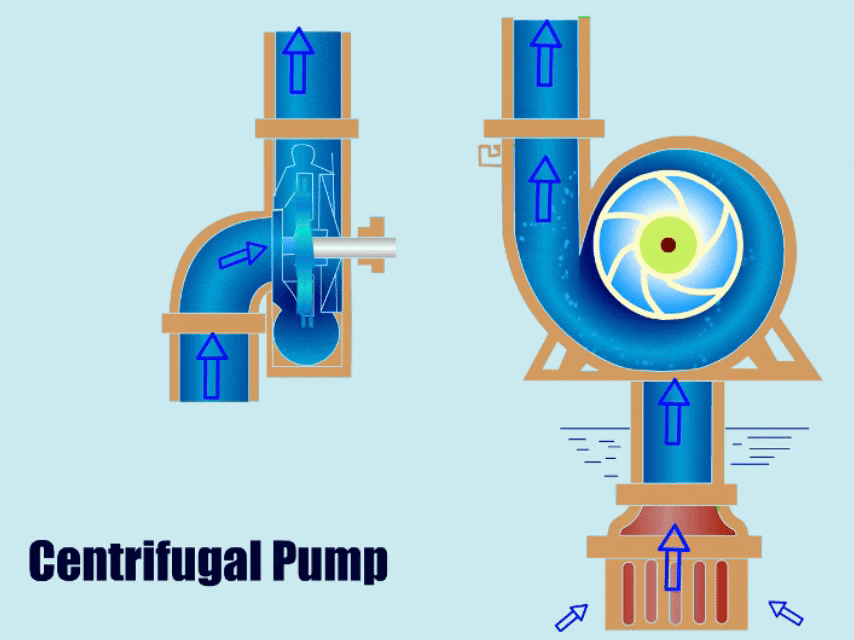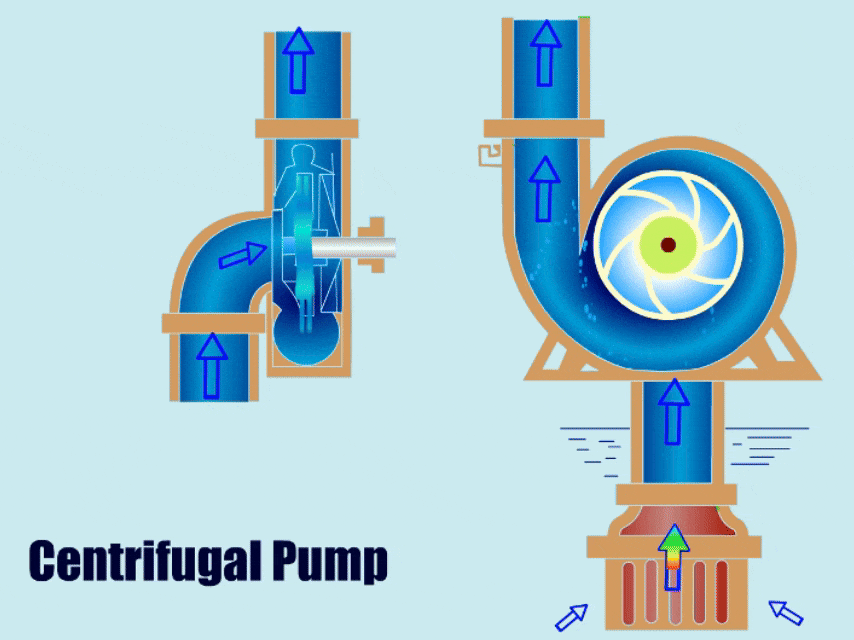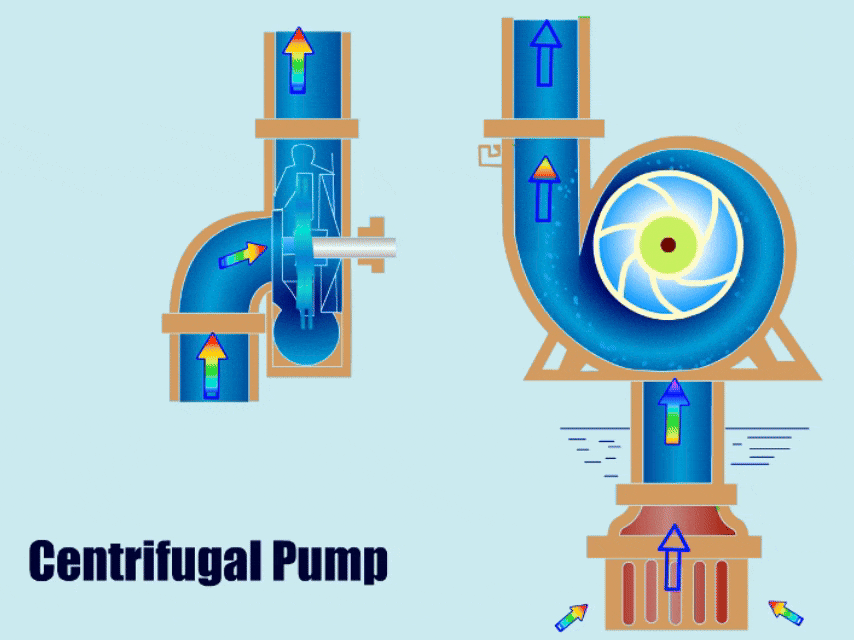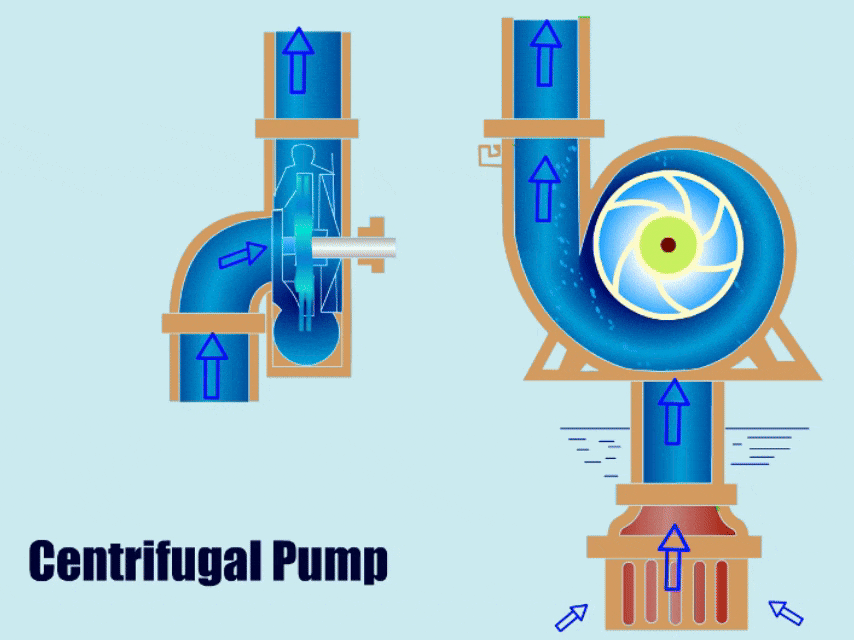
Any plant in the aggregate industry can significantly benefit from knowing what kind of Portable slurry pump to utilize. The wrong type of pump will result in inefficiency, early failures, and, consequently, higher replacement costs. Which type of pump you use will depend, among other things, on whether the interior is lined with rubber or metal.
What is Portable Slurry Pump?
Sand and mud are examples of mixed, abrasive, and high-density materials that can be transported with a vertical portable slurry pump. It is used in mining, metallurgy, coal, energy, construction materials, and environmental protection industries. The coastal shoal farm excavation, river dredging, diking, transformation, sand extraction, fundamental farmland development, underground works, etc., all use the slurry pump.
Application of Portable Slurry Pump
- Water treatment
- Mining
- Civil construction
- Heavy industry
- Mineral processing
- Sumps and basements
- Municipal
Features of Portable Slurry Pump

- White iron impeller with 27% chrome, an integrated agitator, a volute, and a changeable back plate.
- The filter, shaft, and shaft sleeves are 420 stainless steel.
- Water casing clearance with a large cut.
- An electro-submersible motor with low speed offers dependable continuous operation.
- Cast iron engine with heavy-duty construction.
- To protect the motor from damage caused by high temperatures or water infiltration, the engine is equipped with moisture sensors, float switches, bearing temperature sensors, and stator temperature sensors.
- Class motor insulation is included as standard, while H-class insulation is an option for high temperatures.
- Effective sealing between the motor and the wet end is provided by a double mechanical seal lubricated with an oil bath made of tungsten/ceramic on the drive end and carbon/ceramic on the wet end.
- For applications requiring high temperatures, external cooling alternatives are available.
- There are numerous alternatives for paint and protective coatings.
Pumps for Slurry Solution
Metal Pumps
Metal pumps are highly valued in the aggregate business due to their durability. Whereas all sludge machines have excessive wear, some elements, such as polycarbonate or rubber, are more resistant to harm. However, because of this attribute, the initial cost will be higher than for rubber-lined pumps.
Although maintenance frequencies will be greater significant, they will be more sporadic to mitigate the costs. Another factor to consider while using steel piping is the slurry’s composition. A rubber-lined pump may wear out too soon if the slurry contains 3/8′′ or more prominent boulders. When choosing a pump, it is vital to understand what compensates your sludge remedy and how the pump’s components perform.
Rubber-Lined Pumps
Rubber lined slurry pumps will be less expensive than metal-lined slurry pumps. Because the insides of this pump are rubber rather than metal, it will need to be replaced considerably sooner than a metal pump.
Recent technology has allowed rubber-lined pumps to last longer than earlier models, resulting in a less lifespan gap between metal and rubber-lined pumps than ever before. Knowing what is pumping via a rubber-lined pump is also essential in determining if it will function for your system. A faulty rubber-sand mixture in the slurry can cause a pump to fail.
Compressors for Reprocessing Soil, Small stones, and Building Supplies Has To be Powerful and Power Generation.

Pumps specialize in developing and constructing development and construction of pumps for corrosive substances and flood mitigation concerns that are widespread in the accumulated industry, spanning quarrying to processing facilities.
Water handling and management are critical components in quarrying, aggregate washing, and the production of mineral-based construction materials. Pumps have created solutions to solve a wide range of fluid handling challenges, including dewatering a site with submersible pumps and water cleaning for reuse as process production water.
It will Reduce Downtime and Maintenance: It Would be More Convenient
We recognize the importance of dependable, hardworking, and energy-efficient pumps in meeting output requirements and achieving long-term success. When planning, specifying, and installing pump systems, we always keep plant downtime in mind.
Indicators of Aggregate Slurry Pump Wear

Excessive Leakage at the Gland
Different seals have different levels of leakage at the gland, but there is some leaking and some leaking that is significant. To spot a problem, an operator must first become familiar with what the leakage is meant to be.
A simple adjustment may be required, or a minor repair may be necessary. Whenever it is left unattended, it will turn into work in the service that could have been prevented.
Excessive Leakage at the Liner
Most slurry pumps in the aggregate industry include removable liners to protect the pump’s main body. The pump may leak at the liners, depending on how the liners wear. If left alone or you don’t pay attention, the slurry will gradually erode the pump’s metal case.
Product leakage indicates that the liners are worn or torn. Excessive leakage should be handled immediately with a damage inspection. In the end, replacing the liners is much less expensive and safer than replacing both the casing and the liners.
Increased Power Consumption
An abrupt spike or reduction in power consumption should always be seen as a red flag that something is wrong. The optimum solution is to use an automatic trending system, although even manually capturing a data point can help. A well-planned monitoring program will keep an eye on the equipment and can provide an early warning.
Vibration

If there is no vibration from a piece of equipment, it is usually because it is not in use. Some equipment elements (such as screens) produce a lot of beating. High amounts of vibration in a pump can indicate inefficiency or damaged parts. Various factors, including worn bearings, turbulent flow, and inadequate foundations, can cause pump vibration.
Pumps can be outfitted with vibration monitors that measure the course of changes or spikes. Vibration levels, like power usage, will reveal information about the state of the pump. Even without automatic monitors, a good operator who pays attention notices something off.
Bearing Conditions
The bearing assembly is an essential component of any spinning device. Bearings that are worn or broken can scar the shaft, cause vibration, generate noise, generate heat, and reduce pumping efficiency.
Because of the noise and vibration, an observant operator should be able to detect a worn or damaged bearing. A vibration monitor should be installed if there are extended periods between visual checks. To provide an early warning, a thermocouple or heat gun can be utilized to monitor the temperature level.
Because corrosion accelerates the wear rate, keeping the bearings adequately oiled and not exposed to moisture is critical.
Noisy Pump
Listening to a pump might provide you with various early signs. Each of these signs alerts you to a distinct sort of hydrodynamic wear. Cavitation is simply the production of bubbles or cavities in a liquid in low-pressure zones around an impeller. When these bubbles implode or collapse inside the pump, shockwaves form, inflicting considerable damage to the impeller, lining, and pump housing.
Observe the pump’s suction and discharge ends; cavitation sounds like marbles passing through the pump.
Poor Belt Intention and Alignment
The sound you will hear, and the loud noise made by loose belts are annoying, but the significant hazard is the heat generated, which finally causes the straps to shatter. Slipping a slack belt reduces energy transfers between the engine and the compressor.
Excessive tension or improper alignment, on the other hand, will strain the bearing assembly and the motor mount. Something will give, and the bearing assembly with increased wear is frequently the culprit. Excessive stress can also reduce efficiency.
Wearing Parts
The wear rate is directly affected by the slurry and operation points. As previously said, analyzing energy use can suggest when liners are worn out, but nothing beats manually inspecting them during downtimes.
When a procedure is consistent, the liner’s wear rate should really be anticipated once a standard has been established.
Uneven Wear on Liners
Liners will create a wear pattern in stable conditions. Unexpected wear spots, such as a highly turbulent flow channel, wrong equipment application or sizing, incorrect operating points, or unsuitable building materials, can point you in danger.
Repeated Failures
It is unavoidable that a pump will fail at some point. When the same pump repeatedly fails in a short period, it indicates that something is seriously wrong. It is a sign that the complete pump system has to be reviewed, whether it is due to a malfunctioning pump for the demand, poor quality repair parts, or an unsuccessful maintenance approach, and this part must be important.
Tracking and documenting repairs can assist in pinpointing the problem and pave the way for a long-term solution. A repurposed pump may be small or large for application in many circumstances. These scenarios can produce issues, as illustrated by the chart “Effects of operating a pump off”.
If you have questions about the Portable Slurry Pump, you can contact us anytime for faster transactions, and our senior engineers will answer you at any time.