When selecting pumps, performing routine maintenance, or learning about pumps, comparisons are inevitable: centrifugal vs. positive displacement pumps. What exactly are the differences? These are the most common types of pumps.
This guide covers the definitions, key comparisons, applications, selection, and maintenance points for both types of pumps. Learn from this guide to uncover their secrets.
Difference Between Positive Displacement Pump And Centrifugal Pump
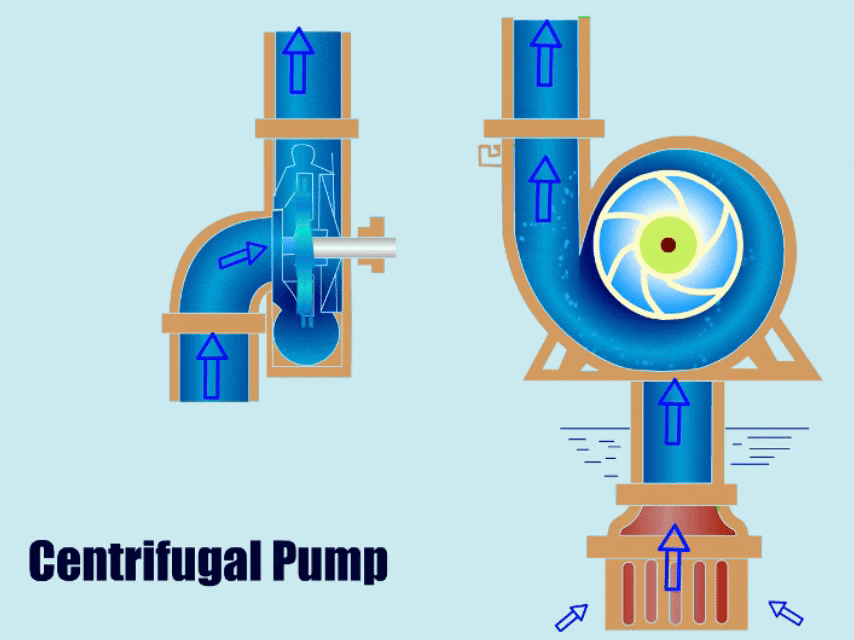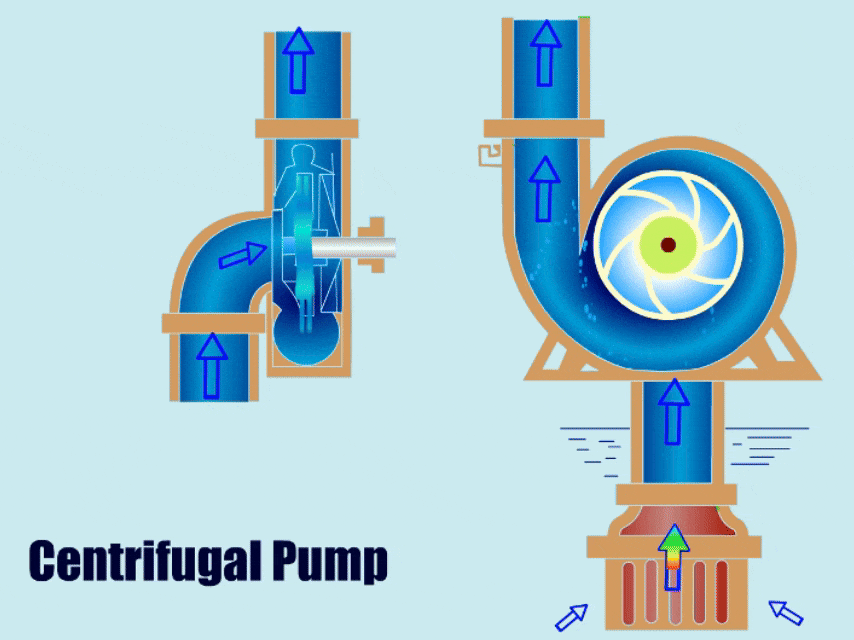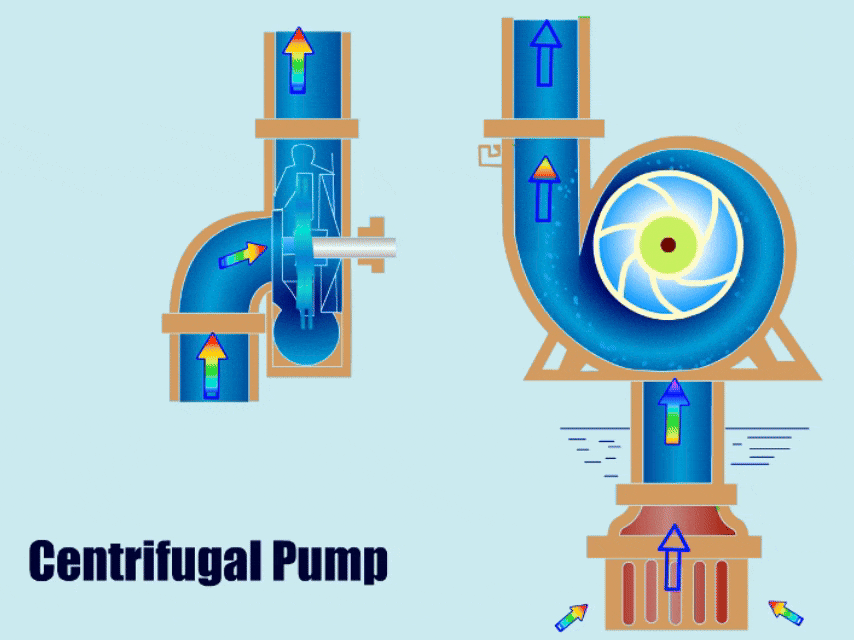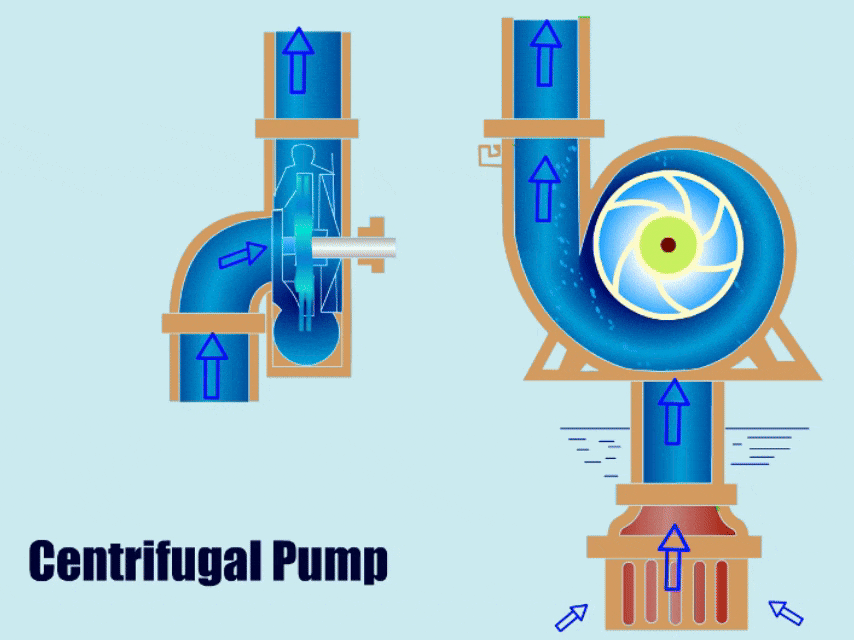
Centrifugal pumps move liquids by rotating an impeller. The high-speed rotation of the impeller generates centrifugal force, converting kinetic energy into pressure energy in the liquid, allowing the high-pressure liquid to be pumped out from the outlet. Centrifugal pumps are suitable for conveying clean water, industrial wastewater containing solids, or applications requiring continuous, high-flow-rate delivery, such as water treatment, slurry processing, and dredging.
Positive displacement pumps, on the other hand, use internal moving parts (gears, pistons, diaphragms) to directly squeeze or push the liquid out through reciprocating motion. Without the impeller’s energy conversion, PD pumps are more efficient and suitable for conveying high-viscosity liquids, requiring stable pressure, or demanding precise flow rates, such as in the pharmaceutical, food, and petroleum industries.
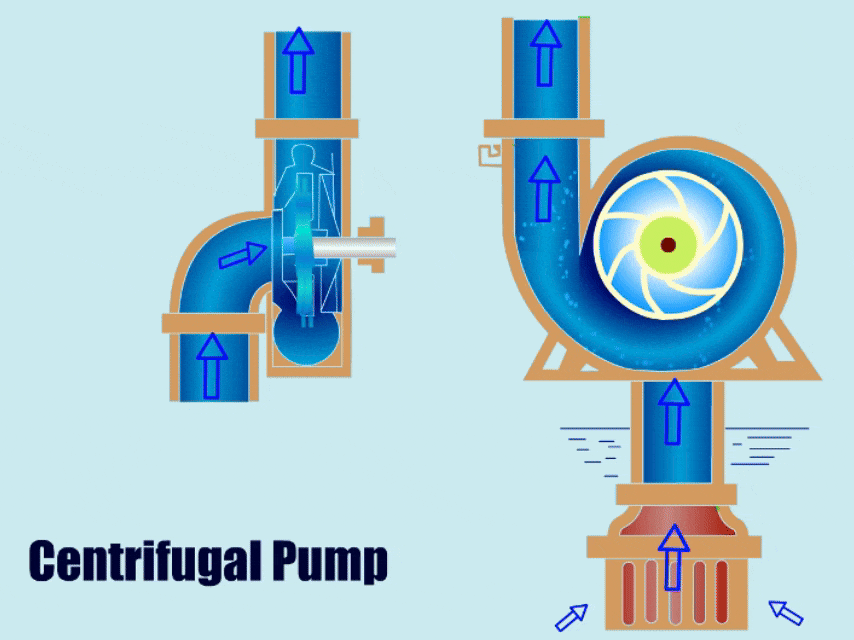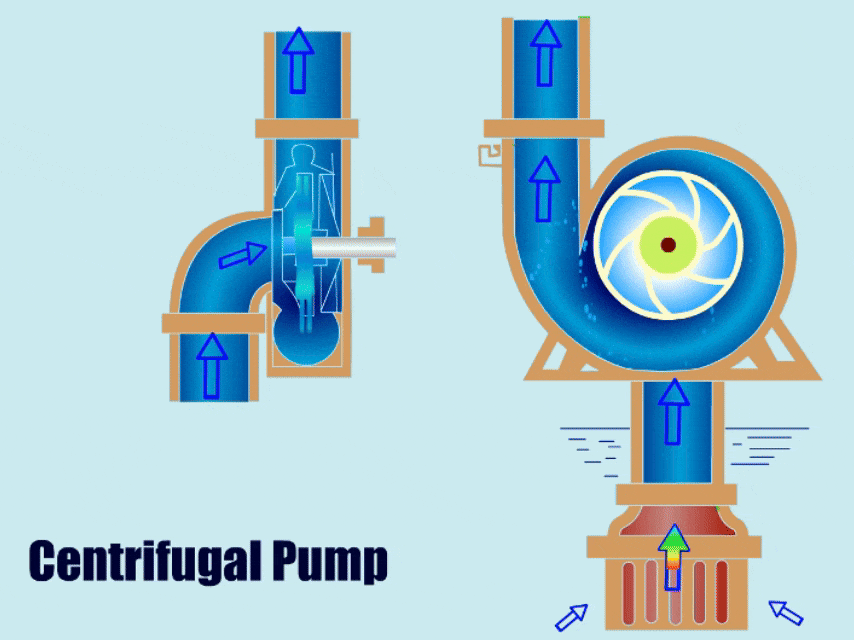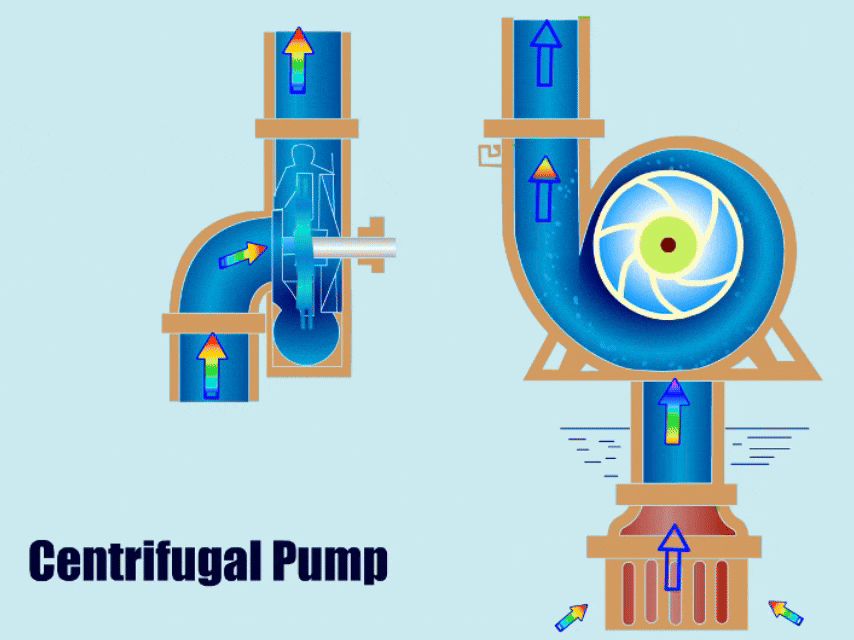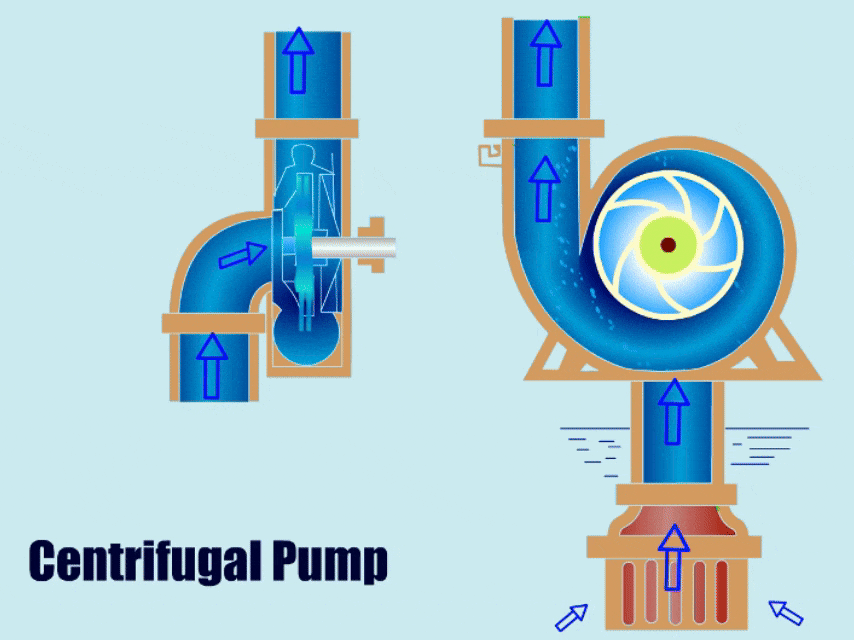
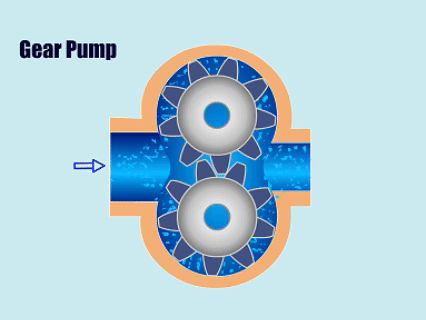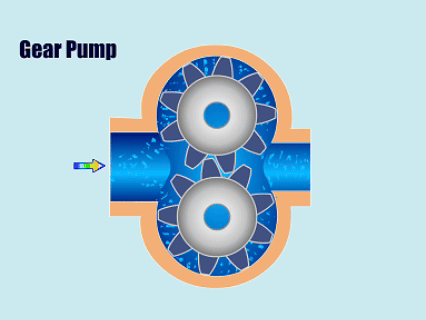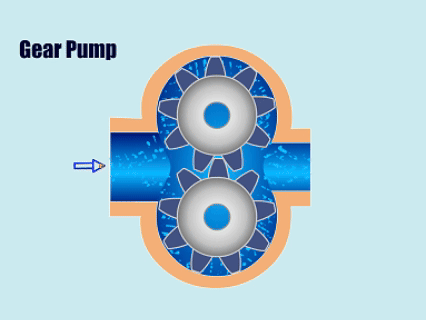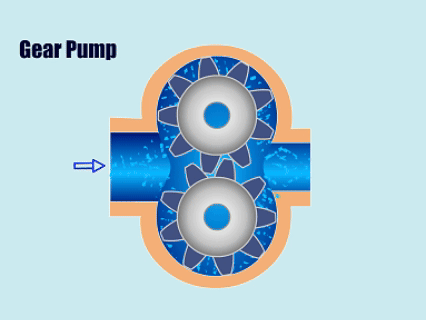
Chart: Positive Displacement Pumps Vs Centrifugal Pumps Comparison
| Centrifugal Pumps | Positive Displacement Pumps | |
| Fluid Type | Clear water, slurry containing solids, low to medium viscosity, high flow rate liquid | High viscosity, stable flow rate, gas-liquid mixture |
| Flow Rate And Pressure | The greater the flow, the lower the pressure; they are inversely proportional. | Flow rate and pressure are almost independent, and the curves are parallel. |
| Viscosity And Solids Content | Suitable for low viscosity, high abrasive solid particles with a solid content of 30-40%. | Suitable for fine, soft solid particles with high viscosity and a solid content of 60-80%. |
| Shearing | High shear force easily disrupts fluid structure. | Low shear force, suitable for biological slurries, oil slurries, etc. |
| Efficiency And Energy Consumption | Efficiency varies with operating conditions, reaching its highest level at the BEP (Best Efficiency Point) with the lowest energy consumption. | Efficiency remains unchanged regardless of operating conditions, indicating high efficiency and relatively stable energy consumption. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance includes daily checks of flow rate, head, vibration, and noise. | Regular maintenance mainly involves checking for any abnormalities in traffic and load. |

Key Points: Positive Displacement Pump Vs Centrifugal
Flow and Pressure
🔸 Centrifugal pumps: The flow rate of a centrifugal pump changes inversely with its head. When the flow rate increases, the head decreases, which means the pressure decreases.
🔸 Positive displacement pumps: In PD pumps, the flow rate is constant. According to the shaft power formula

, flow rate and pressure are unrelated, but they are directly related to power. As pressure increases, the pump requires more power.
Viscosity And Solids Content
🔸 Centrifugal Pumps: As mentioned earlier, centrifugal pumps are driven by an impeller to flow liquid. Therefore, the viscosity of the liquid has a significant impact on the pump’s performance. Increased viscosity requires more energy for impeller rotation, leading to a decrease in pump efficiency.
However, by replacing the materials with wear-resistant ones, centrifugal pumps can handle liquids containing 30-40% hard, highly abrasive solid particles, even large-diameter particles, such as those found in mine tailings or river dredging.
🔸 Positive Displacement Pumps: As previously mentioned, PD pumps rely on the reciprocating motion of internal components to propel the liquid. Almost all the energy is used to move the liquid, with no impeller consumption. Therefore, changes in liquid viscosity do not affect the flow rate, maintaining stable efficiency.
PD pumps can handle soft solid slurries with a solid content as high as 60-80%. However, because they operate within a sealed pump chamber, they are unsuitable for handling fluids containing highly abrasive and large solid particles, as this can easily cause pump jamming or clogging.
Shearing
🔸 Centrifugal pumps: Centrifugal pumps have high shear force and are not suitable for conveying biological slurries and polymer slurries. This is because when a centrifugal pump starts, the impeller rotates at high speed, which means the impeller will disrupt biological cells, colloids, pastes, etc., within the liquid.
🔸 Positive Displacement Pumps: PD pumps expel liquid by slow compression. Without a high-speed rotating impeller, the shear force is greatly reduced, making them suitable for conveying slurries containing polymers, biological cells, colloids, and pastes.
Efficiency And Energy Consumption
🔸 Centrifugal pumps: The efficiency of centrifugal pumps varies with operating conditions. They are most efficient near their best efficiency point (BEP). However, under complex operating conditions, energy consumption gradually increases, and efficiency decreases.
🔸 Positive Displacement Pumps: The efficiency of PD pumps is more stable and less affected by operating conditions. According to the power formula mentioned earlier, power only changes when flow rate or pressure varies. This more linear variation allows for better energy management.
Maintenance
To ensure a long service life, both centrifugal and positive displacement pumps require regular maintenance.
🔸 It’s important to note that for centrifugal pumps, the rotating parts, specifically the impeller, require priority attention. Regardless of whether the pump is handling clean water or slurry, the impeller will experience wear. The impeller’s material, quality, and condition all affect daily operation. We can also check for abnormalities by monitoring temperature, noise, and flow rate. Fortunately, centrifugal pumps have a simple structure, making maintenance relatively convenient and quick.
🔸 Positive displacement pumps require special attention for leaks. Internal leaks will lead to decreased efficiency. Secondly, observe for abnormalities in flow rate and pressure. If abnormalities are found, check for blockages. Also, pay attention to unusual noises and regularly clean valves and filters to remove foreign objects.

Applications of Centrifugal and Positive Displacement Pumps
We previously mentioned the applicable fluid types for these two types of pumps in the Positive Displacement Pumps Vs Centrifugal Pumps Comparison Chart. Next, I will provide a detailed analysis and pump recommendations based on different applications.
When to Use Centrifugal Pump?
Due to their structure and operating principle, centrifugal pumps are generally suitable for conveying clean water, impure water, and medium-viscosity fluids, such as water for high-rise residential buildings, irrigation, sewage, slurry, mortar, silt, fly ash, gravel, and animal manure.
Through optimized impeller structure and the use of highly wear-resistant materials, the application range of centrifugal pumps has been significantly expanded. Even when handling slurries containing hard solid particles, centrifugal pumps can maintain excellent lifespan and performance.
When to Use Centrifugal Pump?
Unlike centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps do not rely on rotating impellers to propel liquids, resulting in lower shear forces. Furthermore, the moving parts within the pump directly actuate the fluid through compression, avoiding energy loss and achieving higher efficiency.
This structure means that the viscosity of the liquid has almost no impact on efficiency, but it is not suitable for conveying slurries containing hard particles. PD pumps are suitable for conveying high-viscosity liquids, applications requiring high shear forces, or scenarios demanding precise and constant flow rates, such as oil and gas, biological and polymer slurries, sludge, food processing, and pharmaceuticals.

Common industrial applications
Water Treatment: Wastewater and domestic water often contain large amounts of impurities, gravel, and long fibers. High-flow-rate, abrasion-resistant centrifugal pumps are the best choice in these cases.
Mining: In wastewater recovery and tailings treatment in mines, liquids contain numerous corrosive and abrasive hard particles. Centrifugal mining slurry pumps can easily handle these demanding conditions.
Food/Pharmaceutical: In food processing and biopharmaceuticals, precise addition of additives or pharmaceuticals is required without compromising the biocompatibility of the materials. Positive displacement pumps can accomplish these tasks with stable flow rates and high efficiency.
Oil & Gas: In oil and gas transportation, especially oil transportation, high-viscosity oil can reduce the efficiency of centrifugal pumps and even cause pipeline blockages. Positive displacement pumps, however, can stably move oil, gas, or high-viscosity fluids.
Dredging: Dredging projects require the removal of silt from riverbeds, ports, and riverbanks, often containing large amounts of gravel and stones. Centrifugal dredging pumps, adept at high flow rates and solids handling, can effectively handle various types of slurries.
Irrigation/Livestock: Centrifugal pumps are often used for large-volume farmland irrigation, while in animal husbandry, efficient handling of animal manure is a challenge. The excellent solid-pass performance of centrifugal pumps ensures the stable delivery of large quantities of animal manure.
How to Choose? Centrifugal Vs Positive Displacement Pump
When selecting a suitable pump, the following five factors should be considered:
Ⅰ. Is a continuous, high flow rate required, or is a precise, stable flow rate required?
Ⅱ. Is high-pressure delivery required, or is stable pressure required?
Ⅲ. Is the fluid you are handling a high-viscosity slurry?
Ⅳ. Does the slurry contain a large number of solid particles, and what is the hardness and size of these particles?
Ⅴ. Does the slurry you are handling contain biological cells, polymers, or other substances that cannot be destroyed?
If you can answer these five questions, you will be able to initially select a pump suitable for your project.

The table below lists the main types of centrifugal pumps and positive displacement pumps. When choosing a pump, we need to consider not only the application scenario, but also the physical properties of the slurry and the pump material, because only by choosing the most suitable pump can we ensure that our production efficiency reaches its maximum.
| Types of Pumps | Common Types | Applications |
| Centrifugal Pumps | Vertical Pumps, Horizontal Pumps, Submersible Pump, Slurry Pumps, Dredge Pumps | Wastewater treatment plants, tailings, dredgers, farms, paper mills, irrigation, and domestic water supply. |
| Positive Displacement Pumps | Piston Pumps, Plunger Pumps, Diaphragm Pumps, Gear Pumps, Screw Pumps, Peristaltic Pumps, Lobe Pumps | Pharmaceutical factories, oil transportation, food processing plants, paper mills, paint factories |
If you have any needs regarding the selection of centrifugal pumps and positive displacement pumps, please feel free to contact Kingda experts. We will provide you with free and timely advice, and if needed, we can also customize fluid delivery solutions for you.