage and leaks.
📌 Monthly
Data Recording: Regularly record the sewage pump’s operating current, voltage, flow rate, head, pressure, and other data.
Grease: Check if grease needs to be replenished and add the appropriate amount according to the pump manufacturer’s maintenance manual.
Frequently Asked Questions
Sump Pump Vs Sewage Pump
Function:
Sump pumps are primarily used to transport solid-free wastewater or wastewater containing fine particles, such as rainwater and domestic water.
Sewage pumps are primarily used to transport wastewater containing solid particles (such as long fibers, garbage, and feces).
Applications:
Sump pumps are primarily used in homes, residences, garages, and other areas to prevent wastewater accumulation.
Sewage pumps are widely used in sewage treatment plants, municipal drainage, and industrial wastewater.
Can A Sewage Pump Be Used As A Sump Pump?
We don’t recommend using a sewage pump as a sump pump. This is because a sewage pump’s primary function is to transport wastewater containing solids, while a sump pump is designed to transport clean water.
Sewage pumps use high-power motors and consume more power than sump pumps. Using a sewage pump to transport clean water results in wasted energy and the pump will not perform at its optimal performance.