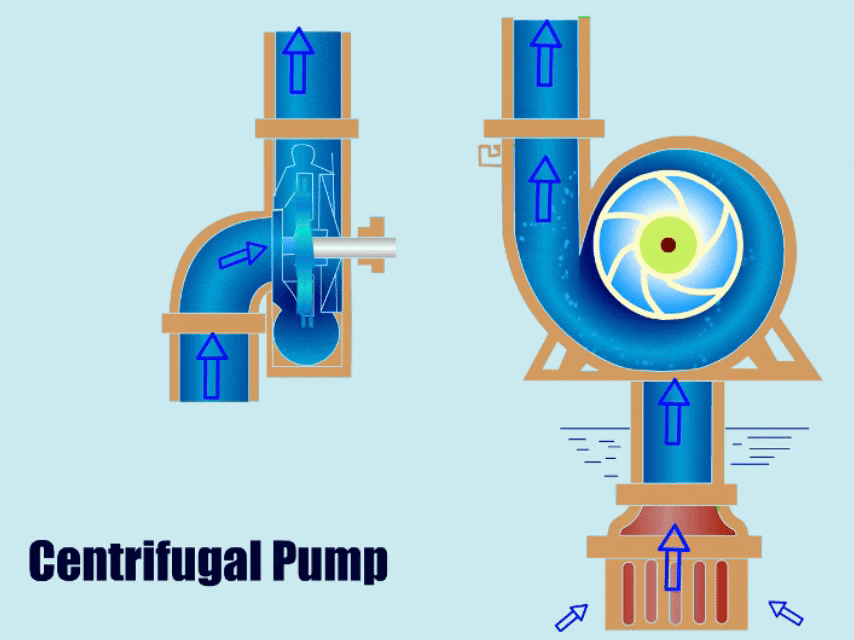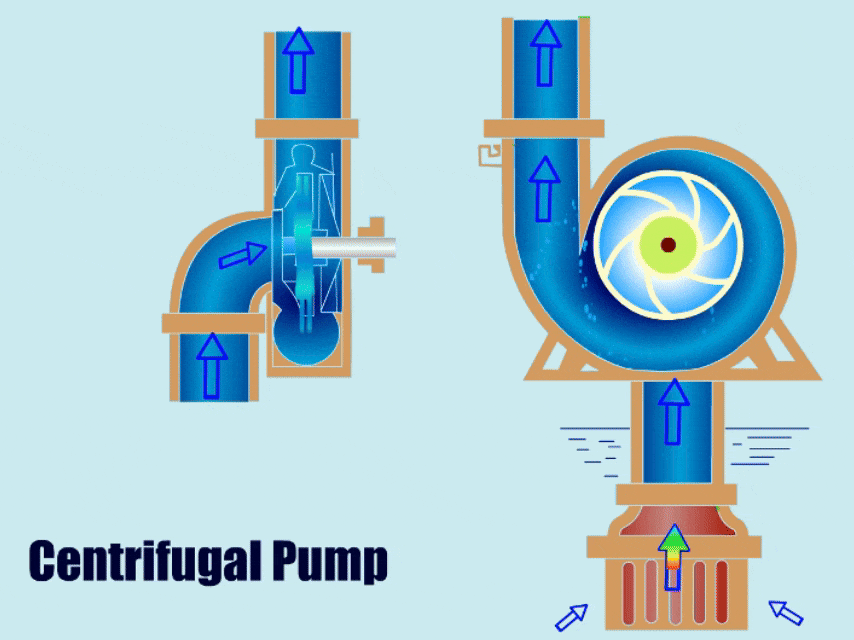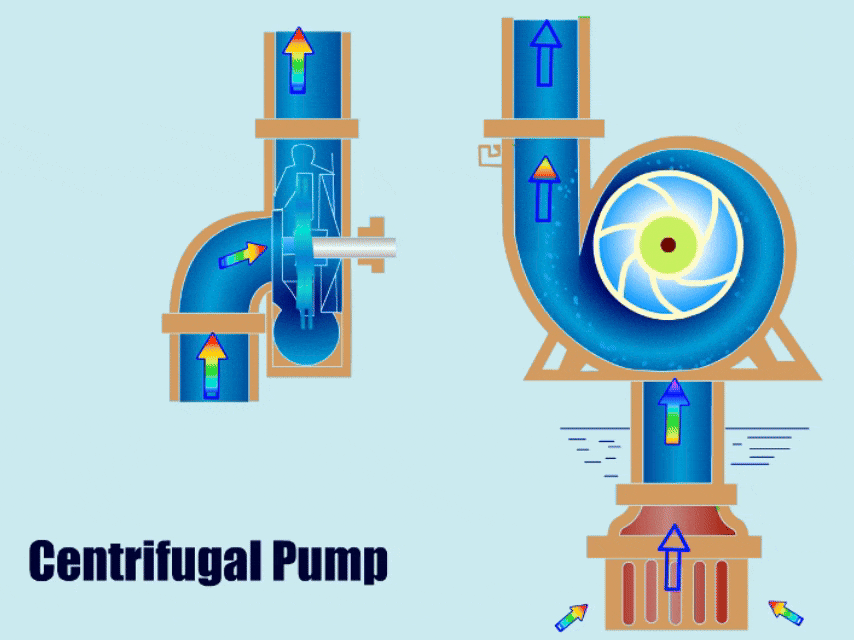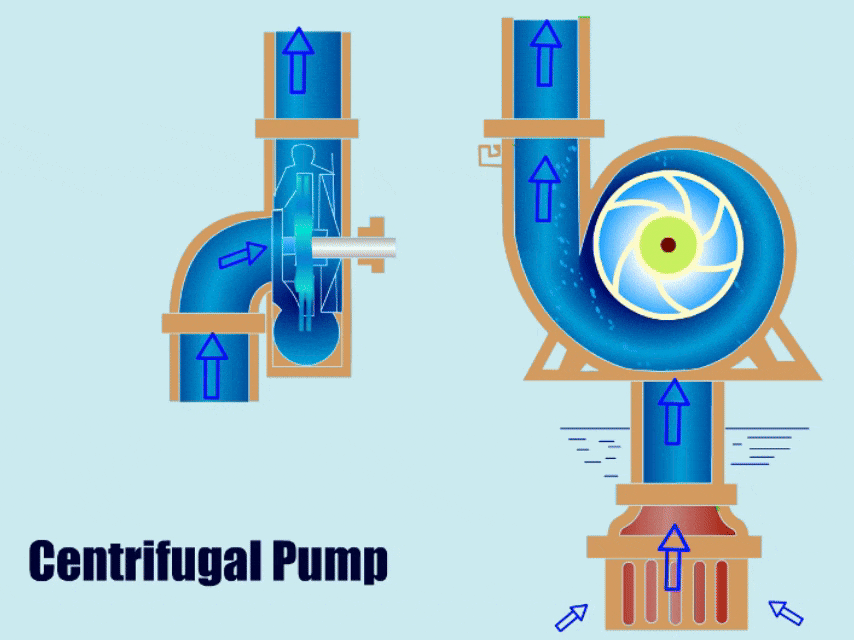
Centrifugal pumps are one of the most widely used pump types today. This article will detail centrifugal pump spare parts and analyze the causes of failure, replacement, and material recommendations for different centrifugal pump parts.
Main parts of a centrifugal pump: The impeller propels the fluid, the casing (or volute) guides the liquid flow into pressure energy, the shaft connects the motor and impeller, transferring mechanical energy to the impeller, the bearing supports the shaft, and the seals prevent liquid leakage.
Centrifugal Pump Parts List
In this section, I will show all the centrifugal pump parts names, including their materials, functions, and malfunctions. Please see the centrifugal pump parts images and list below for more information.

| Centrifugal Pump Parts Name | Material | Function | Malfunction |
| Impeller | ▪Ductile iron ▪High Chromium alloy ▪Rubber | The impeller moves the fluid by rotating. | ▪Abrasion ▪Cavitation ▪Blockage ▪Fracture |
| Casing(Volute) | ▪Ductile cast iron ▪High chromium alloy ▪Stainless steel | Volute is used to guide the movement of fluid within the flow channel. | ▪Wear ▪Corrosion ▪Cavitation |
| Shaft | ▪45# steel ▪Stainless steel ▪Alloy steel | Shaft transfers the mechanical energy of the motor to the impeller. | ▪Vibration ▪Imbalance ▪Wear |
| Bearing | ▪Alloy steel ▪Stainless steel | Bearing is used to support the shaft and ensure its smooth rotation. | ▪Overheating ▪Abnormal noise ▪Looseness ▪Wear |
| Seal | ▪Graphite ▪Stainless steel ▪Rubber | Seal is used to prevent leaks and to prevent external impurities from entering the pump. | ▪Aging ▪Wear |
| Base | ▪Ductile iron ▪Stainless steel | The base supports the weight of the centrifugal pump, enabling the pump to operate stably. | ▪Corrosion ▪Cracks |
Centrifugal Pump Parts Diagram
Centrifugal Pump Diagram with Parts
The centrifugal pump diagram below shows the main spare parts of the centrifugal pump.
This diagram gives you a general idea of the installation location of each spare part and the structural information of the centrifugal pump.

Centrifugal Pump Parts Details
The centrifugal pump parts breakdown diagram shows that a centrifugal pump includes components such as impeller, casing, shaft, bearing, seals, and base. Next, I will explain the function, type, and material of each component in detail. Please continue reading the centrifugal pump spare parts guide.
Impeller

Impeller Definition
The impeller is the core component of a centrifugal pump that generates centrifugal force.
The impeller draws fluid into the pump by rotating, and then throws the fluid in all directions.
The fluid flows through a gradually narrowing flow channel, converting kinetic energy into pressure energy.
Impeller Materials
We can select different impeller materials according to different applications and conveying media, such as ductile iron, high chromium alloy, rubber, etc. Only by selecting the right material can we ensure that the impeller has a long service life and high conveying efficiency.
| Medium | Material |
| Clear water | Ordinary cast iron material |
| Contains large particles and corrosive slurry | High chromium alloy |
| Abrasion, chemical slurry | Rubber |
Types of Impeller
🔸 Closed impellers have guard plates on both sides, forming a closed flow channel inside the impeller. They are robust and offer the highest conveying efficiency.
🔸 Semi-open impellers have a guard plate on one side, while the other side is open to the conveying medium. They are more resistant to clogging than closed impellers, but their conveying efficiency is lower.
🔸 Open impellers have no guard plates on either side, the blades are directly connected to the center of the impeller. Compared to the closed and semi-open impellers mentioned above, they have the strongest resistance to clogging, but their conveying efficiency is lower than the two types of impellers mentioned above.
| Impeller Types | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
| Closed Impeller | ◾High efficiency ◾High pressure resistance ◾Long lifespan | ◾Frequent blockages ◾Difficulty in maintenance | ◾Clear water ◾Sewage ◾Mineral slurry ◾Mortar |
| Semi-open Impeller | ◾It has better efficiency than open impellers and better anti-clogging properties than closed impellers. | ◾Inefficient | ◾Industrial wastewater ◾Fluids containing solids ◾Sludge |
| Open Impeller | ◾Anti-clogging ◾Easy to maintain | ◾Inefficient ◾Easily damaged | ◾Fiber ◾High solids ◾Sludge |
Pump Casing
Casing Definition
The pump casing is a container that holds the fluid and other components. It typically has a volute-like, streamlined rotating structure.
During centrifugal pump operation, the fluid passes through the gradually narrowing flow channel within the volute, converting its kinetic energy into pressure energy, thus allowing it to be discharged from the outlet at a higher pressure.

Types of Pump Casing
Pump casing types generally include three types: volute, diffuser casing, and split case casing.
🔸 Volute casings are further divided into single volute and double volute types. This type of casing has a helical shape, which is more conducive to fluid flow and provides higher delivery efficiency.
🔸 Diffuser casings are generally used in multistage pumps. Diffuser casings have multiple impellers inside, with the flow channels gradually widening. The pressure increases with each impeller stage, resulting in higher pressure and efficiency than ordinary centrifugal pumps.
🔸 Split case casings are centered on the pump shaft and have an upper and lower structure. This type of casing facilitates disassembly, making maintenance easier and more convenient for workers.
| Pump Casing Types | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
| Single-volute | ◾Simple structure ◾Low cost | ◾Not suitable for high-voltage conditions | ◾Clear water ◾Sewage ◾Sump drainage |
| Double-volute | ◾Robust structure ◾Long service life | ◾Higher cost than a single volute | ◾Wastewater ◾Mineral slurry ◾Mud |
| Diffuser casing | ◾High efficiency ◾Higher pressure | ◾High cost ◾Difficult maintenance | ◾Boiler feedwater ◾High-rise water supply ◾Petroleum |
| Split case casing | ◾High flow rate ◾Easy to maintain | ◾Large size ◾Difficult to install | ◾Municipal water supply ◾Drainage |
Pump Shaft

Pump Shaft Definition
One end of the shaft is connected to the motor, and the other end is connected to the impeller. After the motor starts, the shaft will rotate, transferring the motor’s mechanical energy to the impeller.
The shaft is generally made of steel or alloy steel, which gives it greater strength, toughness, and wear resistance.
Pump Shaft Sleeve
Pump shaft sleeves are installed on the pump shaft to protect it, prevent wear, and extend the equipment’s service life. Shaft sleeves are typically made of materials such as stainless steel, alloy steel, or cast iron, giving them enhanced wear resistance and further improving the equipment’s lifespan.
Pump Bearing
Centrifugal Pump Bearing
Centrifugal pump bearings are primarily used to stabilize the pump shaft, ensuring the centrifugal pump remains stable during operation and distributing radial forces to the base.
Pump bearings also reduce wear on the pump shaft, absorb excess vibration and shock, and extend the pump’s service life.

Bearing Lubricant
Bearing lubricant protects bearings by forming a protective film on the bearing surface, reducing wear from debris. Insufficient or contaminated lubricant can cause the bearing to overheat and become damaged.
Lubrication Methods for Bearings
There are three main types of bearing lubrication:
🔸 Grease lubrication: Grease lubrication is the most common type, characterized by its simple structure, easy maintenance, and good sealing effect.
🔸 Water lubrication: Water lubrication is suitable for applications where the pump is submerged in water. It eliminates the need for oil and is relatively environmentally friendly.
🔸 Solid lubrication: Solid lubrication is used in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, corrosion, and chemical reactions.
Pump Seals

Centrifugal Pump Seal
Pump shaft seals are a key component of centrifugal pumps.
They prevent leakage of the pumped medium and prevent external contaminants such as gases and dust from entering the bearings, thus protecting the bearings and preventing unnecessary wear and tear.
Centrifugal Pump Seal Types
🔸 Packing Seal: Packing seals are a common type of pump seal. Materials such as aramid and graphite are compressed into the sealing box and secured with a gland to prevent leakage. However, packing seals have a short lifespan and require periodic replacement.
🔸 Mechanical Seal: Mechanical seals are the most commonly used type of shaft seal. They utilize the liquid film pressure and mechanical elasticity generated between the rotor ring and stationary ring in the centrifugal pump’s mechanical seal parts to achieve a seal. Mechanical seals are more reliable than packing seals, have a longer service life, do not require packing replacement, and are more efficient.
🔸 Expeller Seal: When the centrifugal pump is running, pressure is generated between the impeller and expeller. This pressure restricts the flow of slurry into the pump seal, thus achieving a seal.
Pump Base
Pump Base Definition
The base is the foundation of the entire pump system, supporting the centrifugal pump, motor, bearings, and other components. During pump operation, the base balances most of the radial forces, reducing minor vibrations and noise, thus making the pump more stable.
The pump base is primarily composed of cast iron, carbon steel, and stainless steel. These materials are high in strength and rigidity, ensuring the long-term operation of the centrifugal pump.

Centrifugal Pump Parts Material Guide
As we all know, centrifugal pump parts can be made from many different materials. Does a higher price necessarily mean a better material? Not necessarily. The truly good material is the one chosen based on the medium being pumped and the operating conditions. If you have any questions about this, please read the following:
The following are the available material options for various centrifugal pump parts:
- Impeller: Cast iron, stainless steel, alloy, rubber, ceramic
- Casing: Cast iron, alloy, stainless steel, composite materials
- Shaft: 45# steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, high-end nickel-based alloys
- Bearing: Bearing steel, stainless steel, alloy steel
- Seals: Graphite, silicon carbide, stainless steel, ceramic, rubber
- Base: Carbon steel, cast iron, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, composite materials
| Medium | Impeller | Casing | Shaft | Bearing | Seals | Base |
| Clear water | ◾Cast iron ◾Stainless steel | ◾Cast iron | ◾45# steel ◾Stainless steel | ◾Bearing steel | ◾Graphite ◾Silicon carbide | ◾Cast iron |
| Slurry | ◾Cast iron ◾Alloys ◾Rubber ◾Ceramics | ◾Cast iron ◾Alloy | ◾Alloy steel ◾Stainless steel | ◾Bearing steel | ◾Silicon carbide | ◾Cast iron ◾Carbon steel |
| Corrosive | ◾Alloys ◾Stainless steel | ◾Alloys ◾Composite materials | ◾Stainless steel ◾Alloy | ◾Alloy steel ◾Stainless steel | ◾Ceramics ◾Graphite | ◾Stainless steel |
| High-temperature | ◾Ceramics ◾Alloys | ◾Cast iron ◾Stainless steel | ◾Stainless steel ◾Alloy steel | ◾Stainless steel | ◾Ceramics | ◾Stainless steel ◾Cast iron |
Centrifugal Pump Spare Parts Maintenance
We select different spare parts materials based on the different media to maximize their service life, thereby reducing operating costs, decreasing maintenance frequency, and improving efficiency.
Common Fault List
- Overheating: If the motor or bearings overheat, check for blockages in the delivery pipeline or ensure proper bearing lubrication.
- Abnormal Vibration: If the centrifugal pump vibrates abnormally during operation, check for pump shaft damage and loose base.
- Media Leakage: If the centrifugal pump leaks, check for shaft seal damage, such as aging seal material or insufficient cooling water.
- Insufficient Flow: Insufficient flow during operation may be due to pipeline leaks or severe impeller wear.
- Abnormal Noise: If the pump makes abnormal noises, promptly check for impeller blockage or bearing damage.
Regardless of the issue, address it promptly and follow the pump manufacturer’s operating manual. Replace severely worn spare parts to minimize losses.
Centrifugal Pump Parts Assembly
As we all know, centrifugal pumps have many internal parts. When maintaining them, we need to have a comprehensive understanding of centrifugal pump installation. In the video below, I will provide a comprehensive and detailed introduction to the installation steps of a centrifugal pump. You will learn how to install each component of a centrifugal pump in this video.
FAQ
Learn in Centrifugal Pump Which Part Control The Flow Rate
To a certain extent, the flow rate of a centrifugal pump is determined at the factory; the flow rate is directly determined by the impeller diameter. The larger the impeller diameter, the greater the flow rate.
Additionally, the impeller type also affects the flow rate; for example, an open impeller has a larger flow rate than a closed impeller. Additionally, the motor speed also affects the flow rate; a higher speed means a larger flow rate.
What are The Main Parts of a Centrifugal Pump?
The main components of a centrifugal pump include impeller, casing, shaft, seals, and bearing. These components are important parts of the centrifugal pump and together they form the pump’s frame.
Mechanical seal vs packing: which to choose?
Mechanical seals and packing seals each have their own advantages and disadvantages. We need to choose the optimal one based on the actual situation. You can view the comparison list to make the best choice.
| Types of Shaft Seal | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Mechanical seal | ◾Zero leakage ◾Long service life ◾Wear resistant | ◾High cost |
| Packing seal | ◾Low cost ◾Easy maintenance | ◾Potential for persistent minor leaks ◾Frequent replacements ◾Short service life |
How do I know when the impeller needs replacement?
If the pump vibrates, makes abnormal noises, or experiences unstable flow during operation, it should be stopped immediately to inspect the impeller. If cracks are found on the blades or damage caused by cavitation, the impeller should be replaced promptly.
Whether the impeller needs replacement depends on whether any different faults or phenomena have occurred previously. These faults will help determine whether the impeller needs inspection or replacement.