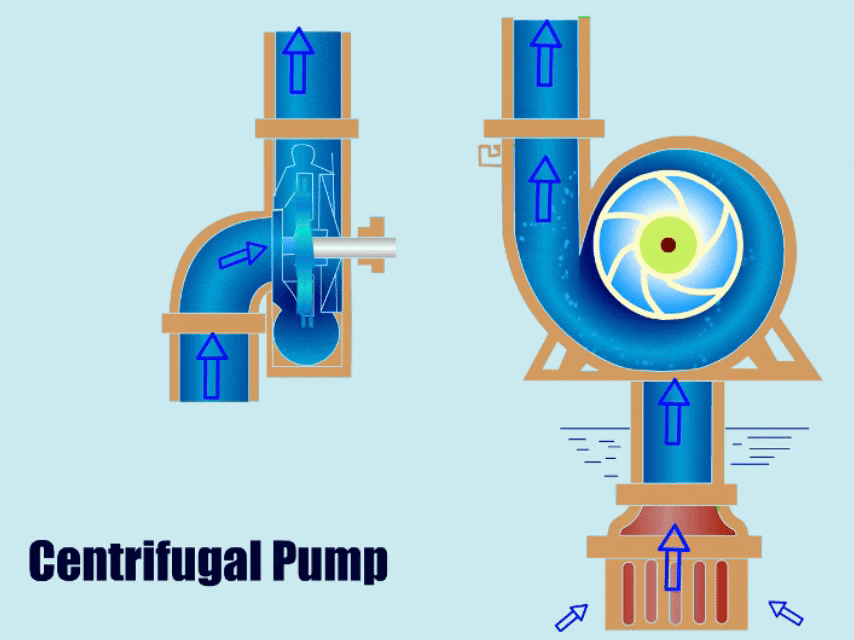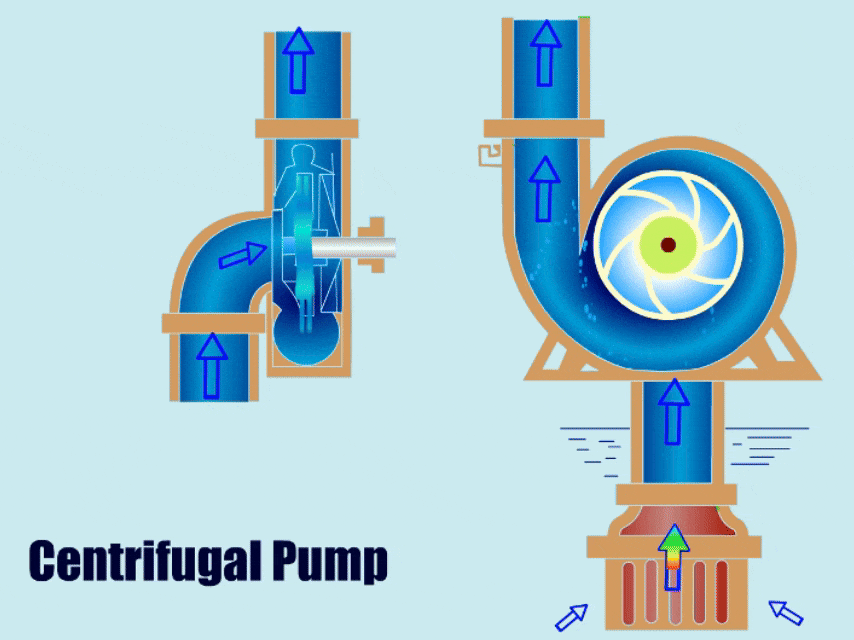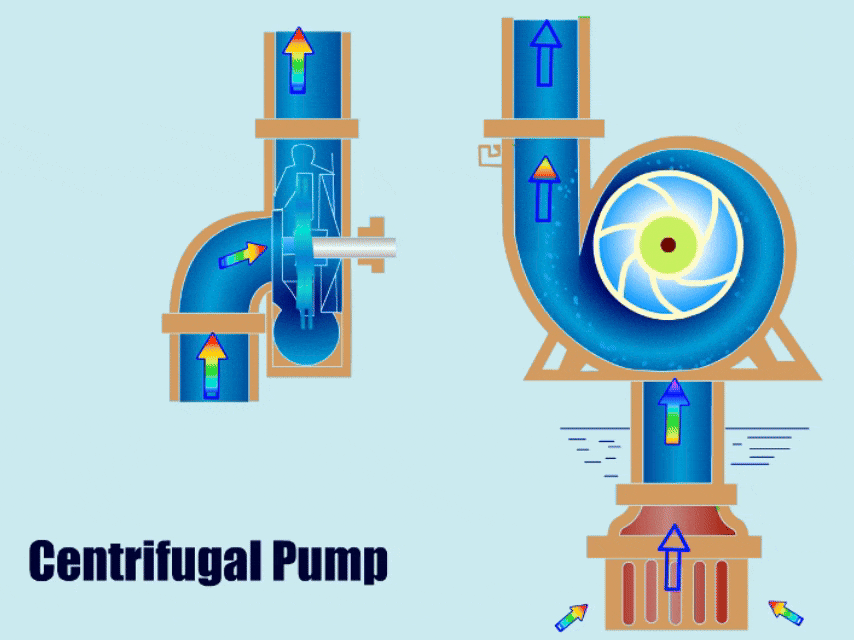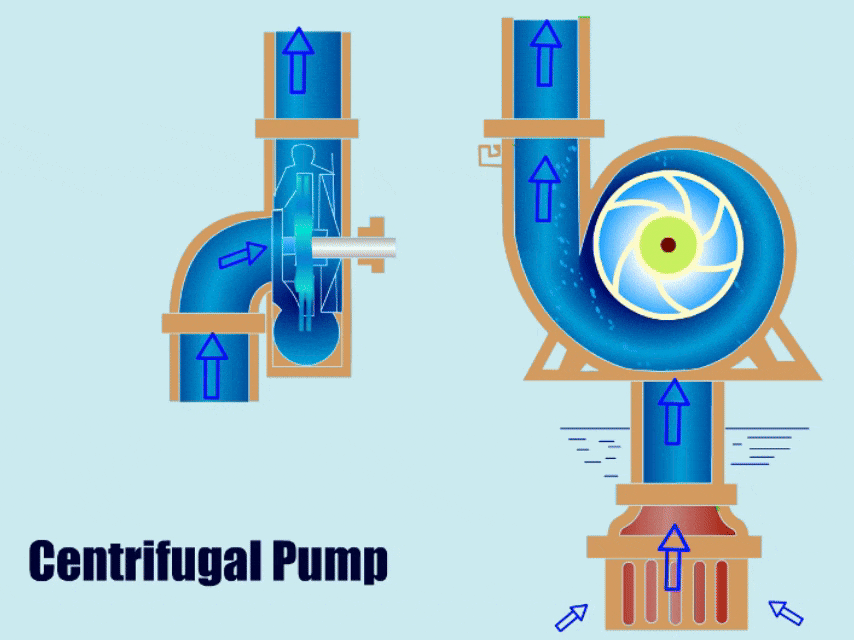
Centrifugal pumps, due to their simple structure and stability, have gained increasing recognition and use from various enterprises. With advancements in technology, engineers have optimized their structures, resulting in many different types of centrifugal pumps applicable across various industries.
This article categorizes centrifugal pumps using 7 of the most widely accepted and authoritative dimensions, encompassing 15+ centrifugal pump types. I will provide a comprehensive guide covering their structure, working principles, applications, and selection methods.
What is a Centrifugal Pump and How They Work?
A centrifugal pump is a type of water pump that uses the rotation of an impeller to drive the movement of fluid. It has a simple structure, with main components including the impeller, volute, casing, and bearing.
When a centrifugal pump is running, the impeller transfers mechanical energy to the liquid, giving the liquid kinetic energy. Finally, under the action of the volute, the liquid converts its kinetic energy into pressure energy and is then discharged from the outlet.
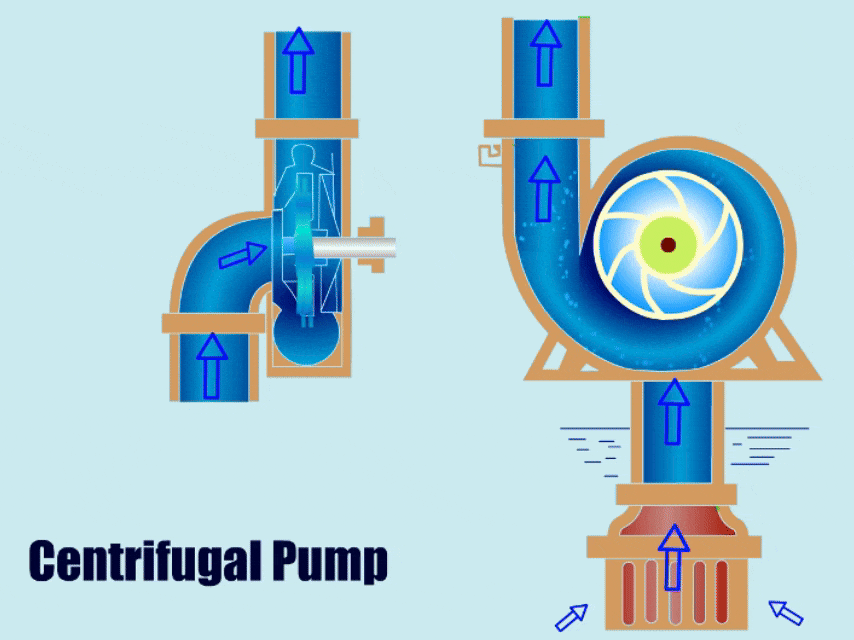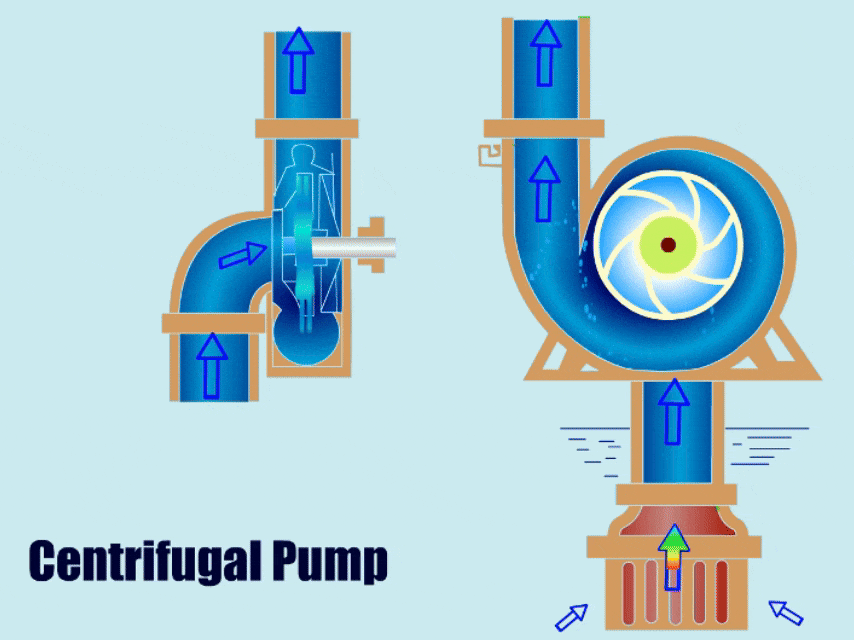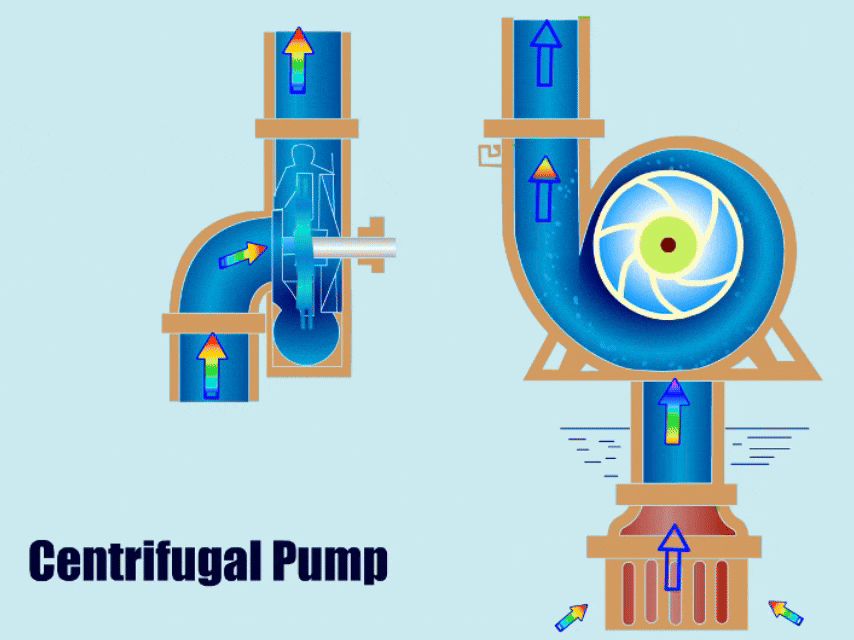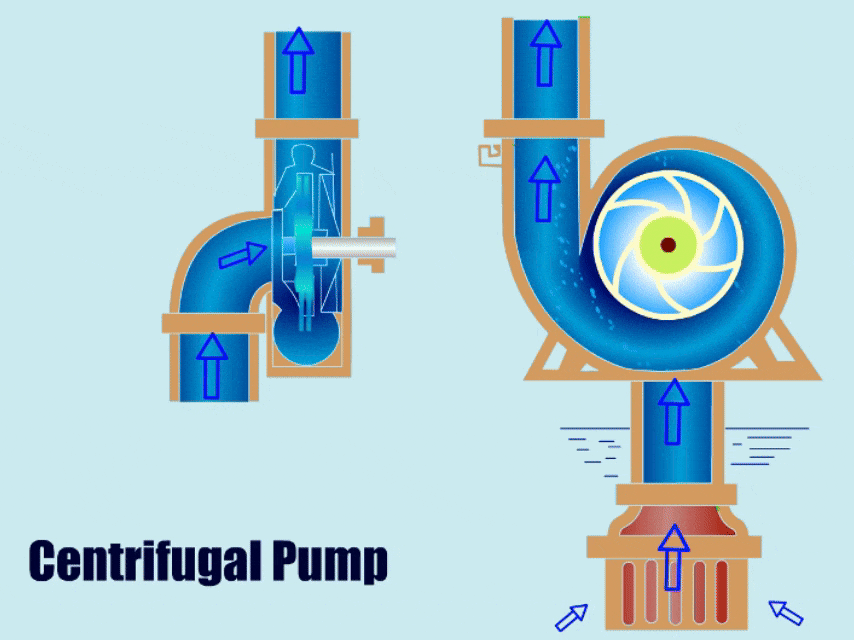
Different Types of Centrifugal Pumps and Their Applications
Centrifugal pumps are mainly classified according to seven dimensions: flow type (radial, axial, and mixed), stages (single and multi-stage), shaft orientation (vertical and horizontal), casing (volute, diffuser, and split case), and other dimensions such as priming, applications, and suction design.

By Flow Types
Radial Flow Centrifugal Pump

The radial flow pumps are the most common type of centrifugal pumps. Radial flow means that after the liquid enters from the center of the impeller, the impeller rotates and throws the liquid radially to the surrounding area, transferring kinetic energy to the liquid. After the liquid increases in pressure in the volute-shaped flow channel, it is discharged from the outlet perpendicular to the pump shaft.
| Radial Flow Centrifugal Pumps | |
| Advantages | Radial centrifugal pumps have a simple structure, are easy to maintain, operate stably, and are suitable for long-term use. |
| Limitations | Efficiency is greatly affected by operating conditions; they are not suitable for conveying high-viscosity fluids. |
| Typical applications | Suitable for conveying medium-flow, low-to-medium viscosity fluids, such as clean water, sewage, slurry, and mortar. |
Axial Flow Centrifugal Pump
Axial flow pumps, also known as propeller pumps, use axial flow impellers (similar to propellers). When the impeller rotates, it generates lift (thrust), which pushes the liquid to move along the pump shaft. After the liquid passes through the impeller, its kinetic energy is converted into pressure energy, and then it is discharged from the outlet.

| Axial Flow Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Compared to radial flow pumps, axial flow pumps act more like a large propeller to propel the fluid, making them suitable for high-flow-rate water applications. |
| Limitations | While axial flow pumps offer high flow rates, their head is lower than that of radial flow pumps, making them unsuitable for applications requiring high pressure. |
| Typical applications | Axial flow pumps are better suited for applications requiring high flow rates but lower head requirements, such as large drainage systems, power plant circulating water systems, and large irrigation systems. |
Mixed Flow Centrifugal Pump

Mixed flow pumps use mixed flow impellers (curved blades). As the name suggests, they combine radial and axial flow. They have a larger flow rate and higher efficiency than radial flow pumps, and they have a higher pressure (pump head) than axial flow pumps.
| Mixed Flow Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Mixed-flow pumps offer higher flow rates than radial-flow pumps and higher heads than axial-flow pumps, while also providing stable operation and reducing the risk of cavitation. |
| Limitations | Mixed-flow pumps are more expensive than axial-flow pumps, and their efficiency fluctuates significantly depending on operating conditions. |
| Typical applications | The versatility of mixed-flow pumps makes them particularly suitable for medium-head, high-flow applications, such as flood control, municipal water supply systems, large-scale irrigation, and wastewater treatment plants. |
By Number of Stages
Single-Stage Centrifugal Pump
A single-stage pump refers to a pump with only one impeller. The number of stages represents the number of impellers. A single-stage pump drives fluid through a single impeller and is the most widely used type of centrifugal pump.

| Single-Stage Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Single-stage centrifugal pumps have a simple structure, are easy to maintain, have readily available spare parts, and low operating costs. |
| Limitations | Single-stage pumps have a relatively low head, making it difficult to efficiently transport liquids under high-head conditions. |
| Typical applications | Single-stage pumps have a wide range of applications and are suitable for transporting clean water, wastewater, and liquids containing small amounts of solids. |
Multi-Stage Centrifugal Pump

A multistage centrifugal pump has multiple impellers inside. As the liquid passes through each impeller, its pressure increases. After being driven by multiple impellers, the liquid achieves a higher head and pressure.
| Multi-Stage Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Multistage centrifugal pumps are ideal for applications requiring high head and high pressure, as their head and pressure are several times that of single-stage pumps. |
| Limitations | Multistage pumps have a more complex structure, are more difficult to maintain, and have slightly higher production and operating costs than single-stage pumps. The numerous impellers mean they are not suitable for conveying liquids containing solids. |
| Typical applications | Multistage pumps are well-suited for high-rise water supply, boiler water supply, urban booster pump stations, and high-pressure cleaning equipment. |
By Shaft Orientation
Vertical Centrifugal Pump
As the name suggests, a vertical centrifugal pump is a centrifugal pump with a vertical structure and vertical installation. Its working principle is the same as that of a centrifugal pump, but it can be installed in a confined space.

| Vertical Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Vertical centrifugal pumps have a small footprint and are more flexible in installation. Part of the pump body in long-shaft vertical pumps can even be submerged in the liquid, resulting in good cavitation performance. |
| Limitations | Vertical long-shaft pumps have higher maintenance costs and require regular inspection of the long shaft. |
| Typical applications | Vertical centrifugal pumps are ideal for use in deep wells, sump pits, or applications requiring submersion in water, such as sump drainage and deep well water intake. |
Horizontal Centrifugal Pump

A horizontal pump is a centrifugal pump that is installed horizontally with its shaft parallel to the ground. Compared to a vertical pump, a horizontal centrifugal pump has a wider range of applications and is easier to maintain.
| Horizontal Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Horizontal pumps have a simple structure, generally employing a pull-out design, making disassembly and maintenance simple and convenient. |
| Limitations | Horizontal centrifugal pumps require a larger footprint than vertical pumps. If the operating environment is harsh, a separate pump house is needed, resulting in higher initial costs. |
| Typical applications | Horizontal centrifugal pumps are widely used in industries such as water supply, irrigation, wastewater treatment, flood drainage, and tailings treatment. |
By Casing
Volute Centrifugal Pump
The volute pumps are pumps with a casing that resembles a volute or a spiral-shaped flow channel. Volute pumps are the most important type of centrifugal pump, as they convert the kinetic energy of the liquid flowing through the volute into pressure energy, thereby allowing the liquid to be discharged.

| Volute Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Volute pumps are technologically mature, easy to maintain, and have relatively inexpensive spare parts, making their operating costs suitable for most users. |
| Limitations | Compared to diffuser centrifugal pumps, traditional volute pumps have lower head and pressure, but under the same operating conditions, diffuser centrifugal pumps are more efficient. |
| Typical applications | Volute pumps have a wide range of applications, such as municipal water supply, irrigation, sewage treatment, mining, and dredging. |
Diffuser Centrifugal Pump

Diffuser pumps work on the same principle as volute pumps. The difference is that in a diffuser pump casing, the impeller is surrounded by a diffuser (fixed blades). When the impeller rotates and throws the liquid in all directions, the diffuser comes into contact with the liquid first, which slows down the liquid speed and thus increases the liquid pressure.
| Diffuser Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Diffuser centrifugal pumps offer higher efficiency, head, and pressure. Under the same conditions (same flow rate), diffuser pumps are more efficient. |
| Limitations | Diffuser pumps require high manufacturing precision and are more expensive than traditional volute pumps. They are not suitable for liquids containing large solids. |
| Typical applications | Diffuser pumps are better suited for applications requiring high head and stable pressure, such as boiler feedwater, high-pressure cleaning equipment, chemical circulating water, and high-rise building water supply. |
Split Case Centrifugal Pump
The main difference between a split case pump and other centrifugal pumps is the structure of its casing. The casing of a split case pump is divided into upper and lower sections with the horizontal pump shaft as the center line.

| Split Case Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | The split-case pump’s modular structure simplifies disassembly and maintenance. The dual-suction design balances axial forces, resulting in greater stability during operation. |
| Limitations | The horizontally split casing structure leads to a larger pump size and weight, making installation inconvenient. It is not suitable for liquids with high solids content, but is better suited for clean water and liquids with small amounts of impurities. |
| Typical applications | Split-case pumps are more suitable for large-scale clean water delivery systems, such as municipal water supply systems, large reservoir drainage, and farmland irrigation. |
By Priming
Self-Priming Centrifugal Pump

As is well known, a centrifugal pump needs to be filled with liquid before starting to prevent air from accumulating inside. A self-priming pump, however, does not require this, as it already contains the necessary liquid for startup, making it more suitable for scenarios requiring frequent start-ups and shutdowns.
| Self-Priming Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Self-priming centrifugal pumps offer easier water intake and start-up/shutdown, effectively reducing maintenance frequency. |
| Limitations | Self-priming pumps have a more complex internal structure, requiring the liquid to overcome more friction, resulting in lower efficiency compared to traditional centrifugal pumps. |
| Typical applications | Portable (mobile) water supply and distribution systems, irrigation, and domestic water collection equipment. |
Submersible Centrifugal Pump
As the name suggests, a submersible centrifugal pump is a pump that can be submerged in water and can operate in vertical wells or deep water, and can pump water containing suspended particles.

| Submersible Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Compared to surface pumps, submersible pumps operate in water with lower noise levels, save significant space, and offer flexible installation. |
| Limitations | Submersible pumps are more complex to maintain than traditional pumps and require higher water quality to prevent chemical corrosion. |
| Typical applications | Submersible pumps can extract lightly polluted water, silt, and sediment, such as for deep well water extraction, sump drainage, and mine drainage. |
By Application
Slurry Centrifugal Pump

The slurry centrifugal pump is made of a high wear-resistant alloy, enabling it to transport highly abrasive slurries. Furthermore, the impeller and flow channel are optimized for long-term transport of slurries containing large particles and high abrasiveness.
| Slurry Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Slurry pumps have a longer service life than traditional centrifugal pumps, are more wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant, and retain the advantages of simple structure and easy maintenance of traditional centrifugal pumps. |
| Limitations | The lifespan of pump components depends on the properties of the medium being pumped. If highly abrasive slurries are to be pumped, frequently worn components need to be replaced; energy consumption is higher than that of ordinary centrifugal water pumps; and costs are higher. |
| Typical applications | Slurry centrifugal pumps are widely used to transport slurries containing media such as gravel and fly ash, for applications such as drainage of sump pits, sewage treatment, tailings transportation, dredging, irrigation, and tunnel boring machine slurry transportation. |
Chemical Centrifugal Pump
The wet end parts of the chemical centrifugal pump are made of a special corrosion-resistant alloy, which allows it to easily transport liquids with corrosive or chemical properties.

| Chemical Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Chemical pumps are more corrosion-resistant than ordinary centrifugal pumps. Different corrosion-resistant materials can be selected for impellers and other components depending on the medium. |
| Limitations | Chemical pumps are generally more expensive to manufacture than ordinary centrifugal pumps, and their service life is significantly affected by the properties of the medium. |
| Typical applications | Petroleum, chemical, natural gas, industrial wastewater. |
Sewage Centrifugal Pump

The sewage centrifugal pump is a centrifugal pump specifically designed for wastewater treatment. The impeller and flow channel of the sewage pump are designed to prevent clogging, and it can smoothly transport slurries containing solid particles, long fibers, and sludge.
| Sewage Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Sewage pumps are more resistant to clogging than ordinary centrifugal water pumps, have a wider range of applications, and a longer service life. |
| Limitations | Sewage pumps are more expensive to manufacture than ordinary water pumps and require regular maintenance and checks for blockages. |
| Typical applications | Sewage pumps can easily handle clean water, sewage, fluids containing suspended particles, and long fibers, such as sewage treatment, sump drainage, and industrial wastewater treatment. |
By Suction
Single-suction Centrifugal Pump
Single-suction centrifugal pumps are one of the most common types of centrifugal pumps. Single suction means that the pump draws in liquid from only one side, and the liquid is pushed out from the other side by the rotating impeller.

| Single-suction Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | Single-suction pumps have a simple structure, mature technology, are easy to maintain, and have low operating costs. |
| Limitations | Compared to double-suction pumps, single-suction pumps are more prone to axial forces and are less stable during operation. |
| Typical applications | Single-suction pumps are widely used in irrigation, water supply and distribution, industrial wastewater treatment, and sump drainage. |
Double-suction Centrifugal Pump

As the name suggests, a double-suction centrifugal pump has two suction inlets, which simultaneously draw in liquid during operation. Unlike a single-suction pump, a double-suction pump has a suction inlet on each side of its impeller for drawing in liquid.
| Double-suction Centrifugal Pump | |
| Advantages | A double-suction pump has a suction inlet on each side of the impeller, which balances the axial force during operation, resulting in greater stability. The two suction inlets also allow for a larger flow rate. |
| Limitations | Double-suction pumps are more expensive to manufacture, and their double-suction structure makes them larger and less flexible to install than single-suction pumps. |
| Typical applications | Double-suction pumps are widely used in municipal water supply, large-scale drainage systems, and industrial wastewater treatment.ewage treatment, sump drainage, and industrial wastewater treatment. |
In summary, I have explained the types of centrifugal pump based on the most common dimensions. I believe you can understand the important aspects of centrifugal pump types through the information above. Of course, the core question is: how to choose the right one? Please continue reading.
How to Choose the Right Centrifugal Pump?
Pump Selection Criteria
1. Flow Rate
Flow rate is one of the important parameters when selecting a pump. It is usually expressed in m³/h and represents the volume of liquid transported over a period of time.
If you are unsure of your required flow rate, you can estimate it based on your project’s production efficiency. For example:
🔸If you need to transport 70 m³ of slurry per hour, then the flow rate = 70 m³/h.
🔸 If you need to transport 60 tons of mineral slurry (density 1.5) per hour, then the flow rate ≈ 60/1.5 ≈ 40 m³/h.
By determining the flow rate, you can decide whether to select a pump suitable for high flow rates.
2. Head
Head represents the height the liquid needs to be lifted after overcoming frictional resistance and other losses. It is usually expressed in meters (m) and is an important index in pump selection.
🔸Low head (<20m): Radial pump, single-suction pump, single-stage pump
🔸Medium head (20-70m): Standard centrifugal pump, axial pump, split case pump
🔸High head (>70m): Multistage pump, diffuser pump, booster pump station
3. Efficiency (η)
As explained above, pump efficiency varies with operating conditions. Each centrifugal pump has an efficiency range, with optimal efficiency achieved only near the Best Efficiency Point (BEP).
4. NPSH Requirements
NPSH is a crucial indicator affecting pump cavitation, typically measured in meters (m). NPSHA (Actual Required NPSH), NPSHR (Minimum Required NPSH)
When selecting a pump, ensure NPSHA > NPSHR to better prevent cavitation.
5. Solids Content/Particle Size
If the material you are pumping contains solid particles or long fibers, pay attention to the solids content and particle size of the slurry, as these parameters affect the pump’s conveying performance.
Notes
The above parameters are the points to consider when selecting types of centrifugal pumps. Only by obtaining as much information as possible can you choose the right one from the many different types of centrifugal pumps.
Pump Recommendations by Application
Choosing the right one from among so many types of centrifugal pump is not an easy task. If you still have questions, you might want to take a look at the recommendation table.
| Application | Recommended Pump Type | Solids Handling | Efficiency | Maintenance | Cost |
| Mine Tailings | Slurry Pump / Gravel Pump | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
| Cooling Water | Single-Stage End Suction / Mixed Flow | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Chemical Transfer | Chemical Centrifugal Pump | ⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Wastewater / Sewage | Sewage Centrifugal Pump / Submersible | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Irrigation / Agriculture | Axial Flow / Mixed Flow Pump | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Firefighting / High-Pressure Water | Multistage Pump / Split Case | ⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Deep Well / Sump Pumping | Submersible Pump / Self-Priming Pump | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
Centrifugal Pump Maintenance TIPS
Although there are many different types of centrifugal pump, I will provide maintenance tips that are mostly general to centrifugal pumps. Only through timely inspection and maintenance can the pump’s lifespan be maximized. For example:
1. Check daily for abnormal noise and vibration, and ensure that the flow rate and head are within ideal values.
2. Regularly clean impurities from the liquid inlet, such as long fibers and solid particles.
3. Regularly check the oil level to ensure the lubricating oil is within the normal range.
Each pump comes with an instruction manual from the manufacturer. We should read the manual before use to understand the maintenance requirements and address any problems promptly to prevent greater losses.
This article has provided important information about different types of centrifugal pumps and how to select the right one. If you have any questions or needs, please contact Kingda Expert for quick and professional guidance.