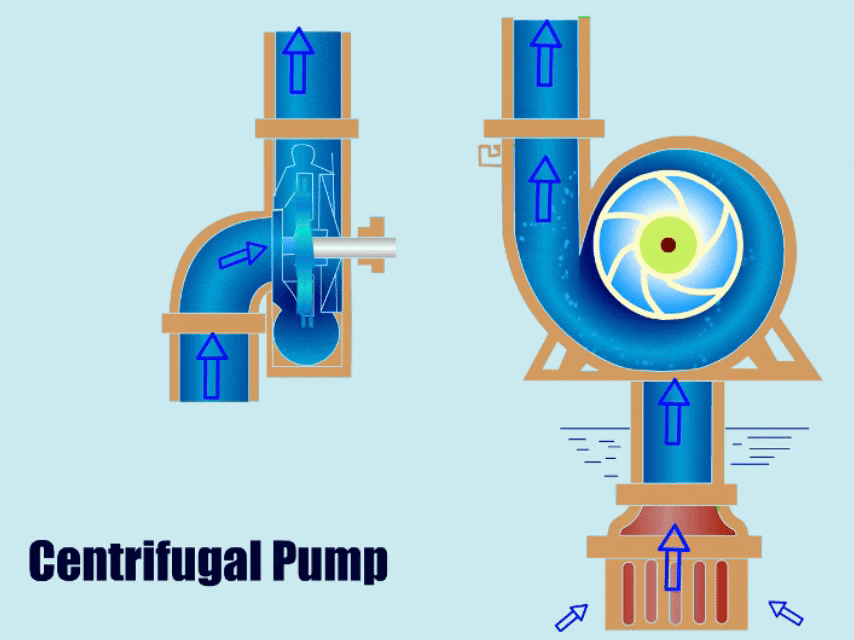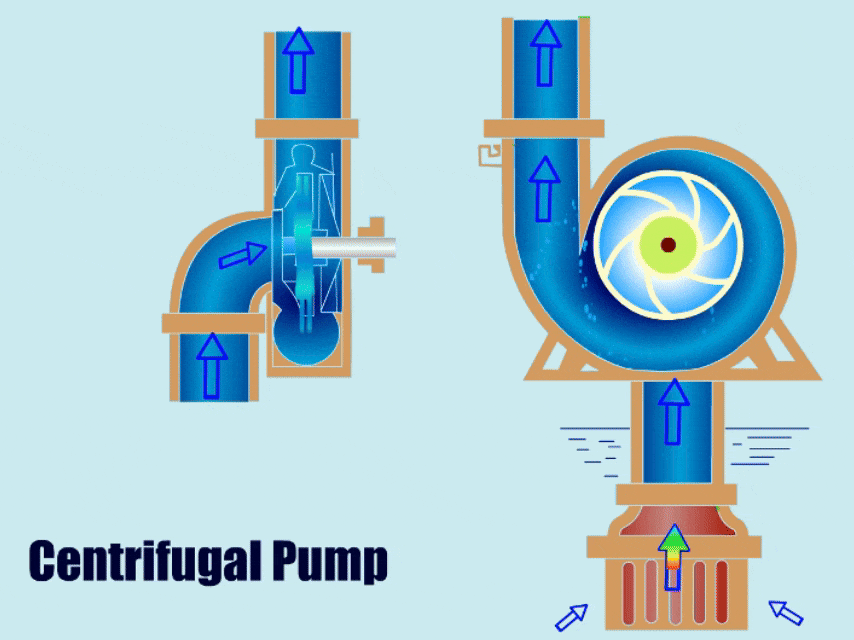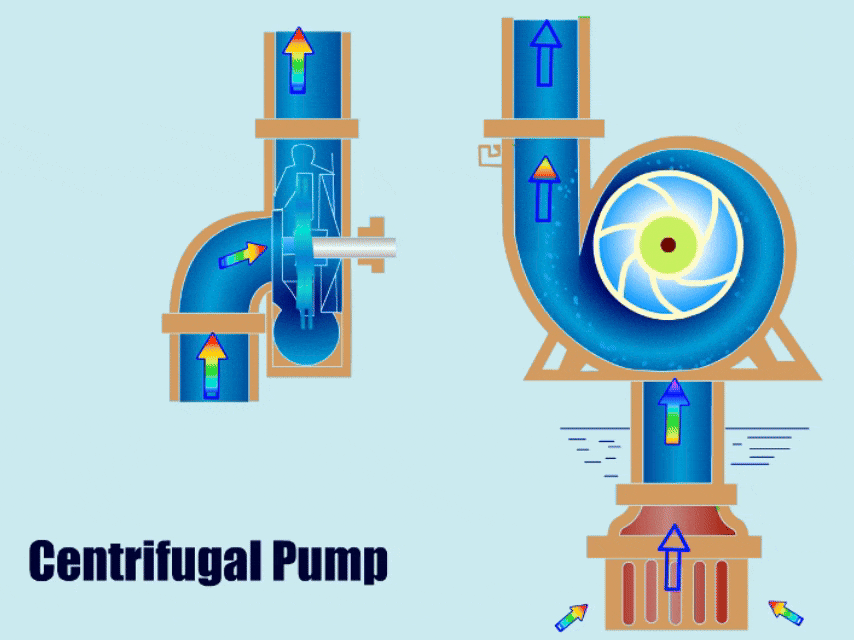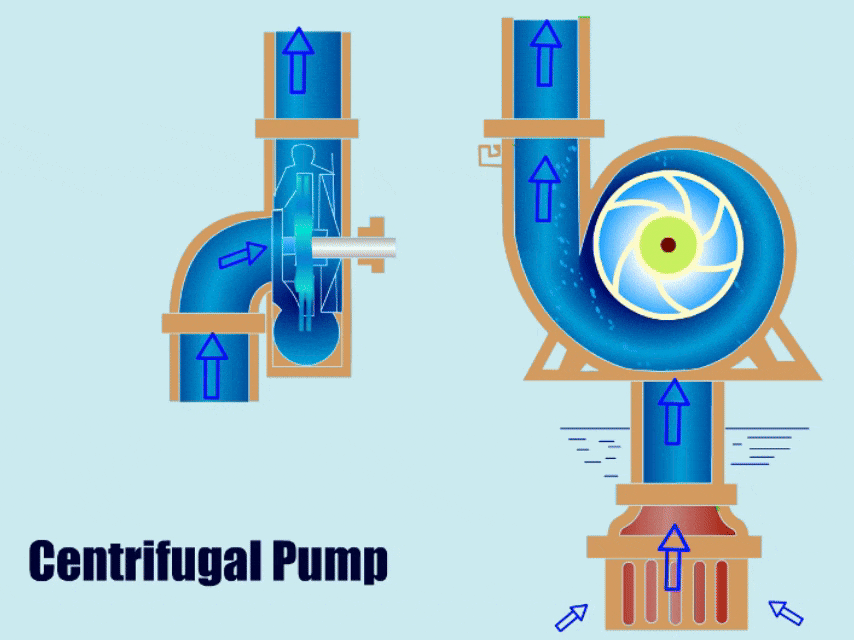
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes

What is a pump failure?
Pump failure refers to a pump’s inability to deliver liquids as initially designed or to consistently perform its intended function, it doesn’t necessarily mean the pump completely stops and becomes inoperable.
During normal operation, a pump delivers liquids steadily. If the pump fails to deliver liquids at a stable flow rate and pressure, or if its delivery efficiency decreases, it indicates a pump failure.
Pump failures are normal during prolonged operation. Our task is to understand the causes of pump malfunctions and how to prevent them from occurring.
What are the main causes of pump failure?
1. Operating and System-Related Issues
Pump Cavitation
When the pump suction pressure is insufficient, the liquid vaporizes, producing steam bubbles and causing pump cavitation.


Pump Overheating
When the pump body and motor temperatures are too high, the pump’s delivery efficiency will decrease.
Pump Blockage
Blockage in the pump delivery pipeline or at the inlet can cause abnormal equipment delivery.

2. Media and Material Compatibility Issues

Pump Corrosion
If the chemical properties of the pumping medium do not match the corrosion resistance of the material, the pump is highly susceptible to corrosion.
3. Mechanical Component Failures
Bearing Failure
After prolonged use, the internal condition of a water pump deteriorates, leading to pump bearing failure.


Pump Mechanical Seal Failure
Pump mechanical seal failure typically occurs when there is insufficient cooling water in the mechanical seal of a water pump or when the sealing elements are corroded.
Impeller Failure
Pump impeller failure can easily occur after prolonged use of the impeller or when conveying slurry containing solid particles.

4. Mechanical Component Failures
Lubricating Problem
After long-term operation, the lubricating oil in the lubrication components will inevitably age and lose its lubrication effect, which will affect the normal operation of the pump.


Electrical Problems
Unstable power supply voltage or quality problems can cause equipment malfunctions.
5. Human and Maintenance-Related Factors
Installation Problems
After long-term operation, the lubricating oil in the lubrication components will inevitably age and lose its lubrication effect, which will affect the normal operation of the pump.


Lack of Maintenance
Due to human error, the personnel responsible for the equipment failed to regularly inspect and maintain it, leading to pump failure.
What are the symptoms of pump failure?
Systemic symptoms
1. No Liquid Discharge
2. Insufficient Flow
3. Noise
4. Pump Vibration
5. Bearing Overheating
Component-level symptoms
6. Pump Overheating
7. Pump Mechanical Seal Leakage
8. Gasket Leakage
9. Increased Power Consumption
How do I troubleshoot a pump failure?
1. No liquid discharge
No liquid discharge is a common phenomenon during pump operation, and its occurrence requires serious attention.
This can lead to dry running of the pump, causing overheating of bearings and seals, and may even damage the motor.
| No liquid discharge reasons | Solutions |
| 🔸Foreign matter blocks the impeller or inlet valve 🔸Pump inlet height is too high 🔸Suction pipe is damaged and air enters 🔸Centrifugal pump is not filled with liquid before starting 🔸The temperature of the delivered liquid is too high 🔸Inlet and outlet valves are damaged | 🔸Remove foreign matter from the impeller or valve 🔸Reduce the height of the pump inlet 🔸Replace the pipe gasket 🔸Reduce the temperature of the liquid 🔸Replace the valve |
2. Insufficient pump flow
Insufficient pump flow means the output flow rate is lower than the design flow rate.
This indicates that the pump is not operating at its maximum capacity. Prolonged operation of this pump will lead to decreased efficiency and may even accelerate the aging of worn components.
| Insufficient pump flow reasons | Solutions |
| 🔸Impeller reversal 🔸Severe impeller abrasion 🔸Inlet valve blockage 🔸Excessive wear of pump inlet seal 🔸Pipeline leakage | 🔸Change the direction of impeller rotation 🔸Replace the impeller 🔸Clean up foreign matter in the inlet valve 🔸Replace the pump inlet seal 🔸Tighten the pipe connections |
3. Abnormal sound
Abnormal operating noise refers to noises that are not indicative of normal equipment operation or an increase in operating sound.
Noise in equipment indicates an abnormal state in the internal operation of the system. Continued operation in this state may accelerate the wear and tear of parts.
| Abnormal sound reasons | Solutions |
| 🔸Foreign matter has entered the pump 🔸Friction between the impeller and the pump body 🔸Bearing damage | 🔸Remove foreign matter in the pump 🔸Adjust the thickness of the pump cover gasket to prevent friction between the impeller and the pump body 🔸Replace the bearing |
4. Pump vibration
Pump body vibration refers to abnormal shaking or increased vibration amplitude that occurs during pump operation.
When abnormal pump body vibration occurs, it indicates a mechanical fault in the equipment. If the vibration continues, it may increase the load on bearings or connecting parts, leading to structural damage to the system.
| Pump vibration reasons | Solutions |
| 🔸The coupling is skewed 🔸The pump shaft is bent 🔸The impeller is skewed 🔸The anchor bolts are loose | 🔸Repair the coupling 🔸Adjust or replace the bearing 🔸Replace the impeller 🔸Tighten the anchor bolts |
5. Bearing overheating
Overheating of the bearing refers to an abnormal rise in bearing temperature beyond the normal range.
Sustained high bearing temperature indicates an unfavorable operating environment, which can lead to lubrication failure and ultimately equipment shutdown.
| Bearing overheating reasons | Solutions |
| 🔸Too little lubricating oil or too many impurities in the lubricating oil 🔸Bearing damage 🔸Friction between the bearing and the pump body | 🔸Clean the bearing and replace the lubricating oil 🔸Replace the bearing 🔸Increase the thickness of the bearing gasket |
6. Pump overheating
Pump overheating refers to an excessively high overall temperature during equipment operation.
High equipment temperature indicates an abnormal operating condition, with excessive energy being converted into heat, reducing transport efficiency.
| Pump overheating reasons | Solutions |
| 🔸The outlet valve is not open or is blocked 🔸The flow rate of the pump during actual operation is too small, lower than the design flow rate 🔸The impeller is blocked | 🔸Open the outlet valve or remove foreign matter 🔸Replace a pump with a smaller flow rate or increase the flow rate 🔸Remove foreign matter from the impeller |
7. Pump mechanical seal leakage
Mechanical seal leakage refers to the leakage of the conveyed medium in the sealed part.
The appearance of a pump seal leak indicates that the seal has failed. If media leakage continues for a long time, the equipment will be corroded by the medium, affecting its stable operation.
| Pump mechanical seal leakage reasons | Solutions |
| 🔸Insufficient cooling water 🔸Insufficient spring pressure 🔸Damaged seal | 🔸Clean the cooling water pipe 🔸Increase the cooling water volume 🔸Adjust the spring pressure, and replace the seal |
8. Gasket leakage
Gasket leakage refers to the leakage of media at the connection point of the equipment.
This indicates that the pump’s seal quality has been compromised. If the leakage persists, it will not only damage the equipment but also increase maintenance costs.
| Gasket leakage reasons | Solutions |
| 🔸Loose fastening bolts 🔸Damaged sealing points | 🔸Tighten the bolts appropriately 🔸Replace the gasket |
9. Increased power consumption
Increased pump power consumption means the pump’s power consumption exceeds its normal operating level.
This phenomenon indicates an increased pump load. Prolonged operation of this pump will increase the load on components such as bearings and motors, potentially leading to pump failure.
| Increased power consumption reasons | Solutions |
| 🔸Friction between the pump shaft and the inlet seal 🔸Parts stuck 🔸The center line of the pump shaft is offset | 🔸Adjust the pump shaft 🔸Check the pump parts 🔸Adjust the center line of the pump shaft |
How to prevent pump failure? (Pump Maintenance)
Daily inspections and monitoring during pump operation are crucial for maintaining stable operation, which is beneficial for the long-term stable work of the equipment. Proactive maintenance can effectively extend the service life of the pump.
1. Lubrication Management

Lubrication plays a crucial role in pump operation, and the quality and cleanliness of the lubricating oil are essential for its long-term stable operation.
During routine inspections, pay attention to the cleanliness and level of the lubricating oil, and ensure that it is changed quarterly.
2. Vibration and Noise Monitoring
Staff should monitor for abnormal vibrations and noise daily, especially checking the condition of anchor bolts, bearings, and lubrication.
Regular daily monitoring is beneficial for long-term operation.

3. Bearing and Temperature Control
During operation, staff should frequently record and observe whether the bearing temperature fluctuates abnormally and whether it is within the normal temperature range:
Sliding Bearings <65℃; Rolling Bearings <70℃.
If it exceeds the normal range, further inspection is required.
4. Operating Performance Monitoring

Flow rate and pressure are important indicators of pump operation.
Operators should regularly check inlet and outlet valves and delivery pipelines, and deal with possible faults in advance to ensure the stability of flow rate and pressure.
Summarize
In general, pump failure occurs when a pump deviates from its design operating conditions, failing to stably complete its preset delivery tasks, ultimately leading to pump malfunction.
Pump failure is not caused by a single factor, it usually involves multiple factors, such as operating conditions, component condition, and maintenance frequency. Only by correctly identifying the fault, carefully troubleshooting, and performing routine monitoring and maintenance can the long-term stable operation of the equipment be guaranteed.