
What is Cavitation in Pump?
Pump cavitation refers to the situation where when the pressure on the liquid in the pump decreases, the liquid will vaporize, thereby generating many bubbles. The bubbles will gradually grow larger.
The moment the bubble collapse, the high velocity fluid in the pump impacts inside the bubble. This impact force will damage the pump, erode the pump body, form cavitation, and reduce its service life.
Why Pump Cavitation Occurs?
To understand why pump cavitation occurs, we must first understand the physical properties of water. As we all know, water and vapor can be converted into each other. When the temperature of water remains unchanged and the pressure drops to a critical value, water will vaporize. This pressure is called vapor pressure.
When vaporization occurs, water will emit vapor and bubbles. This process is called water vaporization, and the vaporization process is the cause of cavitation.

Process of Pump Cavitation
First, the pressure on the water in the pump decreases, the water vaporizes. During this process, a large amount of vapor is produced and the gas dissolved in the water forms bubbles.
As the bubbles flow from the low-pressure area to the high-pressure area in the pump with the water, the bubbles will quickly condense and collapse under the action of the high pressure. At this time, the high-pressure water will quickly flow to the space previously occupied by the bubbles.
Then, the gas in the bubble has not yet condensed, the high-speed water rushes towards the bubble, impacting the bubble into more small bubbles. The small bubbles will continue to condense and collapse under high pressure.
Finally, the vaporization reaction is repeated, the bubbles on the flow channel surface and near the impeller will have a strong impact on the material, and in severe cases, honeycomb cavitation or even fracture of the wear parts will occur. The active gas in the bubbles will contact the metal for a long time, which will corrode the metal.

What Causes Pump Cavitation?
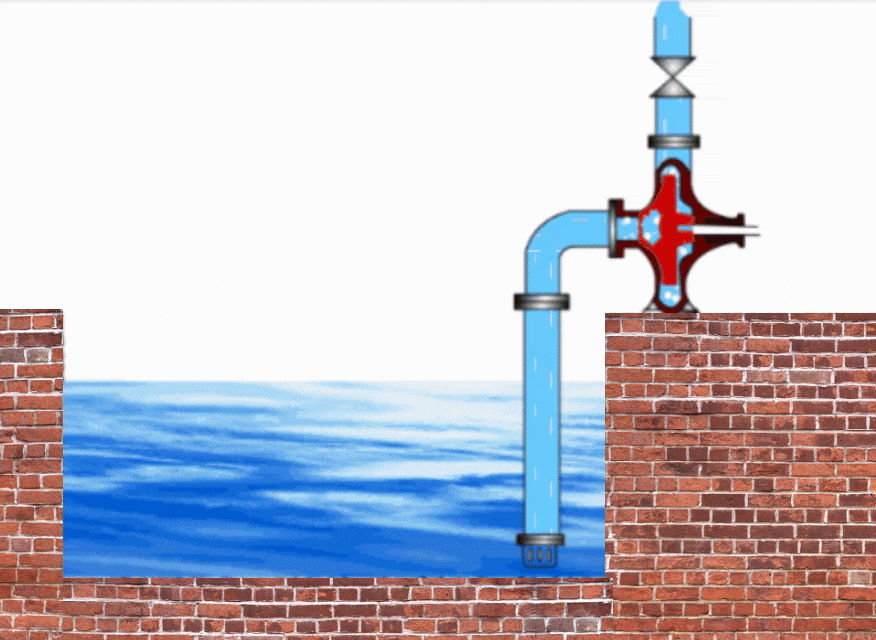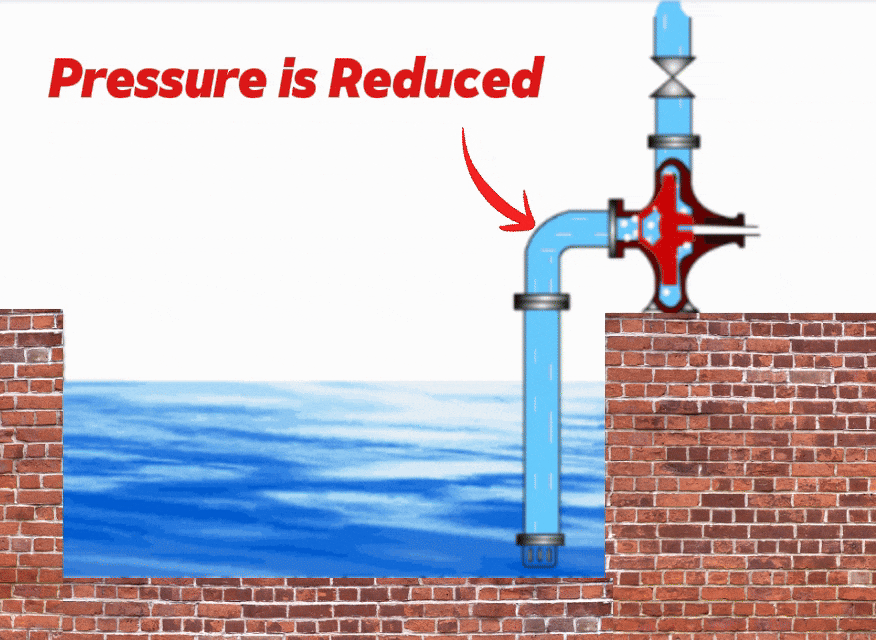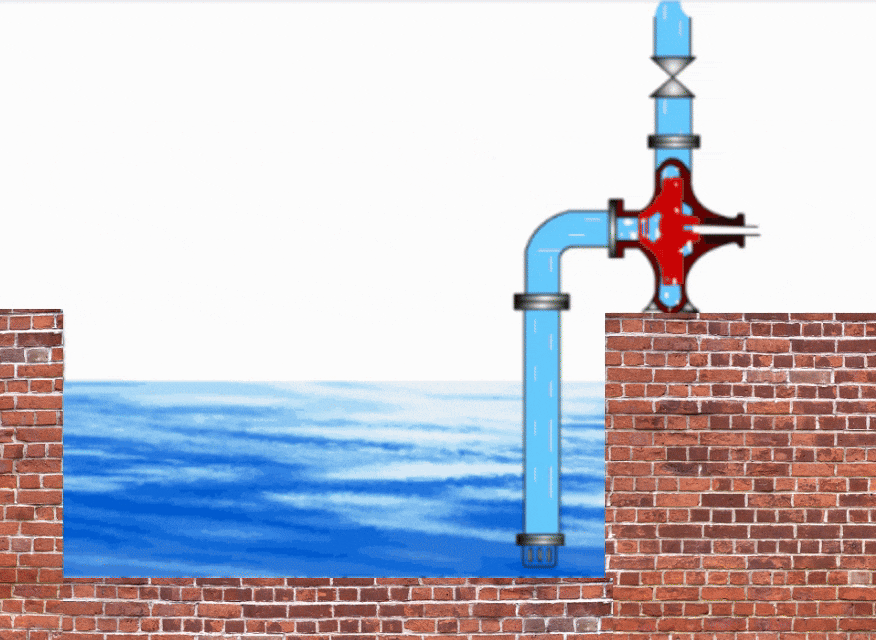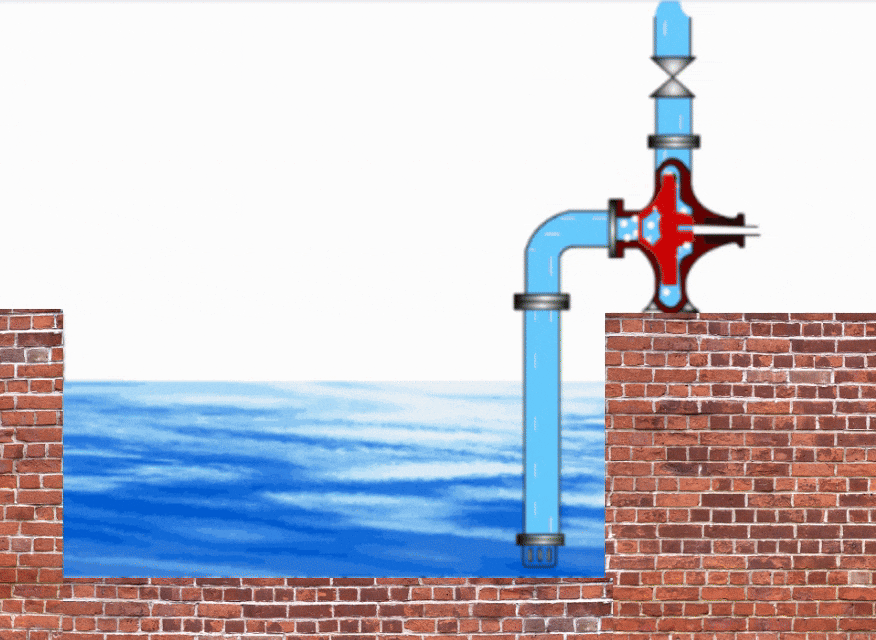
Pump Cavitation Animation
Pump cavitation is a common problem of pumps. Many improper operations can lead to cavitation.
Cavitation is determined by the pump’s own anti- cavitation ability and the suction end device.
The following are several important reasons for pump cavitation.
1. Motor speed is too high
When the pump motor speed is too high, the flow rate at the impeller suction port increases. According to Bernoulli’s principle, when the speed increases, the pressure will decrease. When the pressure is lower than the critical value of the vapor pressure, the liquid will vaporize, eventually leading to pump cavitation.
2. The suction pipe resistance is too large
When the pump suction pipe is too long, has too many elbows, or has blockages in the pipe, the pressure of the liquid will decrease when flowing through the pipe, which may cause cavitation in the pump.
3. Pump installation height is too high
Every pump has an important parameter, NPSH. When the pump is installed too high relative to the liquid level, the pump’s NPSHa (available net positive suction head) will be less than NPSHr (required net positive suction head), which will cause the suction pressure to decrease and pump cavitation to occur.
4. Liquid temperature is too high
When the temperature of the liquid we transport is too high, a small amount of liquid may vaporize before it reaches the suction end, which makes pump cavitation more likely to occur.
5. Multiple pumps in parallel
When our working conditions are more complicated and we use multiple pumps in parallel to transport liquids, if the parallel pumps are unevenly configured, the flow rate of one pump will be too small, the pressure at the suction end will decrease, and pump cavitation will occur.
How to Identify Cavitation? Pump Cavitation Damage
Damage to The Wear Parts
Pump cavitation will impact the wear parts, causing honeycomb cavitation on the wear parts, and even breaking or corroding the wear parts.


Vibration
When the pulsation frequency of pump cavitation is close to the natural frequency of the pump during operation, it will also cause the pump to vibrate violently.
When vibration occurs, the pressure gauge will fluctuate.
Bearing Temperature Increase
Pump cavitation causes the pump to vibrate violently, increases bearing friction, and raises bearing temperature. Use a thermometer to measure the bearing temperature.
If the bearing temperature is higher than usual, cavitation may have occurred.


Noise
When pump cavitation occurs, a large number of bubbles collapse and the high-speed water flow impacts, causing severe noise.
The sound of cavitation is similar to the popping sound of stone hitting metal, and the sound will increase or decrease with the flow rate.
Efficiency Decrease
The large number of bubbles produced by pump cavitation will hinder the flow of water, resulting in a decrease in flow rate, unstable pump head, and reduced pump efficiency.
When the flow meter value is found to be 10% lower than the expected value, it can be inferred that cavitation has occurred.

How to Avoid Pump Cavitation?
1. Reduce Pump Motor Speed
Adjusting the motor speed to the appropriate speed according to the pump parameter table or pump performance curve will effectively avoid cavitation.
2. Pipeline Design
Improve the suction pipe design, reduce the number of elbows, allow the water to always flow at a higher efficiency, and reduce the friction loss of the water in the pipe.
3. Install The Pump Correctly
Each pump has a certain cavitation margin NPSH. Before installing the pump, it must be installed according to the predetermined parameters to ensure that NPSHr is greater than NPSHa.
4. Regular Maintenance
After the pump is installed, regular maintenance should be performed according to the operating manual provided by the pump manufacturer, such as checking the bearing temperature, regular inspection of the impeller wear, pump vibration, etc.
5. Choosing The Right Pump
Before starting your project, you should ask the pump manufacturer to design your project to ensure that the pump you choose meets the expected design of the project. This is the best way to prevent cavitation and minimize the probability of cavitation.
Types of Cavitation
| Cavitation Types | Cause | Common Cavitation Sites |
| Vaporous Cavitation | The liquid pressure decreases, vaporizing to form bubbles | Impeller inlet |
| Turbulence Cavitation | The flow rate in the volute or pump is too high, resulting in a decrease in pressure and the formation of bubbles. | Surface of volute |
| Inertial Cavitation | The flow rate is too high, causing impact on the pump and forming bubbles. | Impeller |
| Vortex Cavitation | The water flow is vortex-shaped and the gas is drawn into the pump | Pump Inlet |
| Gaseous Cavitation | The liquid pressure decreases and the gas dissolved in the liquid forms bubbles | Chemical pumps |
FAQ About Pump Cavitation
What is cavitation in centrifugal pump?
1. Causes of cavitation in centrifugal pump
Centrifugal pumps are more prone to cavitation than other pumps (positive displacement pumps), which is determined by the working principle of centrifugal pumps.
The working principle of a centrifugal pump is that the high-speed rotation of the impeller generates centrifugal force to suck in fluid. Due to the high-speed rotation of the impeller, negative pressure will be generated around the impeller. When the fluid pressure at the pump inlet is insufficient, part of the liquid will vaporize, causing water vapor to enter the pump together.
When water vapor moves from the inlet to the impeller, that is, from a negative pressure state to a high pressure state, the bubbles will burst, causing the centrifugal pump to vibrate and pump cavitation to occur.
2. How to prevent cavitation in centrifugal pump?
Ⅰ. Make sure the centrifugal pump has enough NPSH to avoid too low inlet pressure.
Ⅱ. Usually when the flow rate of the centrifugal pump is unstable, cavitation is prone to occur, so the stable flow rate of the centrifugal pump should be controlled.
Ⅲ. Before installing the centrifugal pump, a comprehensive pipeline design should be carried out to avoid too many elbows or too narrow pipes.
When we change the pump the cavitation?
When cavitation occurs, there is no need to replace the pump immediately. We need to first understand the real cause of cavitation and try to solve the specific cause of pump cavitation.
For example, we can control the speed of the pump according to the pump’s operating manual or performance curve to change the pump’s flow or head to ensure that the pump maintains optimal performance.
Only when cavitation erodes the core components of the pump, such as the impeller and seal, causing the pump to reduce efficiency or fail to work properly, do we need to consider replacing the pump or contact the pump manufacturer’s after-sales engineer for professional maintenance and repair.
What is positive displacement pump cavitation?
Compared with centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps are less prone to pump cavitation because the working principle of positive displacement pumps is different from that of centrifugal pumps.
The working principle of a positive displacement pump is to squeeze the fluid through the volume in the pump, that is, through the reciprocating motion of the plunger or piston, and periodically change the volume in the pump to achieve the function of conveying the fluid.
Because its flow rate and pressure are more stable and will not cause large pressure changes at the pump inlet, positive displacement pumps basically will not cavitate.
However, it does not mean that positive displacement pumps will not cavitate. When a positive displacement pump conveys foam slurry, if the positive displacement pump cannot dissipate the foam better, then the positive displacement pump may cavitate.






