
Centrifugal pumps were first created by French physicist Denis Papin in 1689 and without a doubt that centrifugal pumps play an important role in people’s lives today.
This article summarizes the important knowledge points, including the working principle, diagram, parts, types and applications of centrifugal pumps. Read this guide and you will know everything about centrifugal pumps.
What Is A Centrifugal Pump?
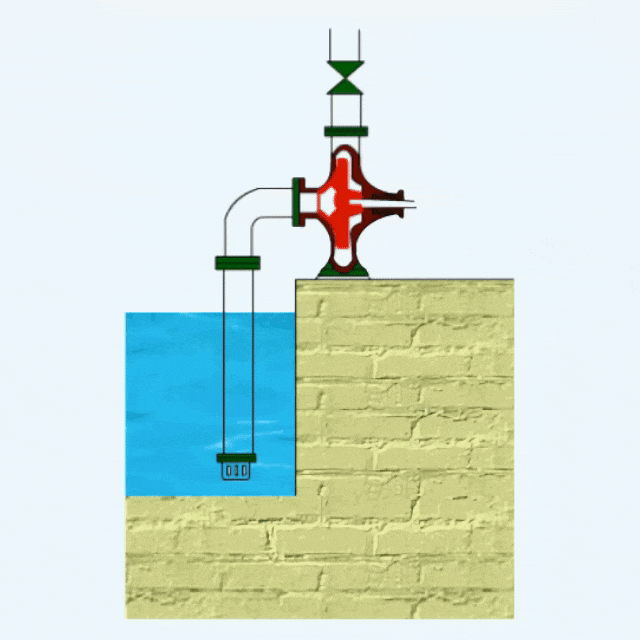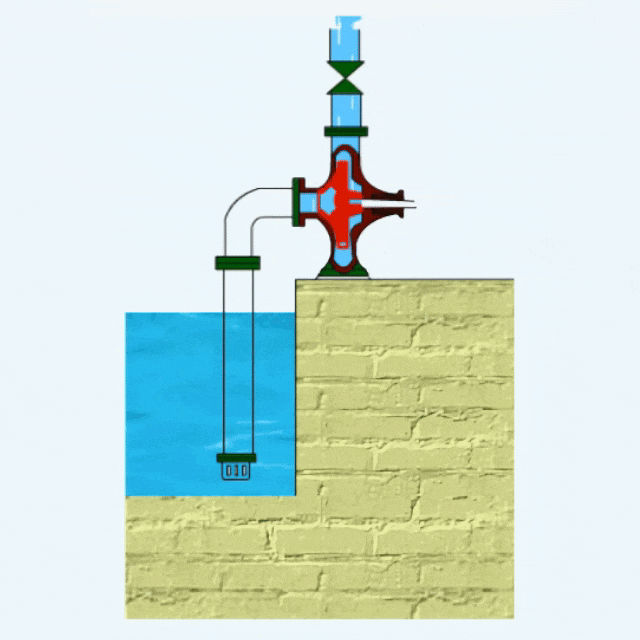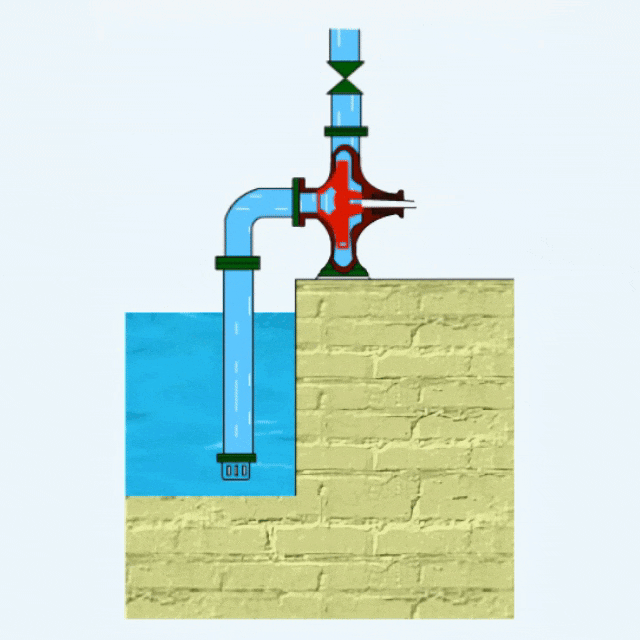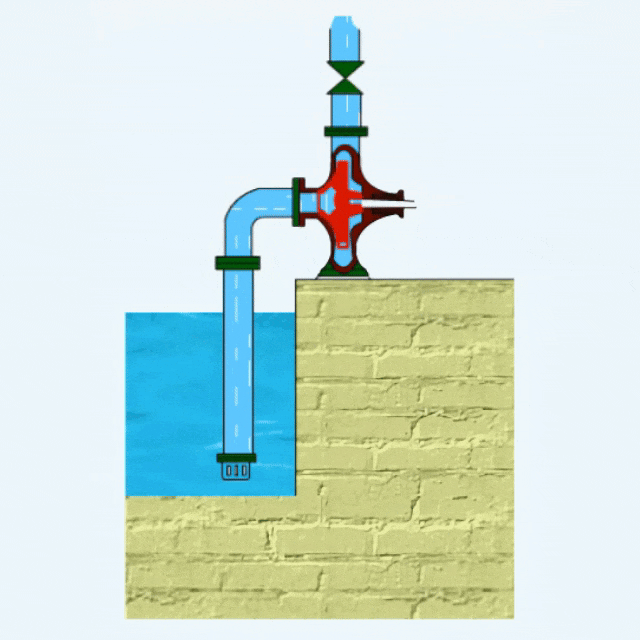
Centrifugal Pump Definition
Centrifugal pumps utilize impeller rotation to generate centrifugal force, which accelerates the fluid and throws it out around the impeller, thus realizing fluid transportation.
The main components of a centrifugal pump include pump casing, impeller, bearings, pump shaft, base, mechanical seal, etc.
Centrifugal pumps belong to a kind of dynamic pumps. There are many types of centrifugal pumps, which can transport almost all types of fluids, such as agricultural irrigation well water, sewage, mining waste, dredging mud and other fluids.
How Does A Centrifugal Pump Work?
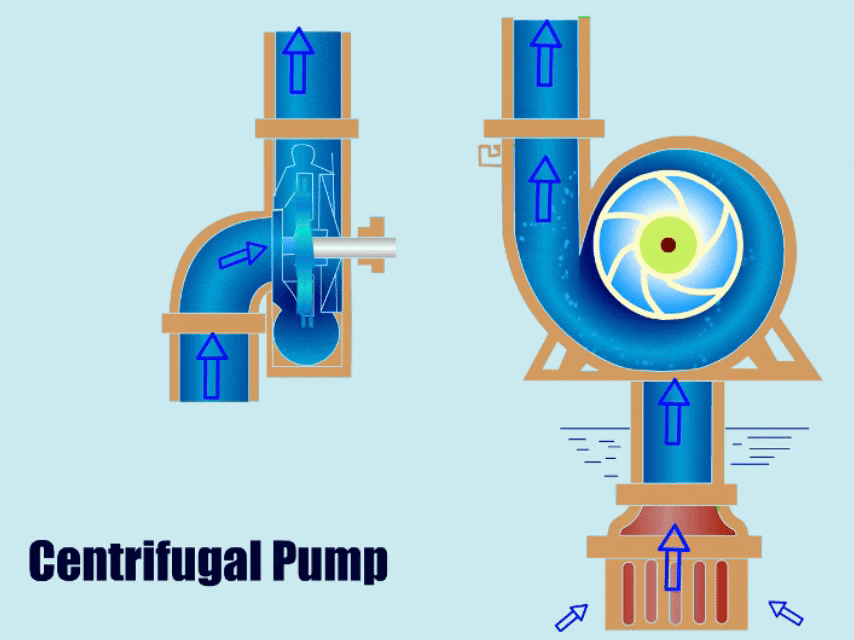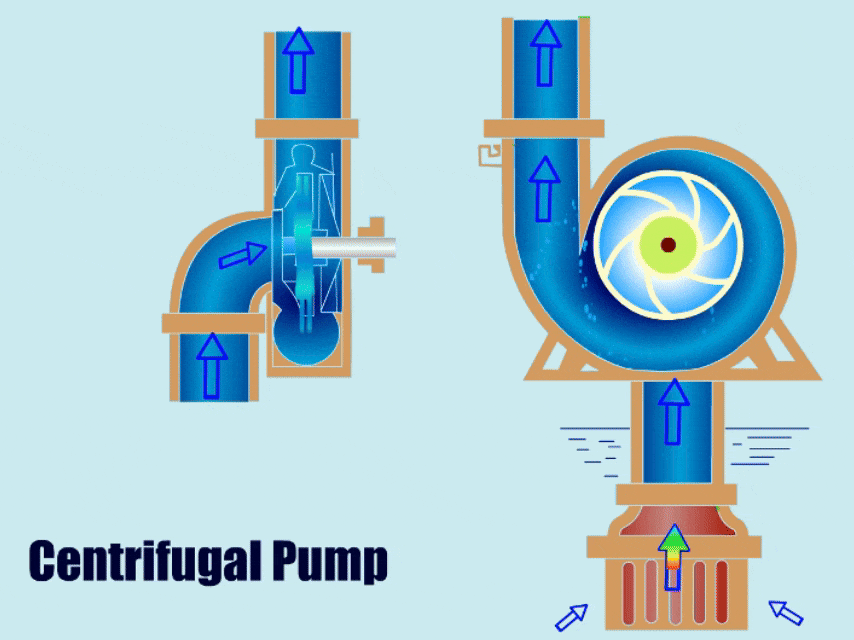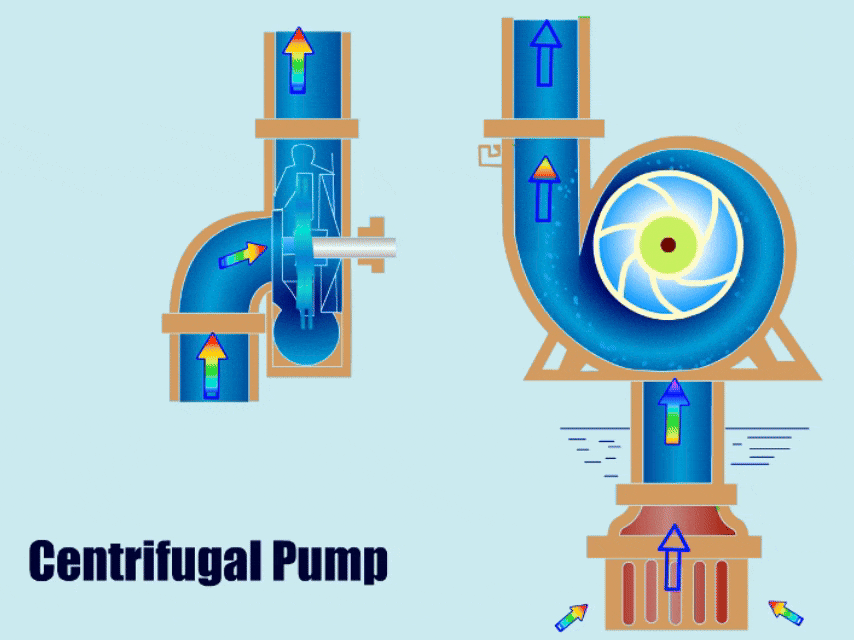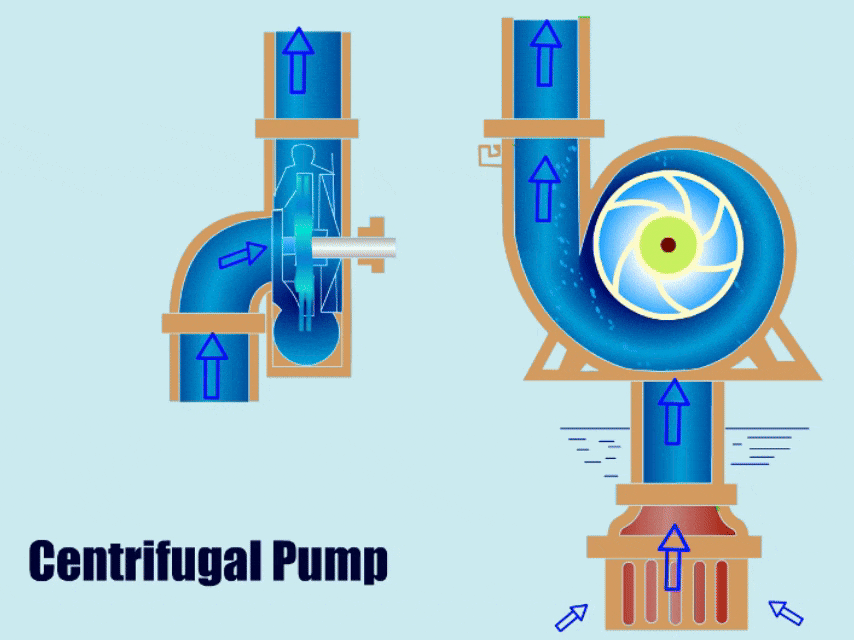
Priming of Centrifugal Pump
Before starting, the pump needs to be filled with liquid to prevent the pump from running dry.
A centrifugal pump uses centrifugal force to increase the pressure of the fluid and then causes the fluid to flow out from the outlet. The operation process has four stages: fluid intake, pressurization, discharge, and water circulation.
The following is a detailed description of the working principle of the centrifugal pump, and you can also watch a more intuitive video explanation.
Working Principle of Centrifugal Pump
Ⅰ. Suction: First, the movement of the pump motor rotor drives the impeller to rotate, and the rotation of the impeller generates centrifugal force, then the centrifugal force accelerates the fluid from the center of the impeller to the periphery of the impeller, and negative pressure is generated around the liquid in the center of the impeller, forming suction. Finally, the pump sucks the fluid from the inlet.
Ⅱ. Pressurization: The fluid accelerates and flows in a vortex in the pump casing. Since the flow channel in the pump gradually narrows, the fluid velocity decreases and the pressure increases in this process, and part of the kinetic energy is converted into pressure energy.
Ⅲ. Discharge: The outlet of the pump is usually of smaller design, the fluid pressure increases at the outlet, and finally, the pump discharges the fluid from the outlet.
Ⅳ. Continuous Work: Under the action of the continuous rotation of the impeller, the pump continuously sucks in and discharges the fluid, so that the pump works continuously.

Video for Centrifugal Pump Working
Welcome to the video about how a centrifugal pump works. This video details how a pump smoothly delivers liquid, and through this video you will gain a clearer understanding of the various components of a pump and their functions.
Centrifugal Pump Types and Applications
Single-stage Centrifugal Pumps
| Overview | Applications |
| Single-stage pumps has only one impeller, simple structure, high head, easy maintenance. | ●Agricultural irrigation ●Mining ●Municipal water ●Electrical power ●Metallurgy |
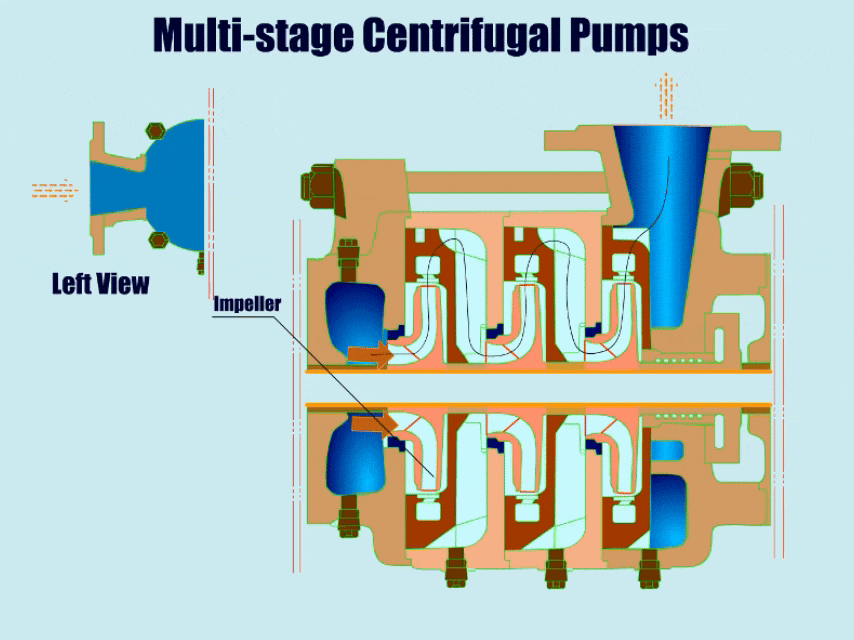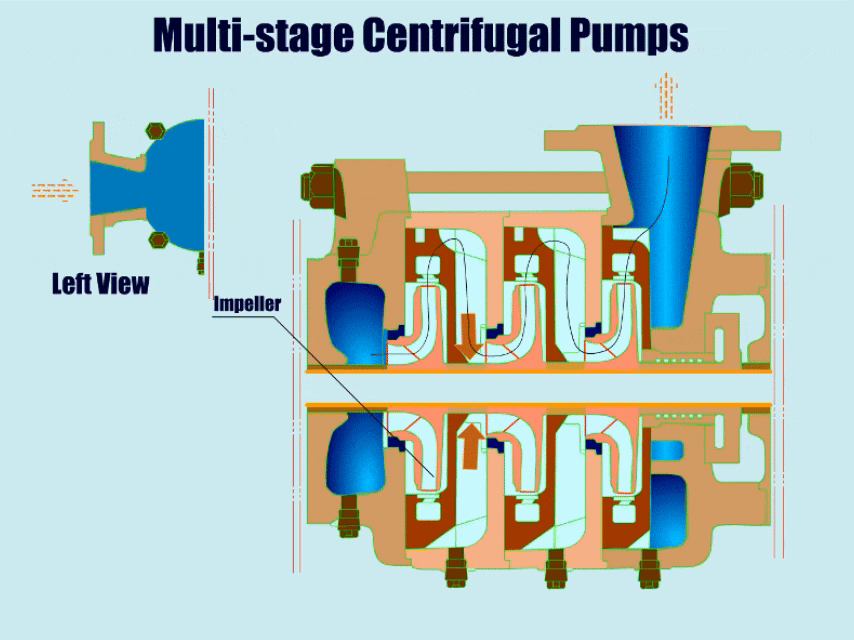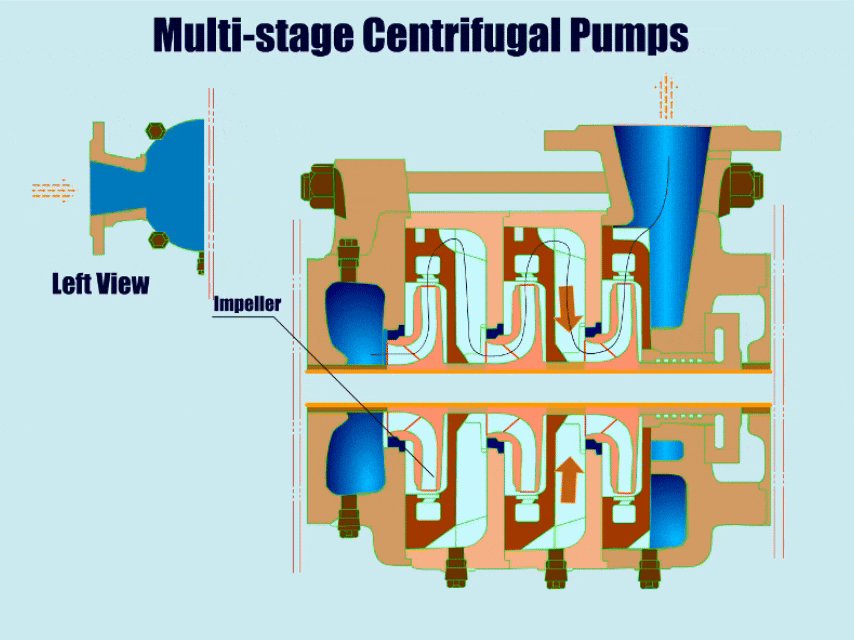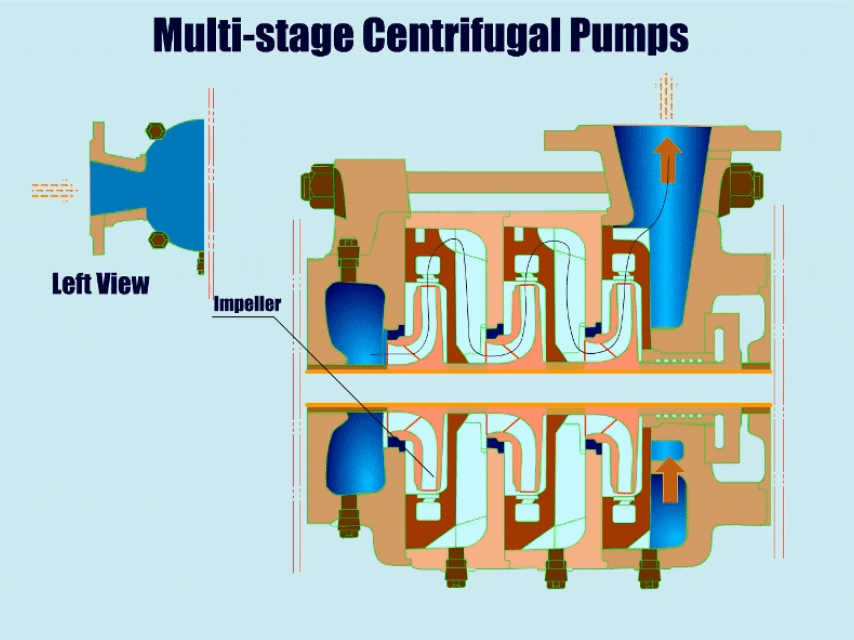
Multi-stage Centrifugal Pumps
| Overview | Applications |
| A multi-stage centrifugal pump has more than two impellers with high head and high pressure. | ●Mine wastewater ●High pressure water supply ●Petrochemical ●Vacuum feeding |
Self-priming Centrifugal Pumps
| Overview | Applications |
| Self-priming centrifugal pumps not necessary to be filled the pump with water in advance before starting, and the pump can be emptied of gas automatically. | ●Petrochemical ●Mining ●Ship Unloading ●Metallurgy |
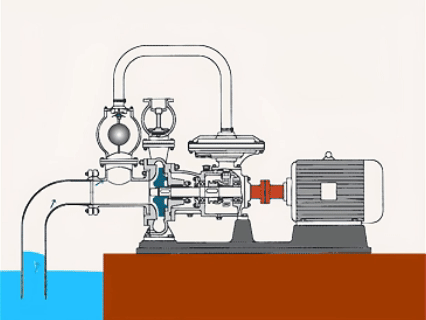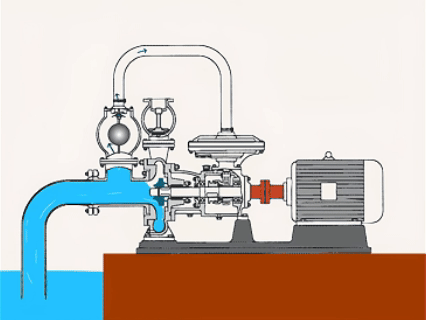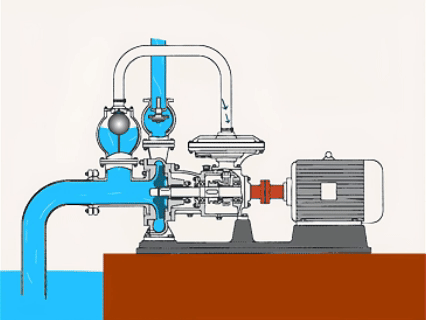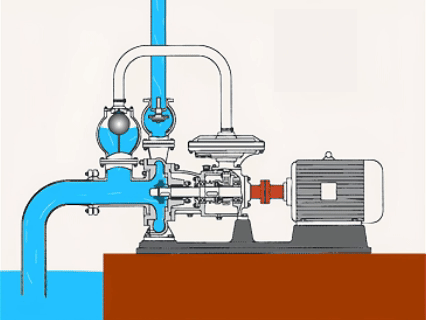

Submersible Centrifugal Pumps
| Overview | Applications |
| Submersible centrifugal pumps work by submerging in water, and the pump has a strong seal. | ●Hydraulic engineering ●Deep-well water extraction ●Dredge ●Agricultural irrigation |
Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
| Overview | Applications |
| Vertical centrifugal pumps have a vertical structure, can work deep under the liquid. | ●Mining ●Cooling tower water supply ●Coals ●Conditions requiring submergence |


Inline Centrifugal Pumps
| Overview | Applications |
| The inline pump’s inlet and outlet are in the same straight line, small size, and high efficiency. | ●Agricultural irrigation ●Metallurgy ●Petrochemical ●Electrical power |
Magnetic Drive Centrifugal Pumps
| Overview | Applications |
| The magnetic drive centrifugal pump’s impeller rotation is driven by magnetic force and it has no shaft seal, which isolates the fluid from the motor. | ●Chemical plant ●Medical care ●Foodstuffs ●Aerospace ●Conveying corrosive, flammable and toxic fluids |


Sewage Centrifugal Pumps
| Overview | Applications |
| Sewage Pumps can handle fluids containing impurities and long fibers. | ●Water treatment plant ●Paper mills ●Industrial wastewater treatment |
Slurry Centrifugal Pumps
| Overview | Applications |
| Slurry centrifugal pump can handle slurries and viscous fluids containing gravel, silt and oil. | ●Mining ●Dredge ●Shield tunnel ●Flue gas desulfurization |

Main Components of Centrifugal Pumps
The centrifugal pumps have a simple structure and are easy to maintain. The main components of the centrifugal pumps include the impeller, pump casing, bearing, volute, shaft, guard plate, stuffing box, and mechanical seal. The following is a detailed explanation of the main components of the centrifugal pumps.
Centrifugal Pump Diagram with Parts

Centrifugal Pump Parts
| Centrifugal Pump Parts Name | Function |
| Bearing Assembly | The Bearing Assembly is an important part of the pump’s operation, ensuring stable impeller operation and supporting the pump shaft. |
| Joint Plate | Joint Plate is used for seals on centrifugal pumps to improve sealing performance. |
| Stuffing Box | The Stuffing Box is part of the packing seal and is used to close the gap between the pump casing and the pump shaft to prevent leakage of the conveyed medium. |
| Centrifugal Pump Seal | Stop liquid leakage or prevent air from entering the pump. |
| Frame Plate Liner | The Frame Plate Liner holds the impeller, guides the flow and reduces wear on the pump internals. |
| Centrifugal Pump Impeller | Impeller is an important part of centrifugal pump operation, centrifugal pump mainly through the impeller rotation to transport fluid. |
| Casing | Centrifugal pump casing is the container that carries the pump internals and is used to direct the fluid in a vortex shape flow motion. |
| Cover Plate Liner | Guiding fluid movement and reducing wear on internal pump parts. |
| Cover Plate | Improve the sealing performance of the pump to prevent leakage of the medium. |
| Lantern Ring | The lantern ring in centrifugal pump is used in the bearing to seal, cool and reduce wear. |
Centrifugal Pump Characteristic Curve
The centrifugal pump performance curve contains many performance parameters and indicators of the pump, including pump head, flow, motor speed, best efficiency point (BEP), NPSH and other parameters.
The pump performance curve is an important tool for us to select the pump type. According to the pump performance curve, we can choose the appropriate pump model to achieve maximum efficiency.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Centrifugal Pump
Advantages
- Simple structure and reliable operation: Centrifugal pumps have fewer main components and are less prone to failure.
- Easy maintenance, long service life: Centrifugal pump spare parts are easy to replace, timely maintenance can greatly extend the service life.
- Wide range of application: Centrifugal pumps can not only convey clear water, but also fluids containing suspended particles, viscous and corrosive.
Disadvantages
- Self-priming: Ordinary pumps do not have self-priming function and cannot automatically discharge the gas in the pump, so we need to fill the pump with liquid before starting.
- Cavitation: When the suction pressure is too low or blockage occurs at the inlet, air bubbles are easily generated, resulting in cavitation of the pump casing and impeller, shortening the service life.
Conclusion
After centuries of development and multiple designs, they have greatly improved productivity, without a doubt, centrifugal pumps play an important role in our production and life.
If you have a problem with fluid transportation in your industrial process, feel free to contact the Kingda experts and we will give you the best option.
FAQ About Centrifugal Pumps
Positive Displacement Pump Vs Centrifugal
| Centrifugal Pump | Positive Displacement Pump | |
| Working Principle | The centrifugal force generated by the rotation of the impeller is utilized to draw in the fluid and discharge it under pressure. | The fluid is pushed through the pump by a cyclical change in the internal volume of the pump. |
| Fluid Type | Suitable for low to medium viscosity fluids | Suitable for high viscosity, high pressure fluid transportation |
| Flow Rate | Suitable for medium to high flow rates | Suitable for conveying low-flow fluids |
| Self-priming | No self-priming capability, pump needs to be filled with liquid before starting. | Self-priming ability, can automatically empty the pump of gas. |
| Applications | Chemical, petroleum, mining | Food, pharmaceuticals, fuel |
Centrifugal Pump Maintenance Checklist
NOISE, VIBRATION: If you find abnormal noise and vibration when the pump is running, there may be impeller imbalance phenomenon or cavitation phenomenon occurs, please stop the machine immediately and check.
MOTOR TEMPERATURE: If the motor temperature is too high, stop the machine immediately, otherwise the motor may burn out.
LEAKAGE: Check lines for fluid leaks.
PRESSURE: Check that the pump pressure value is normal.
REGULAR MAINTENANCE: Carry out regular maintenance according to the contents of the product manual, and replace the wearing parts, such as seals, bearings, impellers, bolts, etc. in time.
How To Prime A Centrifugal Pump?
When starting a pump, it is necessary to fill the pump with water and exhaust the air in the pump, so as to start the pump and put it into normal operation.
Centrifugal pump with self-priming function: Self-priming pumps do not need to be filled with water in advance when starting. Self-priming pumps can exhaust the air in the pump by their own suction force, and can suck up water after a short period of operation and put it into normal operation.
Are Centrifugal Pumps Positive Displacement?
Centrifugal pump is not a positive displacement pump. A centrifugal pump is a type of dynamic pump. A centrifugal pump uses the rotation of the impeller to generate centrifugal force and draws liquid into the pump by the rotation of the impeller.
Working principle of a positive displacement pump: A positive displacement pump mainly relies on the movement of components inside the pump to cause periodic changes in the volume inside the pump, squeeze out the liquid, and the flow rate is relatively stable.
Are Centrifugal Pumps Self Priming?
Most centrifugal pumps do not have a self-priming function and need to be filled with water before starting. Some self-priming pumps are also centrifugal pumps, but they still need to be filled with water before starting for the first time.
Are Submersible Pumps Centrifugal?
A submersible pump is a centrifugal pump that works while immersed in water. Its working principle is the same as that of a centrifugal pump. The rotation of the impeller generates centrifugal force, thereby sucking water above the liquid surface.
Can Centrifugal Pumps Run Dry?
Centrifugal pumps cannot run dry. Before starting, the pump needs to be filled with water to expel the air. Cavitation will occur when the pump runs idly. The impeller, volute and other parts in the pump have no liquid to cool them down, causing the temperature to rise, which will cause damage over time.
What is Vertical Centrifugal Pump?
Vertical centrifugal pumps are installed vertically on the ground, occupying a small area, and do not require the construction of a pump room, saving costs and having high efficiency. When the installation environment is relatively small, a vertical pump can be selected.
What is Horizontal Centrifugal Pump?
Horizontal centrifugal pumps are installed horizontally on the ground, with simple structure, easy maintenance and low vibration. However, they occupy a large area and require a house to house the pump.
What is Cavitation In Centrifugal Pump?
Cavitation is a common problem in centrifugal pumps. When the pump has insufficient suction or the liquid is reduced, some air will enter the pump casing, causing cavitation.
Cavitation symptoms: After cavitation occurs, the impeller, pump casing and other pump parts will experience point cavitation, and even honeycomb cavitation or broken impellers. After cavitation occurs, the pump will have symptoms such as increased noise, high vibration frequency, high motor temperature, and reduced flow.
What is Stainless Steel Centrifugal Pump?
Stainless steel centrifugal pumps refer to pumps whose casing or pump components (impeller, volute, seal, etc.) are made of stainless steel.
Compared with traditional cast iron pumps, stainless steel centrifugal pumps are more corrosion-resistant and pressure-resistant, and are mostly used in the chemical, petroleum, and pharmaceutical industries. However, the price of stainless steel centrifugal pumps is higher than that of cast iron pumps.
Multistage Centrifugal Pump Diagram

Single Stage Centrifugal Pump Diagram

What are the Different Centrifugal Pump Impeller Types?
There are seven main types of centrifugal pump impellers: closed impeller, semi-open impeller, open impeller, recessed impeller, vortex impeller, cutter impeller, and screw impeller. Among these, the three most widely used impeller types are:
- Closed impeller: A closed impeller has guards on both sides, forming a completely closed flow channel inside the impeller.
- Semi-open impeller: A semi-open impeller has a guard on only one side.
- Open impeller: An open impeller is completely open, with the blades directly connected to the impeller center.
What is Total Head in Centrifugal Pump?
Total head refers to the height a pump can lift a liquid to after overcoming all energy losses (pipeline friction, elbow losses, etc.), usually measured in meters.
For details, please refer to the following pump head formula:
Total Head = Hs(Suction Head) + Hd(Discharge Head)
NOTE: This formula is only applicable to simple operating conditions.
Top 10 Centrifugal Pump Manufacturers Worldwide
The table below lists companies that have a significant impact on the centrifugal pump industry globally. You can quickly learn about centrifugal pump manufacturers based on the table’s contents.
| Centrifugal Pump Company Name | Overview |
| Flowserve | Flowserve is located in the United States, and its products include centrifugal pumps, valves, seals, and other equipment, which are widely used in the oil, gas, and power industries. |
| Kingda | Kingda, as one of the earliest manufacturers of centrifugal pumps in China, has a long history and extensive experience. Its main products include centrifugal slurry pumps and dredging pumps, which are widely used in mining, dredging, power and other industries. |
| Grundfos | Grundfos, headquartered in Denmark, offers a wide range of pumps, including circulating pumps, submersible pumps, and centrifugal pumps, serving industries such as water supply systems, wastewater treatment, and construction. |
| KSB | KSB is a German pump and valve manufacturer whose products are widely used in industries such as mining, water treatment, and chemicals, and it has a significant global influence. |
| Sulzer | Sulzer is a Swiss-based international company that focuses on solving fluid transportation problems, and its products play an important role in the oil, gas, and power industries. |
| EBARA | EBARA is a Japanese industrial manufacturing company whose products cover precision equipment such as pumps, compressors, energy equipment, and vacuum pumps. It is one of the world’s leading pump manufacturers. |
| ITT | ITT is located in Stanford, USA, and its pump products mainly focus on industrial centrifugal pump systems, specializing in industries such as mining, energy, and chemicals. |
| Weir | Weir is a UK-based mining equipment manufacturer that acquired the Warman pumps brand in 1999. Its pumps primarily serve highly abrasive environments such as mining and mineral processing, and it provides services globally. |
| Xylem | Xylem is a US-based water technology company specializing in water delivery and treatment, with business operations covering water treatment, municipal water supply, industrial wastewater, and construction industries. |
| Pentair | Pentair originated in the United States and focuses on water treatment and transportation, providing water treatment solutions for businesses and households. Its pump products are mainly used in water supply systems, sewage treatment, fire protection, irrigation, etc. |
What is NPSH of Centrifugal Pump?
NPSH is a crucial reference value for preventing cavitation in centrifugal pumps. During pump operation, only when NPSHA > NPSHR can sufficient suction pressure be ensured, thus preventing pump cavitation.
Parameter Explanation:
NPSHA: The NPSH required for actual pump operation.
NPPSHR: The minimum NPSH required for pump operation.
What is Best Efficiency Point of Centrifugal Pump?
The best efficiency point is the optimal operating point on the centrifugal pump’s efficiency curve. At this point, the pump exhibits the most suitable flow rate, head, and optimal motor efficiency.
The pump reaches its highest efficiency at this point, achieving optimal production capacity while saving energy. Continuous operation at the best efficiency point significantly extends its service life.





